Lipid (Fat) Metabolism Overview, Animation
Summary
TLDRThe video script delves into lipid metabolism, focusing on the digestion, synthesis, and breakdown of fats. It explains how fats, primarily triglycerides, are processed in the small intestine with the help of bile salts and pancreatic lipase, then reassembled into chylomicrons for transport through the bloodstream. The script also touches on the role of lipoprotein lipase in hydrolyzing triglycerides for energy or storage and the connection between lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. It highlights the importance of beta-oxidation in energy production and the creation of ketone bodies during glucose scarcity, while cautioning against the risks of ketoacidosis due to extreme diets or diabetes.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Lipid metabolism primarily involves the breakdown and synthesis of fats, which are triglycerides formed from glycerol and three fatty acids.
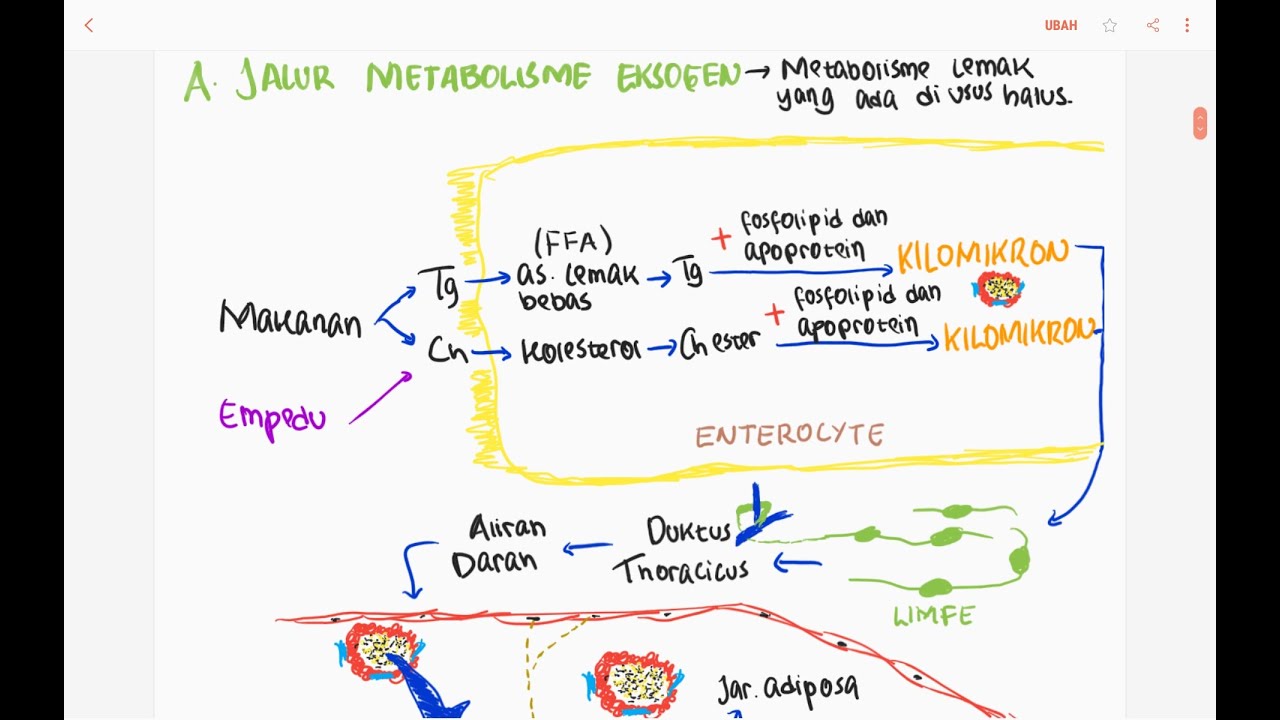
- 🍽 Dietary fats are digested in the small intestine with the help of bile salts and pancreatic lipase, which emulsify and break down triglycerides into monoglycerides, free fatty acids, and glycerol.
- 🚀 These digestion products are reassembled into triglycerides within the enterocytes and packaged into chylomicrons for transport in the bloodstream.
- 🚑 Chylomicrons deliver fats to tissues, where lipoprotein lipase on capillary walls hydrolyzes triglycerides, allowing fatty acids and glycerol to enter tissues for energy or storage.
- 🏭 Fats synthesized in the liver are transported as VLDL (Very Low-Density Lipoprotein) to tissues, where they are similarly processed.
- 🔥 Hormone-sensitive lipase in adipose tissue mobilizes stored fat for energy production in response to hormones like epinephrine.
- 🔗 Lipid metabolism is closely connected to carbohydrate metabolism, with glycerol converted into a glycolysis intermediate and fatty acids undergoing beta-oxidation to generate acetyl-CoA.
- 🔄 Beta-oxidation removes two carbons from the fatty acid chain per cycle, producing acetyl-CoA and high-energy molecules for the electron transport system.
- 🔋 Fats are more energy-dense than carbohydrates, yielding more energy per unit mass.
- 🚫 Excess acetyl-CoA can lead to ketone body production, which, if excessive, can cause metabolic acidosis and serious health complications.
- 🍬 High-carbohydrate diets can lead to the synthesis of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA, stimulated by citrate, an indicator of energy abundance.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of lipid metabolism?
-Lipid metabolism primarily refers to the breakdown and synthesis of fats, which are triglycerides composed of glycerol and three fatty acids.
From where can fats be obtained in the human body?
-Fats can be obtained from the diet, from stores in adipose tissue, or synthesized from excess dietary carbohydrates in the liver.
How do bile salts contribute to the digestion of dietary fats?
-Bile salts emulsify fats, acting as a detergent to break down large fat globules into smaller micelles, making them more accessible to lipase.
What is the role of pancreatic lipase in fat digestion?
-Pancreatic lipase converts triglycerides into monoglycerides, free fatty acids, and glycerol, which can then be absorbed by the cells of the intestinal epithelium.
How are fats transported within the body after digestion?
-Triglycerides are packaged with cholesterol into large lipoprotein particles called chylomicrons, which enable the transport of water-insoluble fats within aqueous environments like the bloodstream.
What is the function of lipoprotein lipase in the bloodstream?
-Lipoprotein lipase, an enzyme found on the walls of blood capillaries, hydrolyzes triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol, allowing them to pass through the capillary wall into tissues for energy or storage.
How are fats synthesized in the liver transported to tissues?
-Fats synthesized in the liver are packed into very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles, which are then transported to tissues where triglycerides are extracted.
What hormone-sensitive enzyme is involved in mobilizing fat stores for energy production?
-Hormone-sensitive lipase is the enzyme that mobilizes fat stores in adipose tissue for energy production, responding to hormones such as epinephrine.
How are lipid metabolism pathways connected to carbohydrate metabolism?
-Lipid metabolism pathways are closely connected to carbohydrate metabolism as glycerol is converted to a glycolysis intermediate, and fatty acids undergo beta-oxidation to generate acetyl-CoA.
What happens to excess acetyl-CoA when it is produced?
-When acetyl-CoA is produced in excess, it is diverted to create ketone bodies, which can serve as an important source of fuel during glucose starvation, particularly for the brain.
What is ketoacidosis and how is it related to lipid metabolism?
-Ketoacidosis is a serious metabolic condition that occurs when ketone bodies are produced in excess, overwhelming the blood plasma's buffering capacity, potentially leading to coma and death. It is a complication of diabetes and can also result from extreme diets that are low in carbohydrates and high in fat.
How does a high-carbohydrate diet affect fatty acid synthesis?
-High-carbohydrate diets generate excess acetyl-CoA, which can be converted into fatty acids. The synthesis of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA is stimulated by citrate, a marker of energy abundance, and is inhibited by an excess of fatty acids.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
Metbolisme Lipid 1 : Jalur Eksogen

Metabolismo dos lipídeos (Jejum e Bem alimentado) - Bioquímica

Fat Digestion and Absorption | Triglycerides

Lipids and Lipoproteins - Part 2 (Exogenous Pathway)

Metabolisme Makromolekul Asam Amino, Peptida, Protein | Biokimia 101

Fettverdauung einfach erklärt│Biologie Lernvideo [Learning Level Up]
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
