How The Oxygen You Breathe Gets Delivered to the Cells of Your Body
Summary
TLDRThe respiratory system regulates oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood, facilitating metabolism and cellular function. Ventilation allows oxygen to enter the body, where it moves into the alveoli in the lungs for gas exchange. Oxygen enters the bloodstream through capillaries and binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells, enabling its transport to tissues. As oxygen is delivered, carbon dioxide is released and converted into bicarbonate for easier transport. This waste product is then exhaled through the lungs. The cycle ensures efficient oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide removal, supporting cellular respiration and overall health.
Takeaways
- 😀 The respiratory system regulates oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood.
- 😀 Respiration includes ventilation, gas exchange, and the use of oxygen for metabolism.
- 😀 Inhalation brings oxygen into the lungs where gas exchange occurs in the alveoli.
- 😀 Alveoli are small air sacs in the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged.
- 😀 Capillaries line the walls of the alveoli and facilitate the exchange of gases.
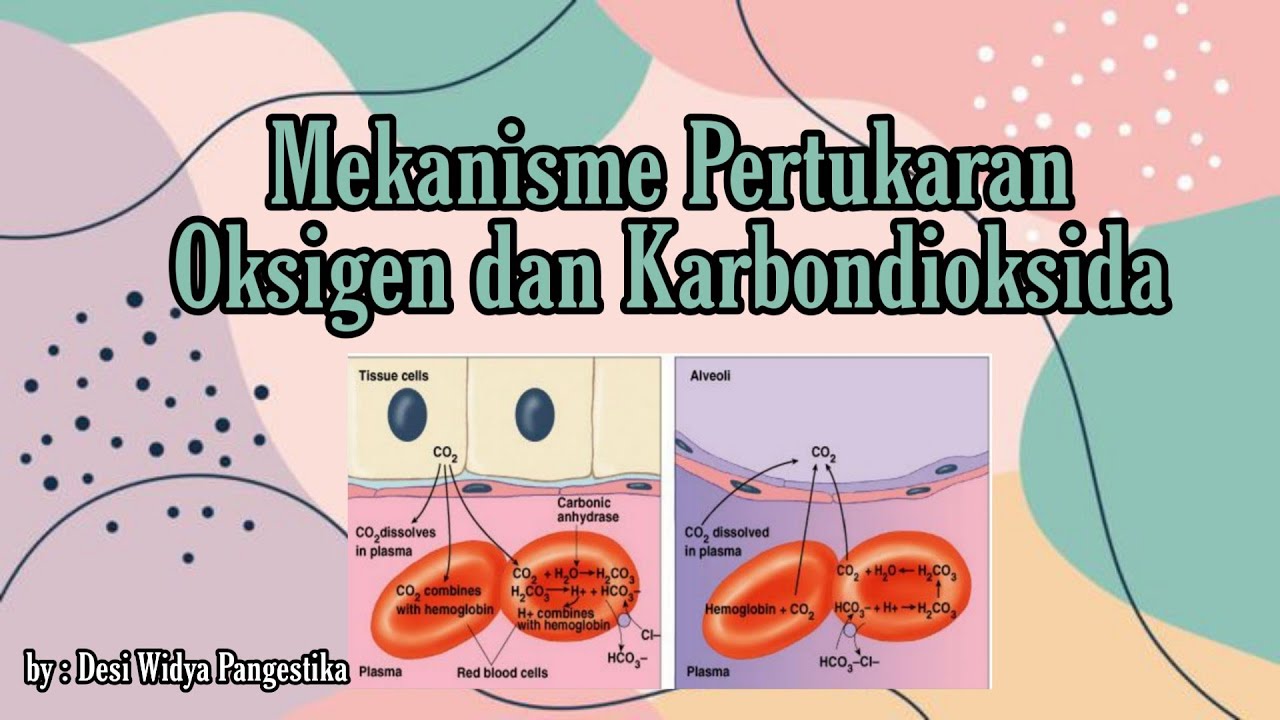
- 😀 Oxygen moves from the alveoli into capillaries, dissolves into plasma, and enters red blood cells.
- 😀 Hemoglobin in red blood cells binds to oxygen and carries it through the arterial bloodstream.
- 😀 The binding of oxygen to hemoglobin increases the ability of the other subunits to bind oxygen.
- 😀 Cellular metabolism produces carbon dioxide, which is transported back to the lungs in the blood.
- 😀 The conversion of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate in the blood helps regulate pH and oxygen release in tissues.
- 😀 The carbon dioxide-rich blood returns to the lungs where bicarbonate is converted back to carbon dioxide, which is exhaled.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
-The primary function of the respiratory system is to regulate oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood by facilitating gas exchange between the air, blood, and tissues.
How does inhalation occur in the respiratory system?
-Inhalation occurs when air is drawn into the body through the nose or mouth. This air travels into the lungs and reaches the alveoli, where gas exchange takes place.
What is the role of alveoli in the respiratory process?
-The alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs. Oxygen from the air diffuses across the alveolar walls into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide moves from the blood into the alveoli to be exhaled.
What is the function of capillaries in gas exchange?
-Capillaries are small blood vessels that line the walls of the alveoli. They allow oxygen to diffuse into the blood and carbon dioxide to move from the blood into the alveoli for exhalation.
What is hemoglobin, and how does it aid in oxygen transport?
-Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that binds to oxygen. It has four subunits, each capable of binding one oxygen molecule, making it highly efficient at transporting oxygen through the bloodstream.
How does hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen change during gas exchange?
-When one molecule of oxygen binds to hemoglobin, the other subunits become more likely to bind additional oxygen molecules. This allows for efficient oxygen loading in the lungs and unloading in the tissues.
What happens to oxygen once it binds to hemoglobin?
-Once oxygen binds to hemoglobin, it is transported through the arterial bloodstream to tissues. In the capillaries of tissues, oxygen is unloaded from hemoglobin and delivered to cells for metabolism.
How is carbon dioxide transported in the blood?
-Carbon dioxide, produced as a byproduct of metabolism, enters the bloodstream and is converted into bicarbonate ions. This conversion helps transport carbon dioxide back to the lungs.
What is the role of bicarbonate in carbon dioxide transport?
-Bicarbonate ions help transport carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs. The conversion of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate also releases hydrogen ions, which decrease hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen, allowing more oxygen to be released to the tissues.
How does the body expel carbon dioxide?
-Carbon dioxide is expelled from the body when it diffuses from the blood into the alveoli in the lungs. It is then exhaled out of the body during the process of breathing.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)