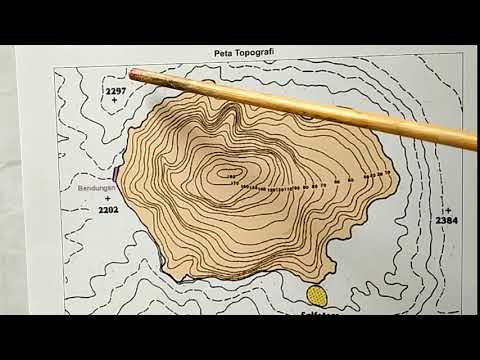
Peta Kontur atau topografi (Pembahasan Soal)
Summary
TLDRThis instructional video explains how to interpret and solve geography problems related to contour maps. It guides viewers through the process of calculating elevations at various points based on contour intervals and map scales. Through practical examples, the video demonstrates how to determine elevation differences, apply scale ratios, and calculate contour intervals to find the height of specific points. The video is designed to help students and learners understand how to use contour maps effectively for geographical analysis and problem-solving.
Takeaways
- 😀 Contour maps are used to determine the elevation of a location relative to sea level.
- 😀 The scale of a contour map is essential for calculating real-world distances and elevations.
- 😀 Contour intervals represent the vertical distance between adjacent contour lines on a map.
- 😀 To calculate the contour interval, divide the denominator of the map's scale by 2,000.
- 😀 A common formula for contour intervals is: Contour Interval = 1/2000 x scale denominator.
- 😀 Elevations increase as you move toward the center of contour circles, indicating higher terrain.
- 😀 The contour interval is consistent across the map, meaning the distance between contour lines is the same throughout.
- 😀 When calculating elevation differences between two points, subtract the lower elevation from the higher one.
- 😀 The elevation of any point can be determined by referencing the nearest contour lines and applying the contour interval.
- 😀 Contour maps also help estimate the elevation of points between marked contour lines using the scale of the map.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of a contour map?
-A contour map is used to represent the elevation or height of different areas above sea level by using contour lines. These lines help show the shape and steepness of the terrain.
How do you calculate the contour interval?
-To calculate the contour interval, you divide the scale of the map by a constant factor (usually 1/2000). For example, with a scale of 1:50,000, the contour interval is 25 meters.
What is the significance of the map scale 1:50,000?
-A map scale of 1:50,000 means that 1 unit of measurement on the map represents 50,000 units in real life, allowing for the calculation of real-world distances and elevations.
How do you determine the elevation of point C using contour maps?
-To determine the elevation of point C, subtract the contour interval from the known elevation at another point (e.g., 125 meters at point A). For example, 125 meters - 25 meters (one contour interval) gives 100 meters for a point lower than A, and further subtracting gives the final elevation.
Why do contour lines closer together indicate higher elevation?
-Contour lines that are closer together indicate a steeper slope, which typically corresponds to higher elevation areas, while lines farther apart suggest a gentler slope.
How can you determine the elevation difference between two points on a map?
-To calculate the elevation difference, subtract the elevation of the lower point from the higher point, using the known elevations at those points. For example, if point A is 150 meters and point B is 100 meters, the difference is 50 meters.
What is the method to calculate the elevation of a point when given distances on a map?
-By multiplying the scale of the map (e.g., 10 meters per centimeter) by the distance in centimeters between two known points, you can calculate the elevation difference. This helps to estimate the elevation of other points along the contour lines.
What is the formula for calculating the elevation change between two points using map measurements?
-The formula is: Elevation Change = (Distance between points in cm on the map) * (Contour interval per centimeter). This allows for the calculation of how much elevation changes as you move along the contour lines.
How does the concept of contour interval apply to varying elevations in the example of the map?
-In the example, the contour interval is consistent (25 meters), and by using this interval, you can determine the elevation of points between known contours. For example, with an elevation of 125 meters and an interval of 25 meters, subsequent points on the map can be calculated by adding or subtracting multiples of 25.
What happens when the contour lines are far apart on a map?
-When contour lines are far apart, it indicates a gentle slope or relatively flat terrain, meaning the elevation is changing slowly over distance.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Perpetaan: Peta Kontur

Cara Menghitung Skala Peta/ Geografi Kelas X/ Kurikulum Merdeka
Pengetahuan Dasar Peta #part 1

Distributional Maps | Std 9 | Geography | Chapter 1 | Maharashtra Board
CINEMÁTICA. GRÁFICAS DEL M.R.U TEORÍA 1 [APRENDE LOS GRÁFICOS DE POSICIÓN, VELOCIDAD Y ACELERACIÓN]

Relasi dan Fungsi [Part 4] - Notasi, Rumus, dan Nilai Fungsi
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
