AQA 3.4 Alkenes REVISION
Summary
TLDRThis educational video provides an in-depth explanation of alkenes, focusing on their reactions, polymerization, and industrial applications. It covers the structure and reactivity of alkenes, including electrophilic addition reactions with molecules like HBr and Br2. The video explores carbocation mechanisms, the formation of polymers such as polyethylene and PVC, and the impact of plasticizers on polymer flexibility. It emphasizes the importance of understanding these concepts for AQA Chemistry students, providing clear insights into the chemistry of plastics and the real-world uses of alkenes.
Takeaways
- 😀 Alkenes, such as ethene and propene, are important monomers used to produce various plastics like polyethylene and polypropylene.
- 😀 Polyethylene is made by polymerizing ethene, where double bonds open up to form long chains, creating a strong and flexible material.
- 😀 Polypropylene is formed by joining propane monomers, resulting in a polymer with repeating units, which are nonpolar and stable, but also non-reactive.
- 😀 The polymerization of alkenes forms saturated molecules, making them stable and non-polar, which contributes to their environmental persistence in landfills.
- 😀 Longer polymer chains tend to have higher melting points due to stronger van der Waals forces, while shorter chains with more branching are more flexible but weaker.
- 😀 PVC (polyvinyl chloride) has a polar structure due to chlorine atoms, making it stronger and more durable, ideal for applications like pipes and outdoor materials.
- 😀 The addition of plasticizers to polymers like PVC makes them more flexible by reducing intermolecular forces between the polymer chains, which is useful in making clothing, bouncy castles, and electrical wiring.
- 😀 Plasticizers work by inserting between polymer chains, allowing them to slide past each other more easily, resulting in a softer and more bendable material.
- 😀 Polymers with minimal branching are generally stronger and more rigid, while those with more branching tend to be more flexible and weaker.
- 😀 Alkenes can be used to create a variety of plastics with different properties by altering the polymerization process and adding different additives, such as plasticizers, to modify flexibility or rigidity.
Q & A
What is the general structure of an alkene?
-Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with the general formula CₙH₂ₙ. They contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond, which is the defining feature of alkenes.
What is electrophilic addition, and how does it work with alkenes?
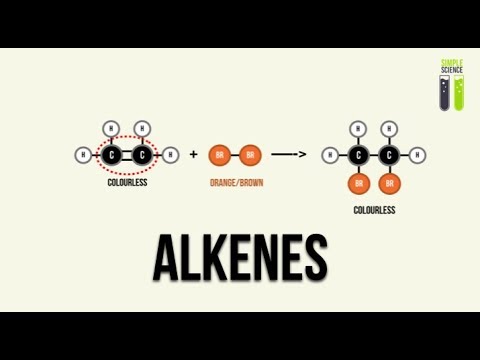
-Electrophilic addition is a reaction where an electrophile reacts with the double bond in an alkene. The double bond opens up, allowing the electrophile to add to the molecule. This process results in the formation of a new molecule, such as a halogenoalkane when an alkene reacts with halogens like Br₂.
How does the addition of bromine to an alkene indicate the presence of a double bond?
-When bromine (Br₂) is added to an alkene, the bromine molecule reacts with the double bond, causing it to break. This results in the decolorization of bromine water, which is a clear indicator that the alkene has a double bond.
What is the role of carbocation stability in electrophilic addition reactions?
-Carbocation stability plays a key role in determining the products of an electrophilic addition reaction. More stable carbocations, such as tertiary carbocations, are formed more readily than less stable primary ones. The stability of the carbocation intermediate affects the major and minor products of the reaction.
What are the different types of carbocations, and which is the most stable?
-The three main types of carbocations are primary, secondary, and tertiary. Tertiary carbocations are the most stable, followed by secondary, and primary carbocations are the least stable. The stability is influenced by the number of alkyl groups attached to the positively charged carbon.
What happens during the polymerization of alkenes?
-Polymerization of alkenes involves the breaking of the carbon-carbon double bond and the linking of multiple monomer units to form long polymer chains. This process results in the formation of plastics such as polypropylene, where the monomers repeatedly join together to form a large, stable structure.
What is the significance of the 'N' in the polymerization of alkenes?
-The 'N' in polymerization notation indicates the number of repeat units in the polymer chain. It represents a large number of repeated monomer units. However, when showing a specific number of repeat units (e.g., two), the 'N' is not included.
How do the properties of polyalkenes differ based on chain length and branching?
-The properties of polyalkenes are influenced by the length and branching of the polymer chains. Longer chains with fewer branches tend to be more rigid and have higher melting points. Shorter chains with more branches are generally more flexible and weaker.
What role do plasticizers play in modifying polymer properties?
-Plasticizers are additives that make polymers more flexible. They work by sliding between polymer chains and pushing them apart, weakening the intermolecular forces between the chains. This results in a softer, more flexible material that is useful for products like clothing, electrical wires, and inflatable structures.
What is PVC, and how does its structure affect its use in various applications?
-PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is a polymer made from the monomer vinyl chloride (C₂H₃Cl). It can be rigid or flexible depending on its structure. When unplasticized, PVC is used for rigid products like pipes, whereas plasticized PVC is more flexible and is used for products like electrical cables and clothing.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
GCSE/IGCSE Organic Chemistry - Part 3 - Alkenes

GCSE Chemistry - Addition Polymers & Polymerisation #56

Composition of Protoplasm (Biomolecules, Condensation & Hydrolysis) Lecture 1 Ch 2 NBF Bio-11

ACIDS, BASES AND SALTS in 1 Shot FULL CHAPTER IN ANIMATION ||| NCERT SCIENCE Class 10th Chapter 2

Important Industrial Polymers | Properties and Applications of PVC | Bakelite | PVAc

Apa Itu Sensor Tekanan dan Cara Kerjanya
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
