DIFUSI DAN OSMOSIS
Summary
TLDRIn this engaging video, David Napitupulu explains the concepts of diffusion and osmosis, highlighting their definitions, processes, and key differences. Diffusion is described as the movement of solutes from high to low concentration, illustrated with examples like ink in water and nutrient absorption. Osmosis, on the other hand, involves the movement of water through a semipermeable membrane from areas of high water concentration to low. The video also features practice questions to reinforce understanding, making it a valuable resource for students seeking clarity on these fundamental biological processes.
Takeaways
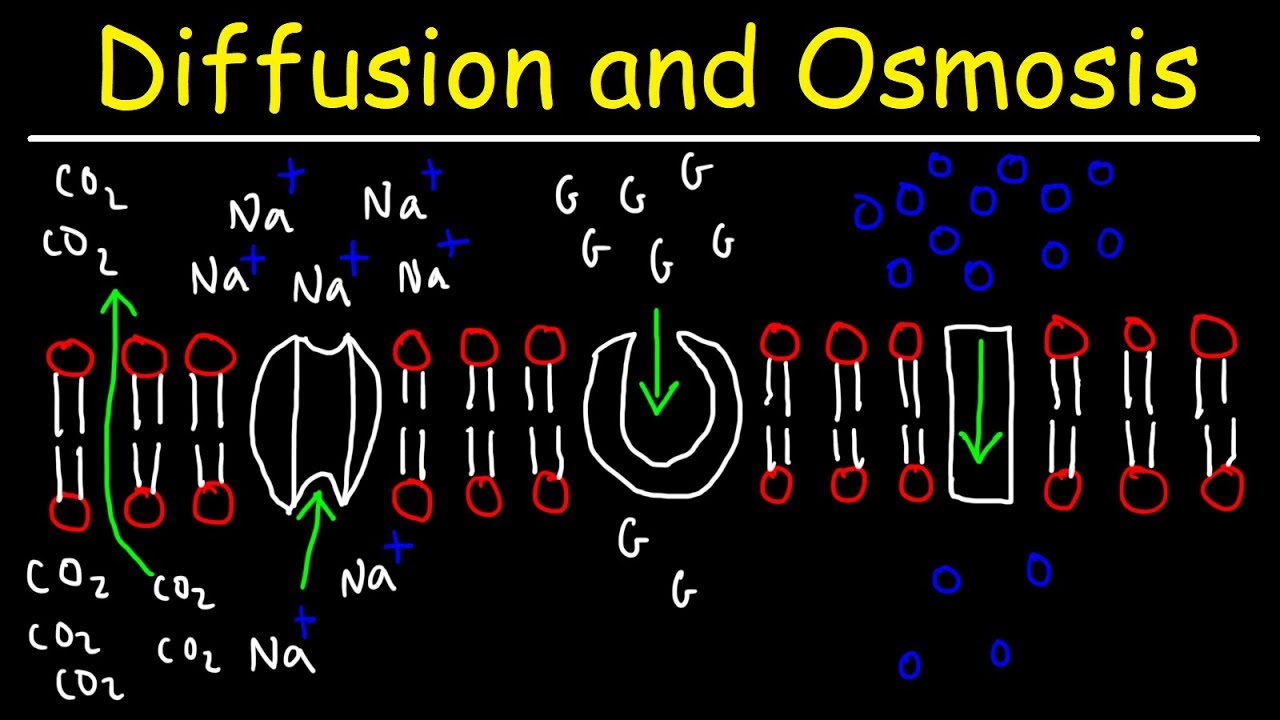
- 😀 Diffusion is the process of solute moving from high concentration to low concentration.
- 😀 Solute refers to substances like sugar or salt, while solvent refers to substances like water.
- 😀 Examples of diffusion include ink spreading in water and the movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide in alveoli.
- 😀 Osmosis is the movement of solvent (typically water) from a region of high water concentration to low water concentration through a semi-permeable membrane.
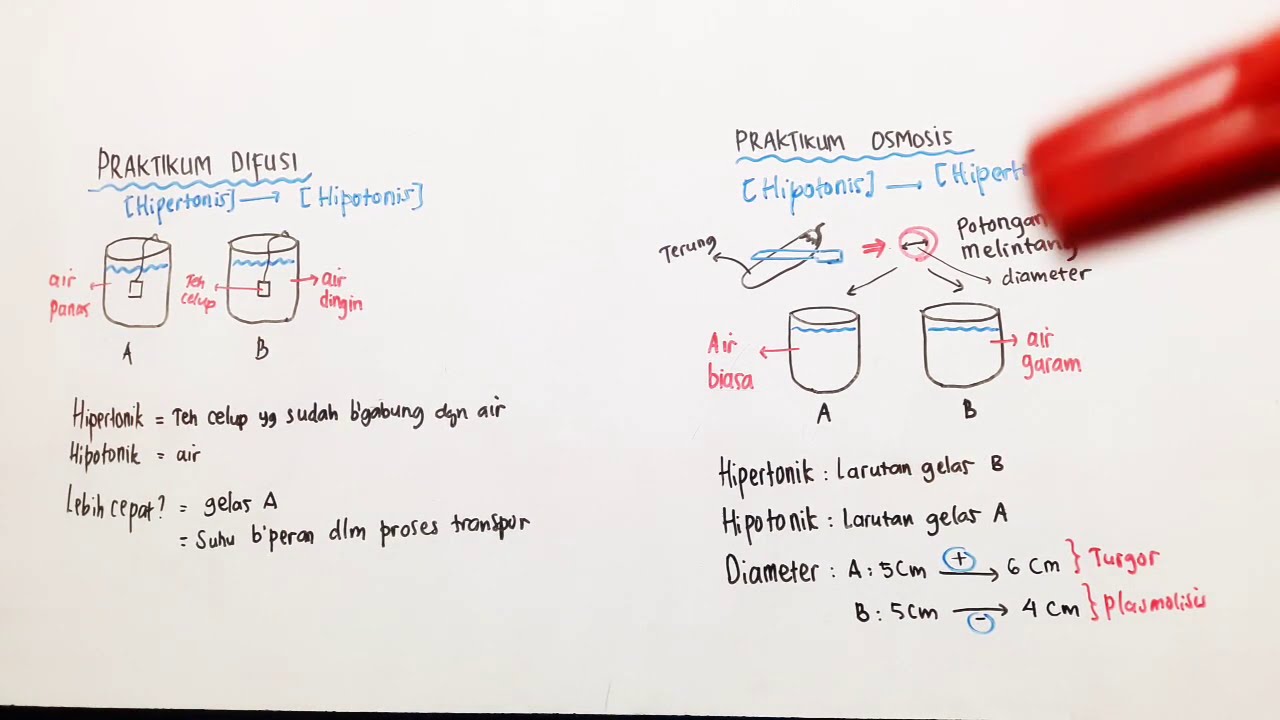
- 😀 Hypotonic solutions have low solute concentration and high solvent concentration, while hypertonic solutions have high solute concentration and low solvent concentration.
- 😀 Osmosis can also involve substances like alcohol and ammonia, not just water.
- 😀 Both diffusion and osmosis are forms of passive transport, meaning they do not require energy.
- 😀 A key difference is that diffusion does not require a semi-permeable membrane, while osmosis does.
- 😀 Diffusion can involve solids, liquids, and gases, whereas osmosis typically involves liquids.
- 😀 Practical examples of osmosis include potatoes absorbing water when submerged in pure water.
Q & A
What is diffusion?
-Diffusion is the process of solute moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
What types of substances are involved in diffusion?
-Diffusion involves solutes, which can be solids, liquids, or gases, such as sugar or salt.
Can you give an example of diffusion?
-An example of diffusion is the spreading of ink in water, where the ink molecules move from a concentrated area to distribute evenly.
What is osmosis?
-Osmosis is the movement of solvent, primarily water, from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration through a semi-permeable membrane.
What role does a semi-permeable membrane play in osmosis?
-A semi-permeable membrane allows the passage of water while restricting the movement of solutes, facilitating the process of osmosis.
How does osmosis differ from diffusion?
-Osmosis specifically refers to the movement of solvent (usually water) through a semi-permeable membrane, whereas diffusion can involve the movement of various substances without the need for a membrane.
What is an example of osmosis in plants?
-An example of osmosis in plants is when roots absorb water from the soil, where water moves from a region of higher concentration in the soil to lower concentration within the plant roots.
What are the similarities between diffusion and osmosis?
-Both diffusion and osmosis are forms of passive transport that do not require energy, and both involve the movement of substances from high to low concentration.
Why is understanding diffusion and osmosis important in biology?
-Understanding diffusion and osmosis is crucial in biology because they are fundamental processes that govern how substances move across cell membranes, affecting cellular function and overall homeostasis.
What did the video suggest about the quiz on diffusion and osmosis?
-The video included a quiz to reinforce understanding, with questions aimed at assessing knowledge about the definitions and examples of diffusion and osmosis.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)