Introduction to Elastic Potential Energy with Examples
Summary
TLDRThis engaging video tutorial explores elastic potential energy, defined as the energy stored in an object due to temporary deformation. Using examples like springs, rubber bands, and rubber balls, the video illustrates how this energy can be converted to kinetic and gravitational potential energy. Key concepts such as the spring constant and Hooke's Law are discussed, along with an example calculation of elastic potential energy using the formula PE = 1/2 k x². The lively interaction between the presenters and students makes complex concepts accessible and enjoyable, encouraging viewers to deepen their understanding of physics.
Takeaways
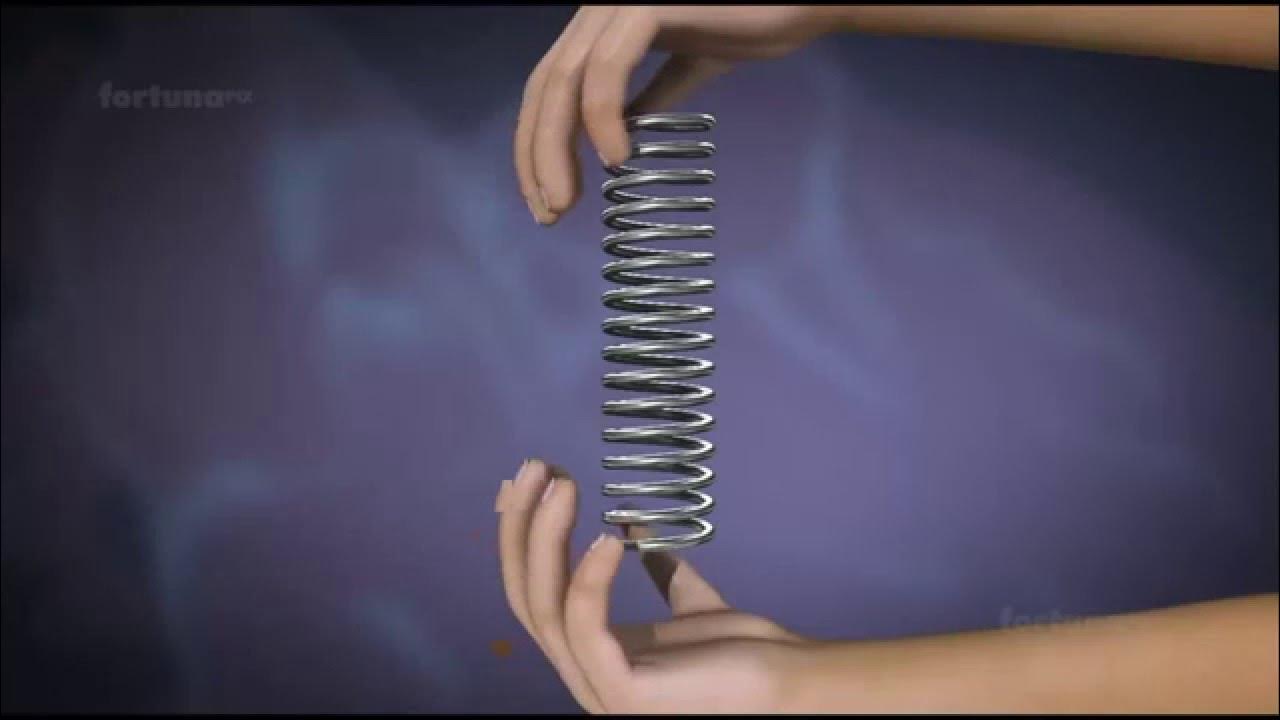
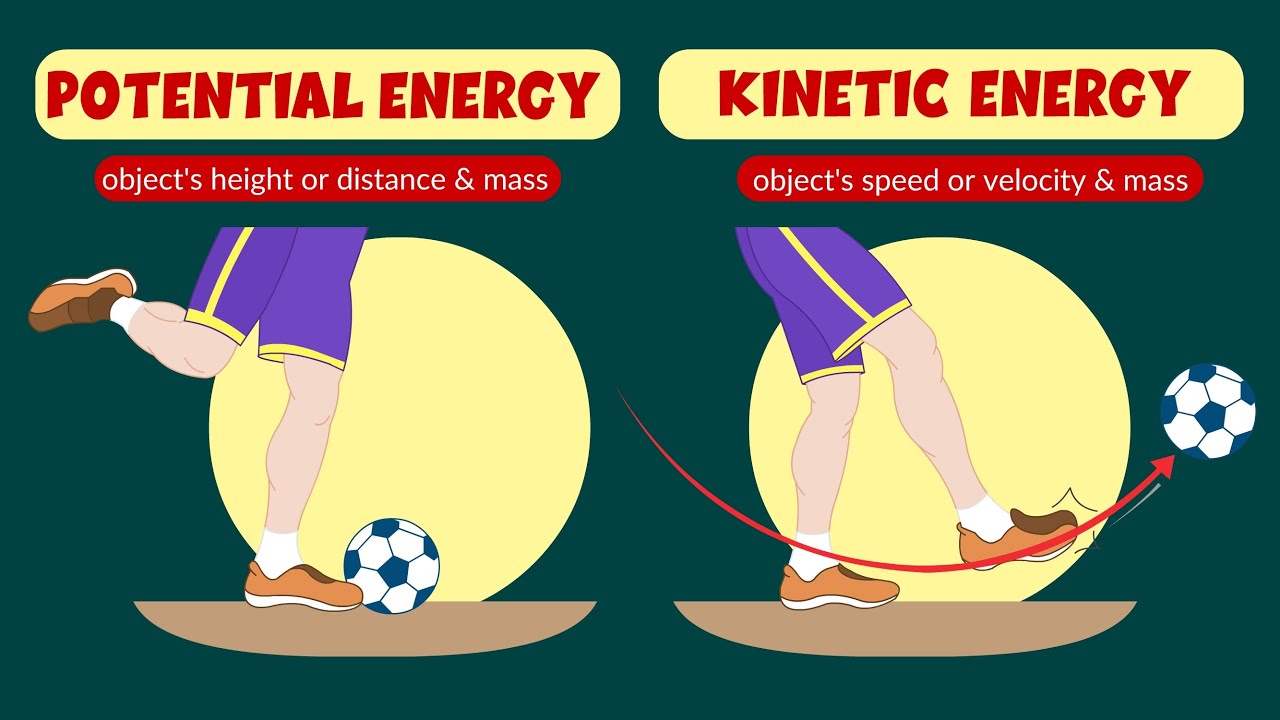
- 😀 Elastic potential energy (PEᵉ) is the energy stored in an object due to its temporary deformation.
- 📏 The formula for elastic potential energy is PEᵉ = 1/2 k x², where k is the spring constant and x is the displacement from equilibrium.
- 🪴 The spring constant (k) measures a spring's resistance to deformation, with larger values indicating stiffer springs.
- 🔄 Common examples of elastic potential energy include springs, rubber bands, and rubber balls.
- 💡 When a spring is compressed or elongated, it stores elastic potential energy that can be converted into kinetic energy upon release.
- 🔬 The spring constant is measured in Newtons per meter (N/m), and it varies between different springs based on their design.
- 🧮 When calculating elastic potential energy, the units will always resolve to Joules (J).
- 📈 A graph of force versus displacement for a spring will show a linear relationship, with the slope representing the spring constant.
- 🤔 The displacement from the rest position can be negative, but elastic potential energy itself cannot be negative due to the squared term in the formula.
- 👨🏫 Understanding elastic potential energy is essential for analyzing mechanical systems and real-world applications in physics.
Q & A
What is the symbol for elastic potential energy?
-The symbol for elastic potential energy is PE with a subscript of e, or sometimes U with a subscript of e.
What is elastic potential energy?
-Elastic potential energy is the energy stored in an object due to its temporary deformation, such as when a spring is compressed or elongated.
Can you provide a common example of elastic potential energy?
-A common example is a spring, which stores elastic potential energy when compressed or elongated.
What is the equation for elastic potential energy?
-The equation for elastic potential energy is PE = 1/2 k x², where k is the spring constant and x is the displacement from the equilibrium position.
What does the spring constant measure?
-The spring constant measures how much force is required to compress or expand a spring per meter of displacement.
How does the strength of a spring affect its spring constant?
-A weak spring has a small spring constant, meaning it requires less force to compress, while a strong spring has a large spring constant, requiring more force to compress.
What happens to the elastic potential energy when a rubber band is stretched?
-When a rubber band is stretched, elastic potential energy is stored, which can later be converted into kinetic energy or gravitational potential energy.
What are the units of elastic potential energy?
-The units of elastic potential energy are Joules, which can also be expressed as Newton-meters.
Can elastic potential energy be negative?
-No, elastic potential energy cannot be negative because while displacement can be negative, it is squared in the equation, resulting in a non-negative value.
What did Mr. Fullerton clarify about Hooke's Law?
-Mr. Fullerton mentioned that Hooke's Law was not defined yet in the discussion, which relates the force exerted by a spring to its displacement.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)