BIOLOGI Kelas 11 - Sistem Pertahanan Tubuh (PART 2)
Summary
TLDRIn this informative video from GYA Academy, the specific immune system is explored as the body's third line of defense against pathogens. Key components such as pathogens, antigens, and antibodies are defined, with a focus on the roles of B and T lymphocytes in the immune response. The video highlights how B cells produce antibodies for humoral immunity while T cells are crucial for cellular immunity. Viewers also learn about different types of antibodies and immunity, including active and passive forms. Engaging practice questions reinforce understanding, making this video a valuable resource for learning about the immune system.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video discusses the body's specific defense system, which is the third layer of immune protection.
- 🤒 Specific immune responses are activated after pathogens bypass the non-specific defense system.
- 🔍 Pathogens are infectious agents, while antigens are molecules from these pathogens recognized by the immune system.
- 🛡️ Antibodies are specific proteins produced by the immune system to combat antigens.
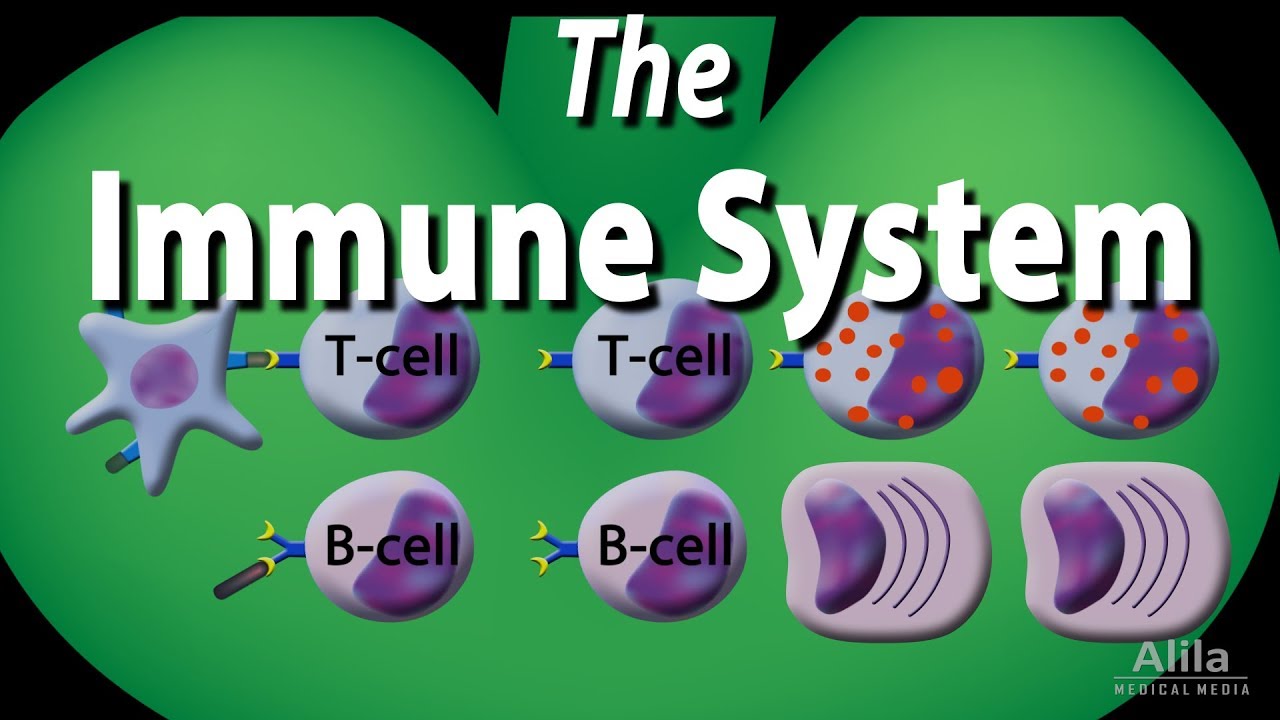
- 🩸 Lymphocytes, which include B cells and T cells, are crucial components of the specific immune response.
- 🧬 B cells produce memory cells and plasma cells that generate antibodies, contributing to humoral immunity.
- ⚔️ T cells directly attack infected cells and tumors, forming the basis of cellular immunity.
- 💉 The immune system can generate active immunity through direct contact with pathogens or passive immunity by receiving antibodies from another individual.
- 🏥 The video outlines the distinction between natural and artificial immunity, as well as active and passive immunity.
- 📚 The importance of memory cells is highlighted, allowing for faster and more effective responses during secondary exposures to antigens.
Q & A
What is the specific immune system?
-The specific immune system, also known as adaptive immunity, serves as the body's third line of defense, activated when pathogens bypass non-specific defenses.
What are antigens and their role in the immune system?
-Antigens are molecules from pathogens that enter the body and can be recognized by the immune system, triggering a specific immune response.
What are the two main components of the specific immune system?
-The two main components are lymphocytes (B cells and T cells) and antibodies, which work together to identify and eliminate pathogens.
What is the difference between B cells and T cells?
-B cells are responsible for producing antibodies and contribute to humoral immunity, while T cells directly attack infected or cancerous cells and are involved in cell-mediated immunity.
What are the types of T cells and their functions?
-There are three types of T cells: Cytotoxic T cells attack and destroy infected cells, Helper T cells assist in the activation of B cells and other T cells, and Regulatory T cells suppress the immune response once an infection is resolved.
How do antibodies function in the immune response?
-Antibodies bind specifically to antigens, neutralizing them or marking them for destruction by other immune cells, such as macrophages.
What are the five types of antibodies and their primary roles?
-The five types of antibodies are IgG (most abundant, crosses the placenta), IgA (found in secretions), IgM (first responder during infection), IgD (involved in initiating immune response), and IgE (related to allergic reactions).
What is the difference between active and passive immunity?
-Active immunity is developed when the body produces antibodies in response to an infection or vaccination, while passive immunity is acquired through the transfer of antibodies from another individual.
What is the role of memory B cells in the immune system?
-Memory B cells remember past infections, allowing for a faster and more robust antibody response if the same antigen is encountered again.
What is the process of humoral immunity?
-Humoral immunity begins when an antigen enters the body, activating B cells to produce plasma cells that generate antibodies, which then bind to and help eliminate the antigen.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Apa itu Sistem Imun ?

Sistem pertahanan tubuh non spesifik eksternal. sistem pertahanan tubuh lapis pertama. biologi SMA
The Immune System Overview, Animation
IMMUNOLOGY- Innate Immunity and Adaptive Immunity (FL-Immuno/01)

BIOLOGI Kelas 11 - Sistem Pertahanan Tubuh (PART 1) | GIA Academy

VIDEO ANIMASI RESPON IMUN
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
