7. Server Load Balancing || Load Balancing Terms and Terminology || F5 Big-IP LTM
Summary
TLDRIn this F5 big-ip LTM tutorial, we explore server load balancing, a technology that efficiently distributes traffic across multiple servers for optimal performance. It covers global server load balancing (GSLB) and the importance of load balancing for scalability, reliability, and high availability. Key terms like client nodes, server pools, and virtual servers are explained, setting the stage for hands-on labs and emphasizing the role of each component in managing network traffic.
Takeaways
- 🌐 **Server Load Balancing**: It's a technology that distributes traffic among several servers to ensure high performance and availability.
- 🌍 **Global Server Load Balancing (GSLB)**: Refers to the intelligent distribution of traffic across multiple geographic locations.
- 🏢 **Server Locations**: Servers can be located on-premises, in a private cloud, or in a public cloud.
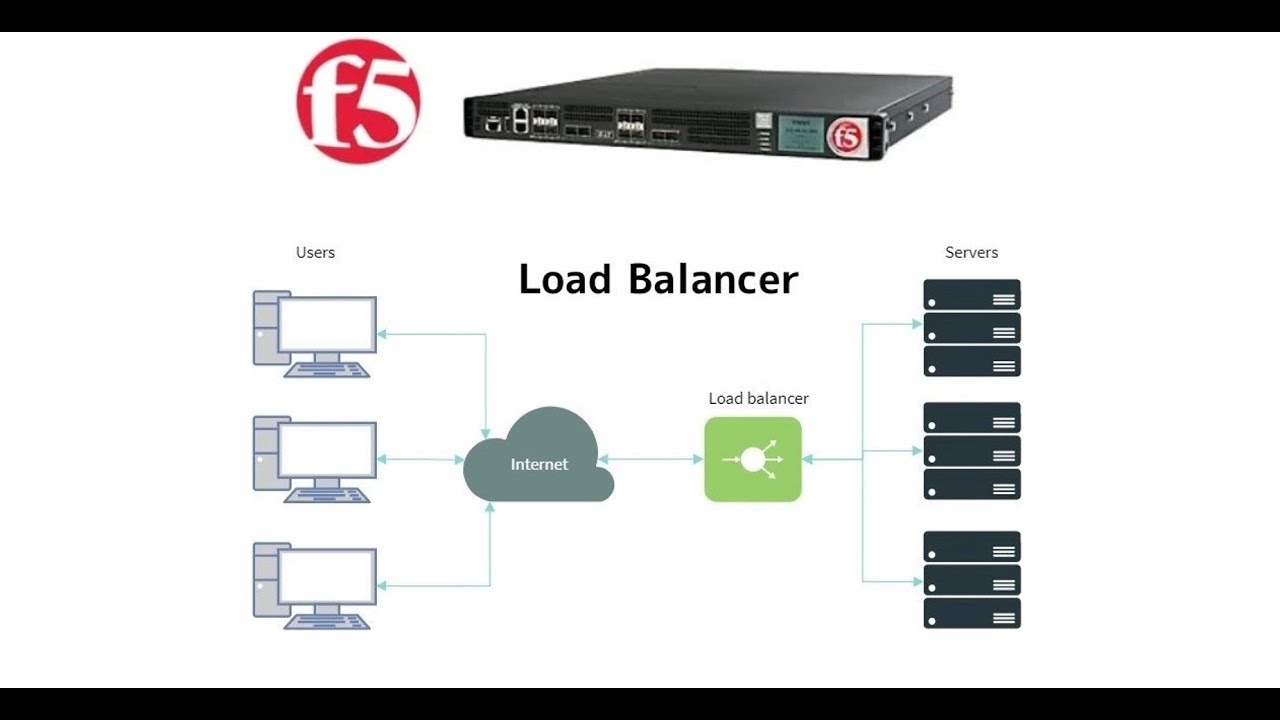
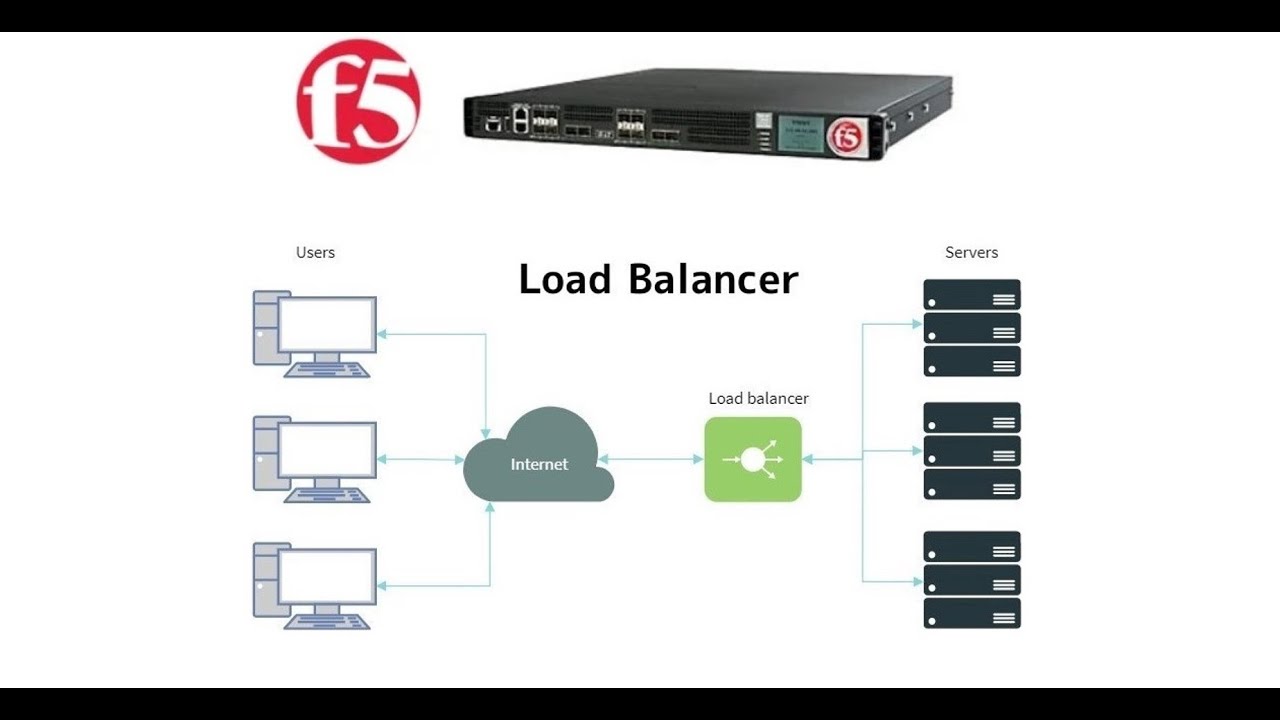
- 🔄 **Load Balancer Function**: It intercepts traffic for a website and routes it through various servers to balance the load.
- 📈 **Load Balancing Algorithms**: These algorithms prioritize responses to client requests to ensure consistent application delivery.
- 💻 **Client Definition**: A client is a machine that sends connections or requests to the F5 load balancer to access web server pools.
- 📚 **Node Explanation**: A node is an individual server device in a server pool configured on an F5 load balancer.
- 🔑 **Multiple Server Pools**: A node can be a member of multiple server pools, running different services.
- 👥 **Pool and Pool Members**: A pool is a group of servers running specific services, and pool members are identified by their IP addresses and server ports.
- 🌐 **Virtual Server**: It's a hypothetical configuration on F5 load balancer where external clients send traffic for web services.
- 🔗 **Virtual Server Identification**: Identified by its IP address and service ports, used by clients to access internal services.
Q & A
What is server load balancing?
-Server load balancing is a technology that distributes high traffic among several servers using network-based hardware or software defined appliances.
What is the difference between server load balancing and global server load balancing (GSLB)?
-Server load balancing is done locally, whereas GSLB involves intelligent distribution of traffic across multiple geographic locations.
Where can servers be located in the context of load balancing?
-Servers can be on-premises in a company's own data center, hosted in a private cloud, or in a public cloud.
What is the role of a server load balancer?
-A server load balancer intercepts traffic for a website and routes that traffic through various servers to ensure high performance application delivery.
What are the benefits of server load balancing?
-Server load balancing ensures scalability, reliability, and high availability of application delivery.
What is a client in the context of load balancing?
-A client is a machine that sends connections or requests to an F5 load balancer to access a web server pool.
What is a node in server load balancing?
-A node is an individual server device in a server pool configured on an F5 load balancer, which can be a member of multiple server pools.
What is a server pool?
-A server pool is a group of servers configured in an F5 load balancer for certain services or applications.
What is a pool member?
-A pool member is a node that is assigned to a specific server pool, identified by its IP address and server ports.
What is a virtual server?
-A virtual server is a hypothetical configuration on an F5 load balancer where external clients send traffic to access web servers connected on the internal side of the load balancer.
Why is a virtual server IP used instead of a physical interface IP?
-A virtual server IP is used to allow clients to access internal services without directly calling the servers' physical IP addresses, providing a layer of abstraction and flexibility that will be further explained in the next tutorial.
What are the key terminologies one must understand when working with F5 Big-IP LTM?
-Key terminologies include client, node, server pool, pool member, and virtual server.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

1. Introduction to F5 Big IP || LTM (Local Traffic Manager)
3. Prerequisites to setup F5 lab || How to install Webserver on windows 10 machine || F5 Big-IP LTM

9. Types and Methods of Load Balancing || F5 Big IP LTM

What is a Load Balancer?

13.Netscaler Load balancing persistency and method
2. F5 Big IP LTM (Local Traffic Manager) || Load Balancer Explained
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
