Introdução à Histologia Vegetal (Tecidos) - Aula 07 - Módulo 5: Botânica
Summary
TLDRThe video lesson discusses plant histology, focusing on the importance of understanding basic plant tissues. The instructor explains two types of plant tissues: meristematic (responsible for cell multiplication and plant growth) and adult tissues (involved in protection, filling, and conduction). By using simple analogies and encouraging students to take notes, the teacher stresses the value of foundational knowledge for future lessons on plant structures like stems, roots, and leaves. The lesson also touches on plant growth mechanisms, the significance of meristems, and the differentiation and de-differentiation of cells. The video ends with motivational advice on effective studying.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Understanding plant histology is crucial for learning botany, especially when studying plant structures like stems, roots, and leaves.
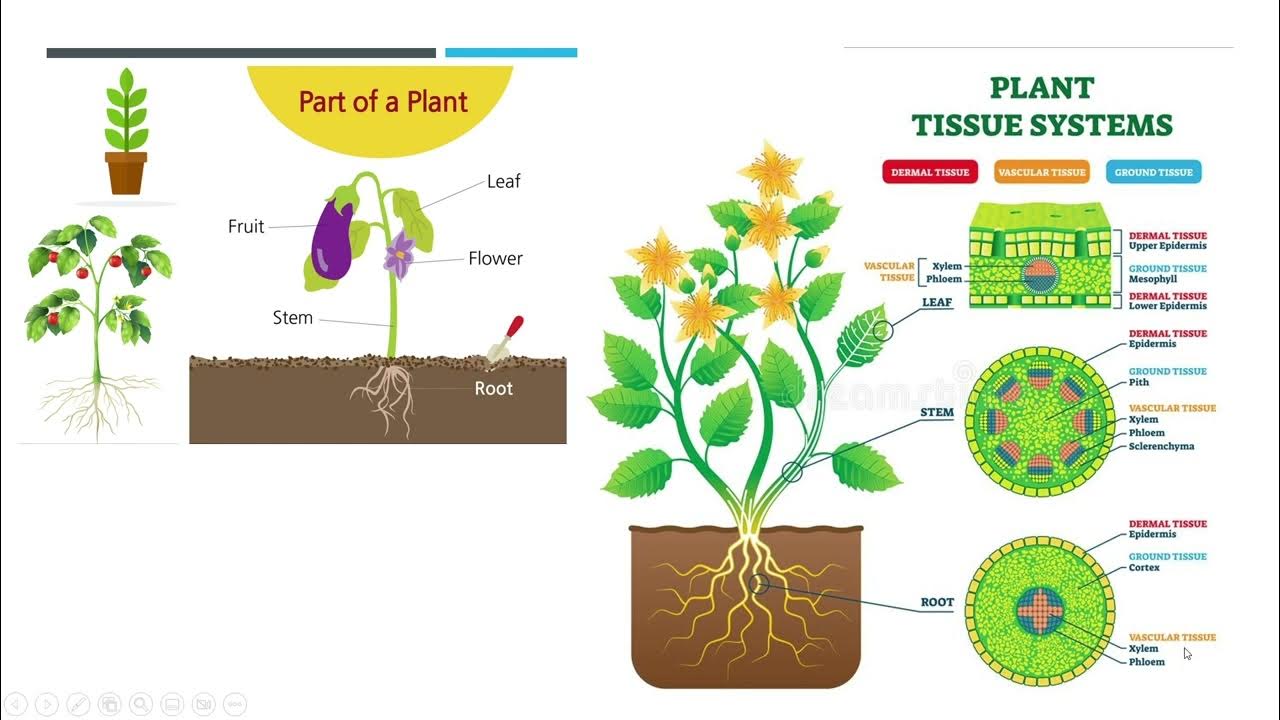
- 📚 Two main types of plant tissues exist: meristematic tissues (capable of cell division) and adult tissues (non-dividing).
- 🌿 Meristematic cells, which drive plant growth, are similar to stem cells and primarily responsible for plant growth through cell division (mitosis).
- 🧠 Adult plant cells have three main functions: protection (e.g., epidermis), filling and supporting (e.g., parenchyma), and conducting sap (e.g., xylem and phloem).
- 🧪 Key differences between meristematic and adult cells include: meristematic cells have thinner cell walls, larger nuclei, and smaller vacuoles, while adult cells have thicker walls, larger vacuoles, and smaller nuclei.
- 🌳 Differentiation is the process by which a meristematic cell becomes an adult cell, and in rare cases, some adult cells can revert back to meristematic form (dedifferentiation).
- 🌱 Primary meristems (like protoderm, fundamental meristem, and procambium) are responsible for plant growth in length (apical growth), while secondary meristems (like cambium and phellogen) contribute to growth in thickness (lateral growth).
- 🌿 Protoderm gives rise to the epidermis (outer protective layer), fundamental meristem forms parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma (filling and support tissues), and procambium generates xylem and phloem (conducting tissues).
- 🌾 Parenchyma cells can dedifferentiate into secondary meristematic cells, promoting growth in thickness. This leads to the formation of tissues like cork (phellogen) and vascular cambium, which produce secondary xylem and phloem.
- 💡 The teacher emphasizes strategic, thoughtful studying over simply spending long hours on the material, as a planned approach can yield better learning outcomes.
Q & A
What are the two main types of plant tissues discussed in the video?
-The two main types of plant tissues are meristematic tissues, which can multiply, and adult tissues, which no longer multiply.
What is the primary function of meristematic tissues in plants?
-Meristematic tissues are responsible for plant growth as they are constantly undergoing mitosis to produce new cells, contributing to the growth of the plant in length and thickness.
What is the significance of a cell's ability to differentiate in plants?
-Differentiation is when a meristematic cell transforms into an adult cell, adopting specific functions such as protection, support, or conduction in the plant.
What are the three main functions of adult plant cells?
-Adult plant cells have three primary functions: protection (revestment), filling spaces and providing support, and conducting water and nutrients through the plant.
How do meristematic and adult plant cells differ in structure?
-Meristematic cells have thin cell walls, large nuclei, and fewer organelles due to constant division, while adult cells have thicker cell walls, larger vacuoles for water storage, and smaller nuclei.
What is dedifferentiation, and why is it important in plant tissue development?
-Dedifferentiation is when an adult plant cell reverts to a meristematic state, allowing it to divide again. This process is crucial for secondary growth, especially in the thickening of stems and roots.
What are the two types of meristems, and what are their roles?
-The two types of meristems are primary meristems, responsible for growth in length (found in the tips of stems and roots), and secondary meristems, responsible for growth in thickness (in stems and roots).
What role does the protoderm play in plant tissue formation?
-The protoderm is a primary meristem that differentiates into the epidermis, the plant's outer protective layer.
What are the differences between parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma cells?
-Parenchyma cells primarily fill spaces and perform functions like photosynthesis. Collenchyma cells provide flexible support, while sclerenchyma cells provide rigid support and are dead at maturity.
What is the cambium, and how does it contribute to plant growth?
-The cambium is a type of meristematic tissue that produces xylem on the inside and phloem on the outside, facilitating secondary growth in plants by increasing stem thickness.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)