2-Minute Neuroscience: Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland
Summary
TLDRIn this episode of '2 Minute Neuroscience,' the focus is on the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. The hypothalamus, located above the brainstem, is crucial for maintaining homeostasis and controlling hormones. It influences the autonomic nervous system and regulates the pituitary gland, known as the 'master gland,' which secretes vital hormones affecting growth, reproduction, stress response, metabolism, and lactation. The pituitary gland has anterior and posterior lobes, with the former releasing hormones like growth hormone and the latter releasing oxytocin and vasopressin, which are synthesized by the hypothalamus. These hormones play key roles in childbirth, lactation, social bonding, urine output, and blood pressure regulation.
Takeaways
- 🧠 The hypothalamus is a small region above the brainstem that plays a crucial role in controlling homeostasis and hormones.
- 🌡️ Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of balance or stability within a biological system, and the hypothalamus can influence it directly or through hormone release.
- 📉 The hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland, which is located just below it and is often called the 'master gland' due to its regulatory functions.
- 🔬 The pituitary gland has two lobes: the anterior and the posterior, each with distinct roles in hormone secretion.
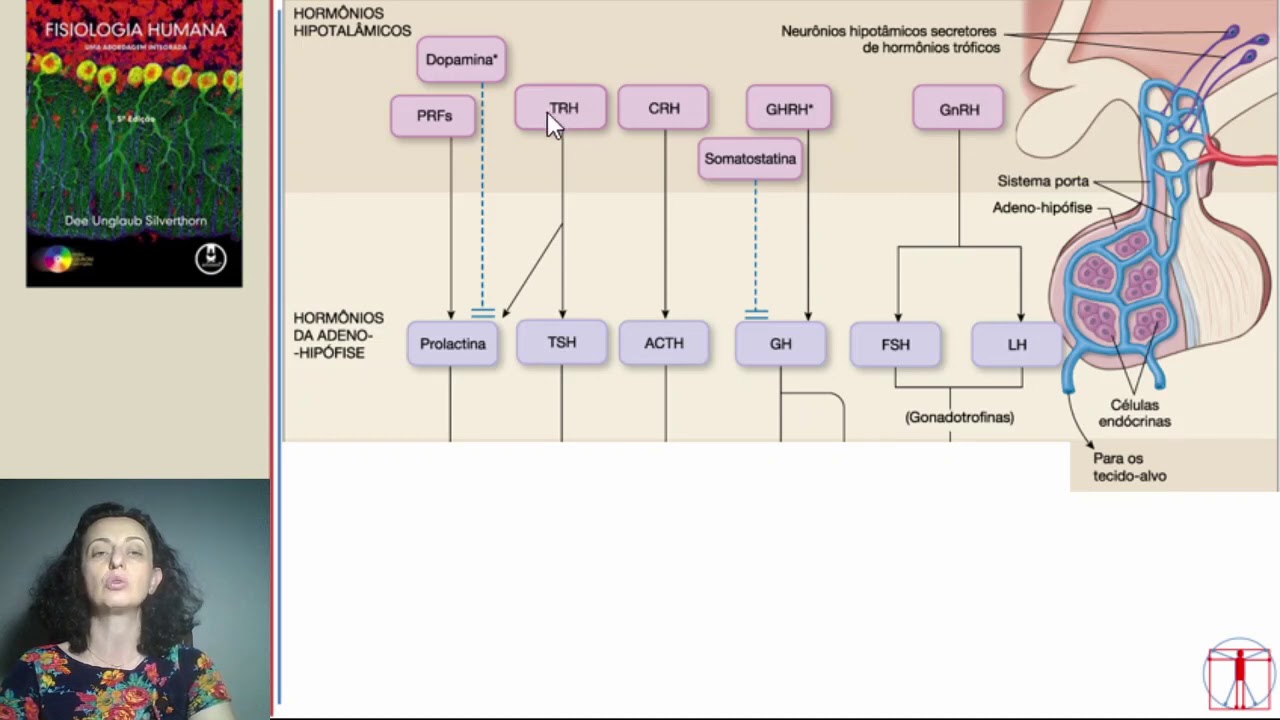
- 🌱 The anterior pituitary releases hormones such as growth hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, and prolactin.
- 📈 The hypothalamus regulates the release of anterior pituitary hormones by sending releasing hormones as signals.
- 💧 The posterior pituitary secretes oxytocin and vasopressin, which are not synthesized there but by the hypothalamus.
- ❤️ Oxytocin is known for facilitating childbirth, lactation, and is believed to play a role in social bonding and compassion.
- 💧 Vasopressin primarily controls urine output and blood pressure regulation.
- 📌 The hypothalamus-pituitary interaction is essential for the body's hormonal balance and various physiological processes.
Q & A
What are the primary functions of the hypothalamus?
-The hypothalamus is involved in controlling homeostasis and hormones. It maintains balance and stability in biological systems and influences the release of hormones by controlling the pituitary gland.
Where is the hypothalamus located in the brain?
-The hypothalamus is located directly above the brainstem, in the central region of the brain.
How does the hypothalamus maintain homeostasis?
-The hypothalamus maintains homeostasis by exerting direct influence over the autonomic nervous system and by controlling the release of hormones.
What is the primary role of the pituitary gland?
-The pituitary gland secretes various important hormones and regulates the activity of other hormone-secreting glands in the body, earning it the nickname 'master gland.'
What are the two lobes of the pituitary gland, and how do they differ?
-The pituitary gland consists of the anterior and posterior lobes. The anterior pituitary synthesizes and releases multiple hormones, while the posterior pituitary releases hormones that are synthesized by the hypothalamus.
What hormones are secreted by the anterior pituitary gland?
-The anterior pituitary gland secretes growth hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, and prolactin.
How does the hypothalamus control the release of hormones from the anterior pituitary gland?
-The hypothalamus sends releasing hormones to the anterior pituitary, signaling when to secrete specific hormones into the bloodstream.
What hormones are released by the posterior pituitary gland?
-The posterior pituitary gland releases oxytocin and vasopressin, which are synthesized in the hypothalamus.
What are the primary functions of oxytocin?
-Oxytocin facilitates childbirth and lactation and is thought to play a role in compassion and social bonding.
What is the role of vasopressin in the body?
-Vasopressin helps regulate urine output and blood pressure, playing a key role in maintaining fluid balance and vascular health.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

The hypothalamus and pituitary gland | Endocrine system physiology | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy
Endocrinologia 2 - Eixo hipotálamo-hipófise

Understanding the Hypothalamus and Pituitary

Endocrinology | Hypothalamus: Posterior Pituitary Connection

KELENJAR HIPOFISIS - MODUL ADRENAL DAN HIPOFISIS - dr Reza Rinadhi Bramantya, SpPD-KEMD

Fisiologi Siklus Menstruasi (1/5) - Pengenalan Hypothalamus dan Hipofisis Anterior
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
