Seismic Waves: On Exploring Earth's Interior
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the use of seismic waves for exploring Earth's interior. It explains the difference between the focus and epicenter of an earthquake, and how geophysicists use the speed of seismic waves to infer the density and composition of Earth's layers. The script details the properties of P and S waves, their interaction with Earth's layers, and how their travel times help determine earthquake locations. It also discusses how seismic waves refract and reflect within the Earth, and the significance of different wave paths like PKP and PP in understanding Earth's structure.
Takeaways
- 🌏 Seismic waves are crucial for exploring Earth's interior, helping us understand its composition and structure.
- 📍 The focus is the point within Earth where an earthquake originates, while the epicenter is the point on the surface directly above it.
- 🌊 Seismic waves propagate in all directions from the focus, with their speed influenced by the density of the materials they travel through.
- 🔍 Geophysicists use the speed of seismic waves to infer the properties of Earth's interior, including density and composition.
- 📊 Seismographs record seismic activity, with P waves (compressional) arriving first, followed by S waves (shearing), and finally surface waves.
- 🏗 Surface waves, although the slowest, are the most damaging during earthquakes due to their extensive ground shaking.
- 🔄 P waves cause particles to move back and forth in the direction of wave propagation, similar to a slinky's compression and dilation.
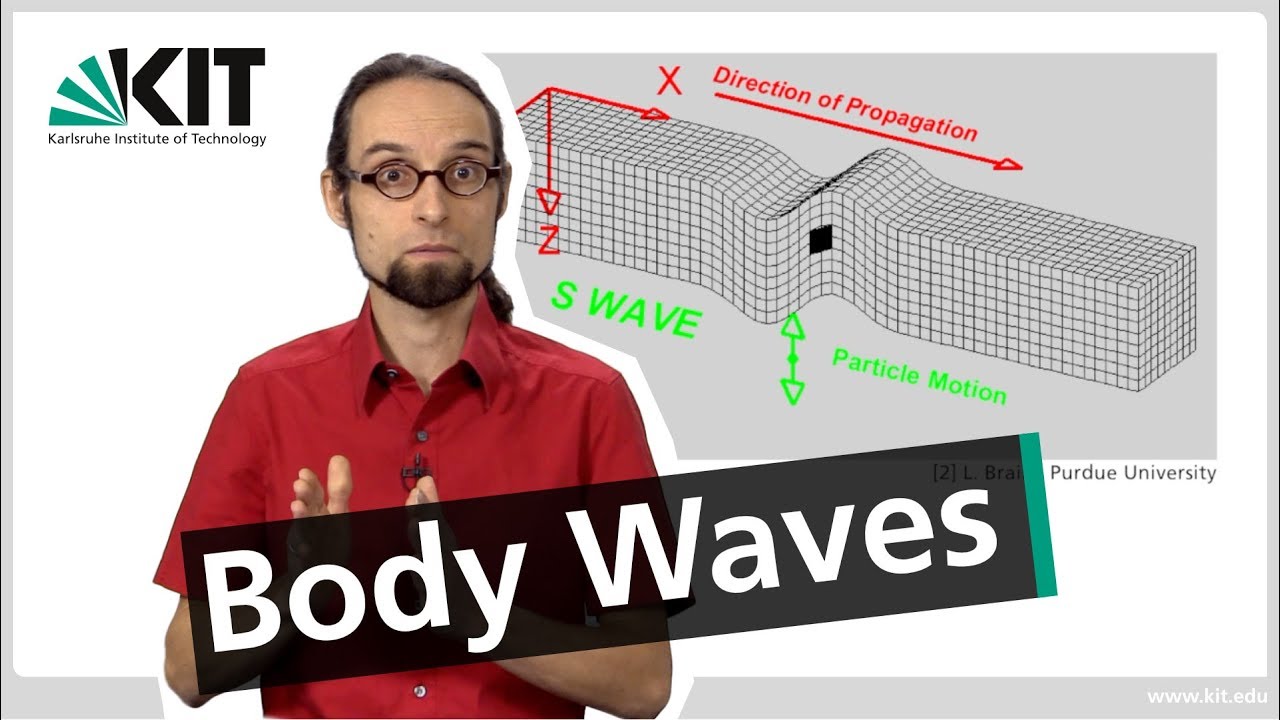
- 📉 S waves involve side-to-side particle movement, perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, and cannot travel through liquids.
- 📈 The velocity of P and S waves changes with depth due to variations in density, with significant changes at the mantle's transitions.
- 🔮 Geophysicists analyze wave paths, such as PP, PCP, and PKP waves, to understand how seismic waves travel through Earth's layers.
- 🌐 Snell's law explains how seismic waves refract as they move through materials of different densities, leading to curved paths within Earth.
Q & A
What is the focus of an earthquake?
-The focus of an earthquake is the location where the earthquake originates below the Earth's surface.
What is the difference between the focus and the epicenter of an earthquake?
-The focus is the point within the Earth where the earthquake originates, while the epicenter is the point on the Earth's surface directly above the focus.
How do geophysicists use seismic waves to explore Earth's interior?
-Geoscientists use seismic waves by measuring their speed and direction to infer the density and composition of the Earth's interior.
What is a seismograph and what does it measure?
-A seismograph is an instrument that measures seismic activity, specifically the shaking of the ground caused by earthquakes.
What are the three main types of seismic waves and in what order do they typically arrive at a seismic station?
-The three main types of seismic waves are P waves, S waves, and surface waves. They typically arrive in the order of P waves first, followed by S waves, and then surface waves.
Why are surface waves significant in terms of earthquake damage?
-Surface waves are significant for earthquake damage because they cause the most ground shaking and can be the primary cause of damage to buildings.
How does the motion of a P wave differ from that of an S wave?
-P waves are compressional waves that move particles back and forth in the direction of wave propagation, while S waves are shearing waves that move particles perpendicular to the direction of propagation.
What causes the abrupt changes in seismic wave velocity at certain depths within the Earth?
-Abrupt changes in seismic wave velocity at certain depths are caused by changes in the Earth's composition, which leads to a sudden increase in density, rather than a gradual increase due to pressure.
Why do seismic waves curve as they travel through the Earth?
-Seismic waves curve as they travel through the Earth due to refraction, which occurs when waves encounter changes in density or material boundaries, bending towards or away from the perpendicular based on Snell's law.
How do geophysicists determine the location of an earthquake using seismic waves?
-Geoscientists determine the location of an earthquake by analyzing the difference in arrival times between P waves and S waves, which is a function of the distance from the seismic station to the earthquake.
What is the significance of the PKP wave in studying the Earth's interior?
-The PKP wave is significant because it travels through the Earth's core, providing information about the core's density and composition, which helps scientists understand the Earth's interior structure.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Earthquakes and Seismology in Earth’s Interior

GRADE 10 SCIENCE QUARTER 1, MODULE 2 WEEK 2, EARTHQUAKE AND TYPES OF WAVES MELC BASED.

How earthquakes show us the inside of the Earth

Por que a terra treme no Brasil
Basic Geophysics: Body Waves

Earth’s Interior, Seismic Waves and Tsunami | Grade 8 Science DepEd MELC Quarter 2 Module 2
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
