Social Influence: Conformity and the Normative Influence
Summary
TLDRThe video script delves into conformity as a social influence, distinguishing between informational and normative influences. It explains that individuals conform to gain accurate information or to be socially accepted. Highlighting Solomon Asch's experiments, the script reveals that conformity is more likely with larger group pressure. A recent study suggests that when a sense of belonging is threatened, conformity increases due to a heightened desire for group acceptance. The script concludes that conformity, driven by the need to belong, is a natural and often beneficial aspect of human nature.
Takeaways
- 😌 Conformity is a form of social influence where individuals change their attitudes, beliefs, or behaviors to align with others.
- 📚 Social influence is divided into two main types: informational influence, driven by the belief that others have accurate information, and normative influence, motivated by the desire for social acceptance.
- 🔍 The literature supports the conceptual uniqueness of these two types of social influence, although they are interrelated and can be difficult to distinguish in practice.
- 🧐 Conformity is motivated by the need for an accurate perception of reality (informational influence) and the need for social acceptance and belonging (normative influence).
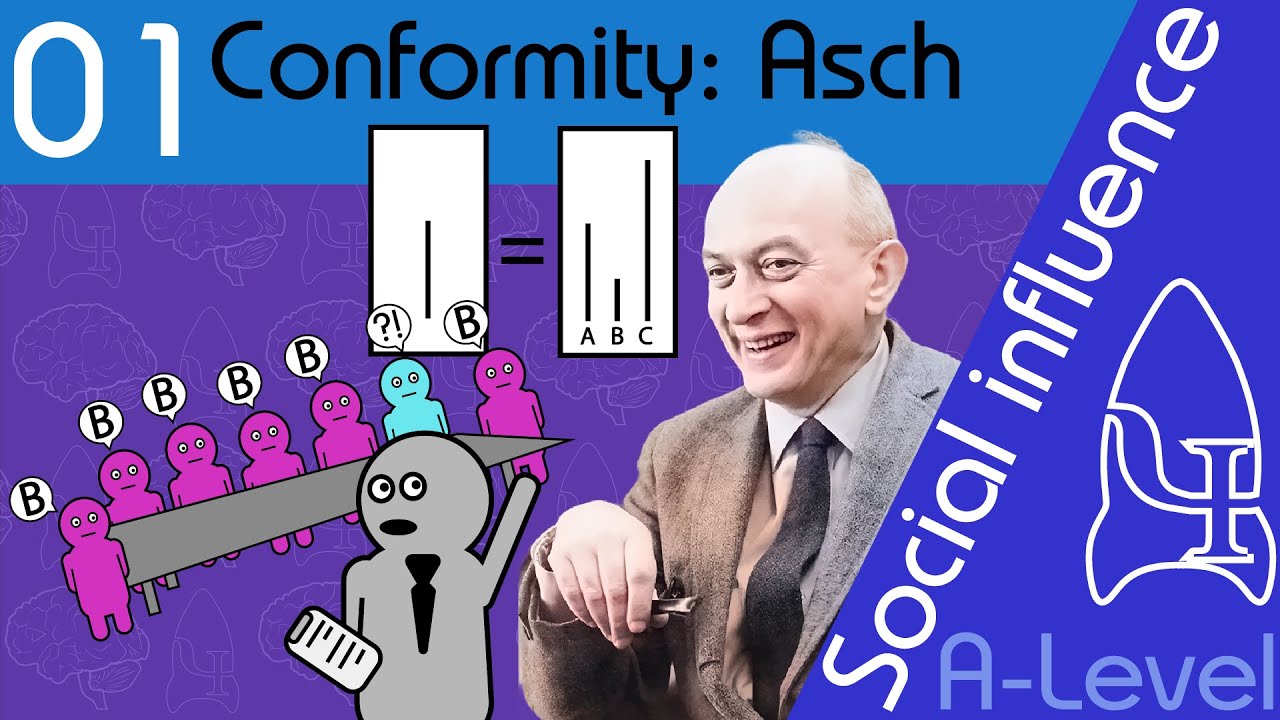
- 🕵️♂️ Solomon Asch's experiments in the 1950s are a classic study of conformity, demonstrating how social pressure can lead individuals to conform to incorrect answers.
- 👥 A meta-analysis of over 130 studies revealed that group size is a significant factor in conformity; larger majorities increase the likelihood of conforming.
- 🧩 Motivation plays a crucial role in conformity; when individuals feel ignored or their sense of belonging is threatened, they are more likely to conform to gain acceptance.
- 🎮 A recent study found that participants ignored in multiplayer video games were more likely to conform on a perceptual task, highlighting the impact of social exclusion on conformity.
- 🤔 Conformity is a complex psychological process that is not inherently negative, as it is tied to fundamental human desires such as the need to belong.
- 🌐 Conformity is a widespread phenomenon, reflecting a basic part of human nature and the influence of normative factors on behavior.
Q & A
What is conformity and how does it relate to social influence?
-Conformity is a form of social influence where an individual changes their attitudes, beliefs, or behaviors to align with those of others. It occurs due to the desire to fit in or to be accepted by a group.
How are informational and normative influences different in the context of conformity?
-Informational influence happens when individuals conform because they believe others have accurate information they lack. Normative influence occurs when individuals conform to gain acceptance and liking from others.
What does the literature suggest about the relationship between informational and normative influences?
-The literature supports the conceptual uniqueness of these two types of social influence, but also acknowledges that they are interrelated and can sometimes be difficult to distinguish in terms of their impact on behavior.
What are the motivational reasons behind conformity according to the script?
-Conformity is motivated by the desire for an accurate perception of reality (informational influence) and the need for social acceptance and belonging (normative influence).
Can you describe Solomon Asch's experiments on conformity conducted in the 1950s?
-Solomon Asch conducted experiments to examine how social pressure influences conformity. In these studies, participants would sometimes conform by giving incorrect answers after hearing obviously incorrect responses from confederates, which happened about 1/3 of the time.
What factor did a meta-analysis reveal as relevant to conformity in line experiment studies?
-A meta-analysis showed that group size is a relevant factor in conformity, with larger majorities increasing the likelihood of participants conforming and giving incorrect answers.
How does the sense of belonging relate to conformity according to a recent study mentioned in the script?
-A recent study found that when participants felt ignored in a multiplayer video game, they were more likely to conform with a new group on a perceptual task, indicating that a threatened sense of belonging increases the motivation to conform.
What is the fundamental human desire that is linked to normative influence and conformity?
-The fundamental human desire to belong and to feel socially accepted is linked to normative influence, which is a major factor leading to conformity.
Is conformity always a negative aspect of human nature according to the script?
-No, conformity is not always negative. It is a basic part of human nature and can be beneficial as it fulfills the human need to belong and be socially accepted.
How can altering motivational states influence conformity as suggested in the script?
-Altering motivational states, such as the need for social acceptance or the desire for accurate information, can influence conformity by either increasing or decreasing an individual's likelihood to conform to group behaviors or beliefs.
What is the prevalence of conformity in human behavior as described in the script?
-Conformity is described as a prevalent psychological process and a basic part of human nature, suggesting that people conform quite frequently in various aspects of life.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Asch conformity studies (Asch line studies) | Behavior | MCAT | Khan Academy

Asch Conformity Experiment
Asch: Conformity - Social influence [ A Level Psychology ]

Three Types of Social Influence

POURQUOI NOUS SOMMES INFLUENÇABLES - Mécanismes de l'influence sociale (Psychologie Sociale)

Asch Conformity Experiment
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
