Basic Electricity - Resistance and Ohm's law
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into the concept of electrical resistance and Ohm's Law, crucial for safely incorporating LEDs into circuits. It explains how resistors, available in various forms, control current flow by converting kinetic energy into heat due to atomic collisions. The script teaches how to read resistor color codes and apply Ohm's Law (V=IR) to calculate the appropriate resistor value for an LED circuit. Practical examples, such as calculating a 1000-ohm resistor for a 10V source with a 10mA limit, are provided. The video also touches on the importance of staying within component voltage limits to prevent damage.
Takeaways
- 🔌 Electrical resistance is crucial for controlling the flow of current in a circuit, and resistors are devices designed to provide this resistance.
- 🌡 Ohm's Law (V=IR) is the fundamental principle that relates voltage, current, and resistance in electrical circuits.
- 🔍 Different types of resistors exist, from basic hobbyist resistors to tiny surface mount resistors found in devices like smartphones, and large power supply resistors.
- 🌟 The resistance in a material occurs due to the inefficient movement of electrons, which can be caused by atomic vibrations or unsuitable atomic arrangements.
- ⚡ Resistance is measured in ohms (Ω), with very low resistance under 1 ohm and very high resistance around 1 megaohm.
- 🛠 A multimeter is a tool that can measure the resistance of almost any material.
- 🎨 Resistors often have colored bands that represent their resistance value, which can be decoded using a color code or a resistor calculator app.
- ⚙️ By selecting resistors with specific values, one can control the amount of current flowing through a circuit, such as in an LED setup.
- 💡 LEDs require a specific forward voltage and current to operate safely, and resistors are used to limit the current to this safe level.
- 🔆 Ohm's Law can be rearranged algebraically to solve for any of the variables (voltage, current, resistance) if the other two are known.
- 🔥 Exceeding the recommended voltage for electronic components can lead to sudden failure or damage.
- 📐 The equation for calculating the resistor value for an LED circuit is derived from Ohm's Law, but there are limitations to its application at very high voltages.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of a resistor in an electrical circuit?
-The main purpose of a resistor is to limit and control the flow of electrical current in a circuit, preventing components like LEDs from receiving too much current and getting damaged.
Why did the LED blow up when connected directly to 7.5V in the example provided?
-The LED blew up because the voltage was too high, causing an excessive amount of current to flow through it, exceeding the LED's safe operating limits.
What is the fundamental principle behind how resistors work?
-Resistors work based on the principle that as electrons move through a material, they sometimes collide with atoms that are in the way, causing the flow of current to be resisted and some of the kinetic energy to be converted into heat.
What is the unit of measurement for electrical resistance?
-The unit of measurement for electrical resistance is the ohm, symbolized by the Greek letter omega (Ω).
What does the color code on resistors represent and how can it be used?
-The color code on resistors represents their resistance value. Each color corresponds to a specific number, and the sequence of colors can be translated into a resistance value using a resistor color code chart or a calculator app.
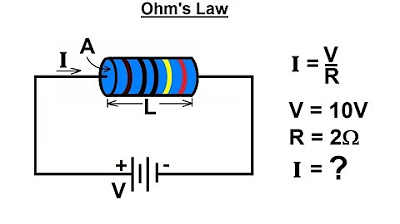
What is Ohm's Law and how is it used in calculating the resistance needed for an LED circuit?
-Ohm's Law is the fundamental relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R), expressed as V = I * R. It can be rearranged to calculate any of these variables if the other two are known. In an LED circuit, it is used to determine the appropriate resistance value needed to achieve a desired current flow.
Why is it important to consider the tolerance of a resistor?
-The tolerance of a resistor indicates the possible variation in its resistance value from the nominal value. It is important because a real-world resistor might have a resistance slightly higher or lower than its rated value, and for most home circuits, a tolerance of +/- 5% is usually sufficient.
What happens when the voltage across a resistor is doubled while keeping the resistance constant?
-According to Ohm's Law, if the voltage across a resistor is doubled and the resistance remains constant, the current flowing through the resistor will also double.
How does the polarity of a resistor differ from that of an LED in a circuit?
-The polarity of a resistor does not matter in a circuit, meaning it can be connected in either direction. In contrast, the polarity of an LED is crucial, as it must be connected with the correct polarity to function properly.
What is the recommended maximum current for the LED used in the script's example circuit?
-The recommended maximum current for the LED in the example circuit is 20mA.
Why did the resistor get too hot when connected to a 140V power supply?
-The resistor got too hot because the voltage was significantly higher than what the resistor and LED circuit were designed for. This resulted in a higher current flow than the resistor could safely handle, leading to overheating.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
Chapter 2 - Fundamentals of Electric Circuits

Video Pembelajaran Modul 2 & 3 Praktikum Rangkaian Listrik 2024/2025 (DK)

Ohm’s Law Tutorial with easy practice problems | Basic Circuits

Electricity | Grade 8 Science DepEd MELC Quarter 1 Module 5 Part 1 Voltage, Current, Resistance

Hukum Ohm
Electrical Engineering: Basic Laws (2 of 31) Ohm's Law
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
