Introduction to Stereolithography
Summary
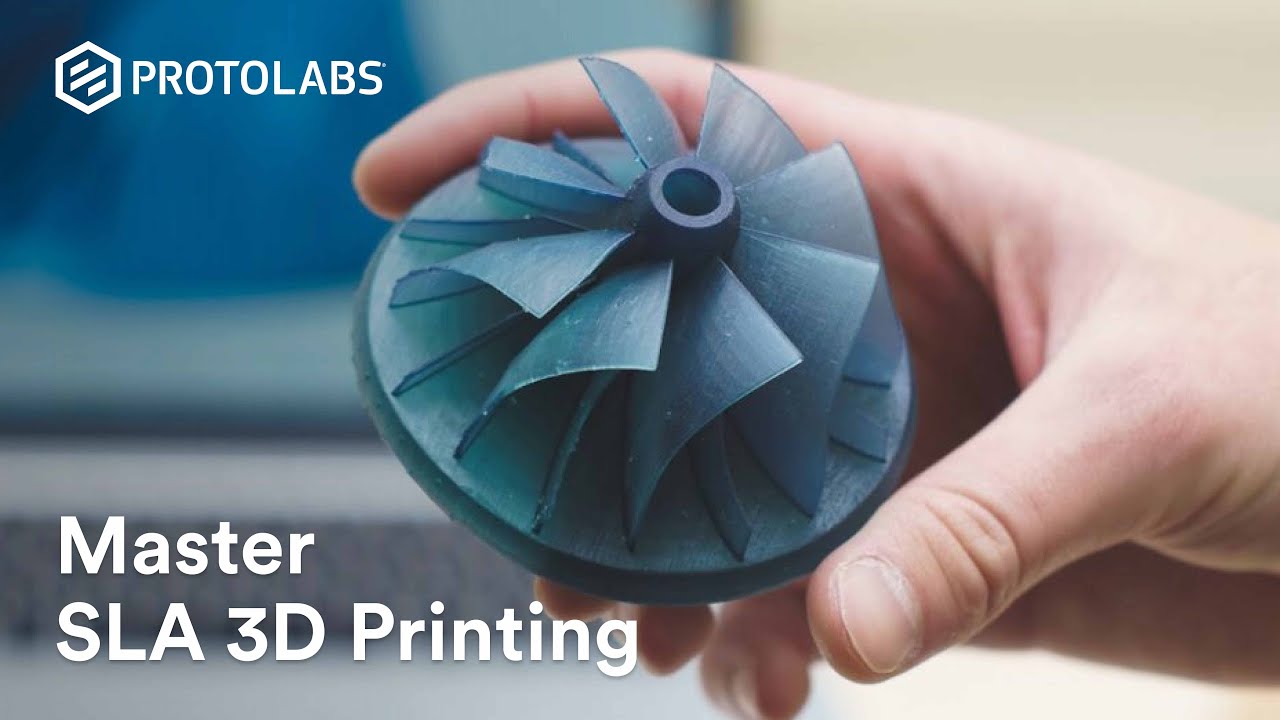
TLDRThe Form 1+ is a stereolithography 3D printer known for its precision and high detail, capable of producing parts with layers four times finer than a human hair. In this video, we explore how it works, including the resin tank, ultraviolet laser curing process, and the post-printing cleaning steps. Various resin types, such as Castable, Flexible, and Tough, are highlighted for their unique applications. The Form 1+ is compared to filament-based printers, showing superior smoothness and strength in parts. The video provides a comprehensive introduction to stereolithography printing and its advantages over other methods.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Form 1+ is a stereolithography 3D printer that uses ultraviolet light to cure resin.
- 😀 The build platform in the printer is where the parts are created, and it sits above a resin tank.
- 😀 The resin tank has a clear window, allowing the laser to cure the resin into solid layers.
- 😀 To start printing, you upload a file and fill the resin tank up to the indicator line.
- 😀 The laser passes back and forth inside the printer, curing the liquid plastic layer by layer.
- 😀 After printing, the part is washed in rubbing alcohol to remove excess resin.
- 😀 Stereolithography offers high detail, with layers as fine as four times thinner than a human hair.
- 😀 The Form 1+ supports a wide range of materials, such as Castable Resin, Flexible Resin, and Tough Resin.
- 😀 Castable Resin is ideal for producing inexpensive metal parts, useful for jewelers and engineers.
- 😀 Flexible Resin allows for simulating different textures, while Tough Resin is strong and resistant to impact.
- 😀 When compared to filament printing, stereolithography parts are smooth, while filament parts show visible ridges.
- 😀 Filament prints tend to snap along layer lines when stressed, while stereolithography parts are more durable due to their chemical bonding.
Q & A
What type of 3D printer is the Form 1+?
-The Form 1+ is a stereolithography (SLA) 3D printer, which uses a laser to cure resin layer by layer to create detailed prints.
How does the Form 1+ 3D printer begin the printing process?
-The printing process begins by uploading a file to the printer, filling the resin tank to the indicated line, and then the laser starts curing the resin to create the print.
What role does the build platform play in the printing process?
-The build platform is where the printed parts are created. It is positioned inside the printer and moves during the printing process to form each layer of the object.
What happens to the part once it’s printed in the Form 1+?
-Once the part is printed, it is removed from the build platform and washed in rubbing alcohol to remove excess resin.
What are 'supports' in the context of 3D printing, and why are they needed?
-Supports are structures added to the print to help hold up overhanging parts during the printing process. They are removed after the print is finished to reveal the final object.
What is the resolution of the Form 1+ compared to human hair?
-The Form 1+ is capable of printing with layers that are four times finer than a human hair, enabling extremely detailed prints.
What types of resins can be used with the Form 1+?
-The Form 1+ offers a variety of resins, including Castable Resin for metal parts, Flexible Resin for simulating different textures, and Tough Resin for high-impact resistance.
How does the Form 1+ compare to filament-based 3D printers in terms of smoothness and durability?
-The Form 1+ produces smooth, detailed prints without visible ridges, while filament-based prints tend to show ridges and are more likely to break along the layer lines due to weaker bonds between layers.
What is the key difference in durability between prints from the Form 1+ and a filament printer?
-Parts printed using the Form 1+ are much stronger because of the chemical bond created by the SLA process, whereas filament prints break more easily along their layer lines.
What is the overall advantage of using stereolithography (SLA) over filament-based printing for detailed parts?
-Stereolithography (SLA) produces much finer details and stronger prints, making it ideal for high-precision parts, whereas filament printing tends to be rougher and less durable.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

The Formlabs Form 3 SLA 3D Printing Workflow | From Design to 3D Print

AnyCubic Tries Multicolor: The AnyCubic Kobra 3 Combo

JENI isn't a 3D printer, it's tool-less injection moulding.
SLA 3D Printing - What Is It And How Does It Work?
🧫 Impressora 3D em LEGO fabrica tecido humano

BEST TIPS FOR BETTER PRINTS WITH PETG | Everything you need to succeed with PETG filament
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
