4.9.2 Secure Hash Algorithm Part 2 in Tamil
Summary
TLDRThis video script explains the block-by-block processing of a cryptographic hash (like SHA-256). It covers message segmentation, padding, and how the final block may be 896 bits followed by zeros. The presenter describes message length encoding, how message blocks (M1, M_last) are prepared, and the creation of the message schedule W0…W79. Initialization uses eight 64-bit registers (A–H) seeded from the fractional parts of square roots of prime numbers, while round constants come from cube roots of primes. The algorithm runs 80 rounds, updating buffers and combining values to produce the final digest. Clear, technical, and step-focused.
Takeaways
- 💡 The discussion focuses on processing data in blocks, specifically emphasizing block-by-block input handling.
- 🧩 Each block of input is processed as 24-bit segments, forming the basis for the next computational steps.
- 📏 The value 'L' represents the length of the message before padding is applied.
- 🧮 Padding is added after the message to ensure proper block alignment for processing.
- 📦 The message is divided into blocks, labeled as M1, M2, and so on, with the last block often being 896 bits in size.
- 🧱 The last message block may be followed by zeros (padding) to complete the final data block.
- ⚙️ Multiple 64-bit registers (E, F, G, H, etc.) are initialized and used during computation.
- 🔢 The process uses the first eight prime numbers and their square roots to initialize specific constants or parameters.
- 🌀 The algorithm includes 80 rounds of processing, where message blocks (W1 to W79) are iteratively transformed.
- 🧠 Constants derived from the cube roots of the first 80 prime numbers are used, with the first 64 bits of each fraction playing a key role.
- 📚 Overall, the script describes a cryptographic hashing process, likely inspired by the SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm) family.
Q & A
What is the significance of processing the input 'block by block'?
-Processing the input 'block by block' ensures that data can be handled in manageable sections, allowing for better error detection and correction, as well as simplifying the computational process.
What does '24 bits' refer to in the script?
-The '24 bits' refers to the size of each block being processed. It is a standard size for data chunks in various encoding and cryptographic systems.
What is the role of 'padding' in the message processing?
-Padding is used to ensure the message reaches the correct length for processing. It helps to make the message's size a multiple of a certain block size, preventing data loss or misalignment.
What does 'M last block' signify in the context of the script?
-'M last block' refers to the final data block in the message sequence, which may be followed by padding (usually zeros) to make the block size consistent with other blocks.
Why is '896 bits' important in the script?
-'896 bits' is the size of the last block in the message, and this specific size plays a role in how the message is processed and padded for encryption or hashing.
What does the term 'registers' (such as H1, H2, etc.) refer to?
-Registers, like H1, H2, etc., refer to specific memory locations used in the cryptographic process to hold intermediate values, which are updated during the computation or encryption rounds.
How are prime numbers involved in this process?
-Prime numbers are used in the script to assist with mathematical operations, such as finding the square root or cube root. They play a role in generating key values for the encryption or hashing process.
What does the script mean by '80 rounds'?
-'80 rounds' refers to the number of iterations or cycles the algorithm goes through while processing the input message. Each round typically involves updates to the internal registers based on the data and prime number transformations.
What is the significance of 'W1, W2, ..., W79' in the script?
-The 'W' values represent message blocks or words that are used during the 80 rounds of processing. These blocks are updated and transformed based on the message and the cryptographic algorithm being applied.
What is meant by 'cube root' and how does it relate to the message processing?
-The 'cube root' in the script refers to a mathematical transformation applied to certain values (e.g., prime numbers), which is likely used in the key expansion or message transformation process to generate more complex results.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
SHA256 and Symmetric Encryption Examples
What is a Cryptographic Hashing Function? (Example + Purpose)

How secure is 256 bit security?

Akademi Hamster: Segala hal yang perlu kamu ketahui tentang blockchain

Wie viele verschiedene Hashwerte gibt es für SHA-256? (Mit Datenspeicherung veranschaulicht)
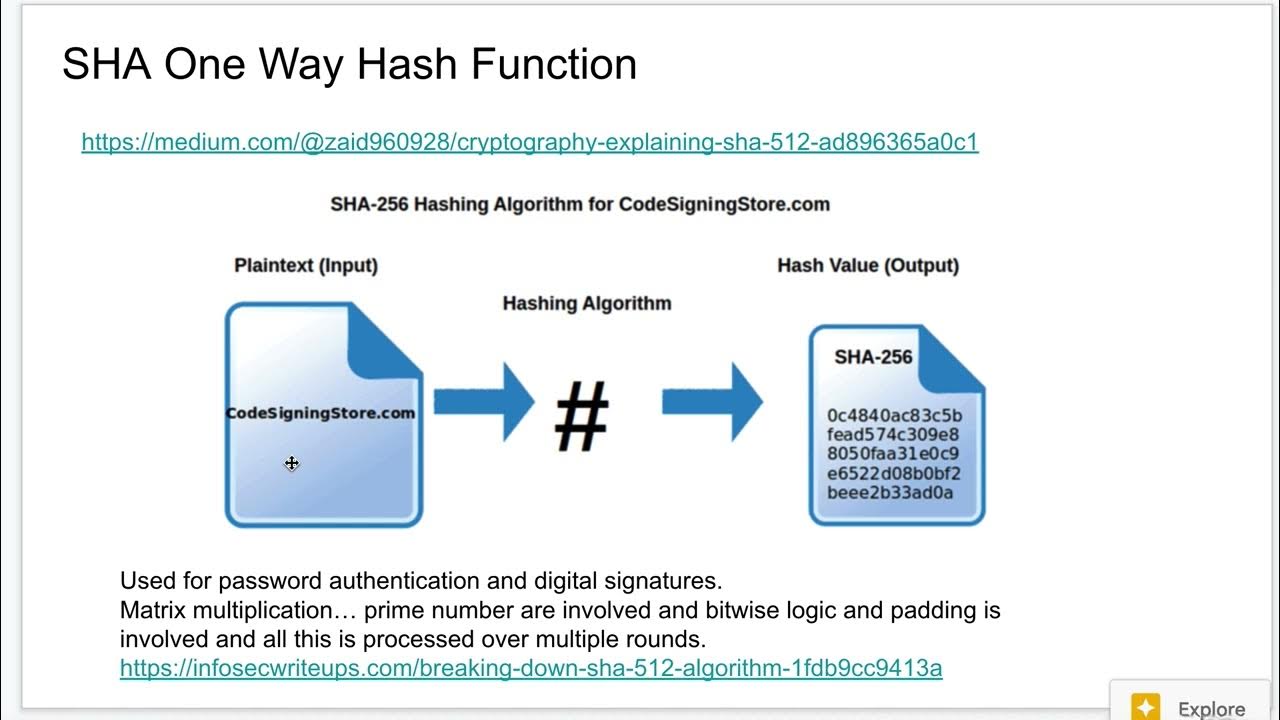
One Way Hash Explained
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
