Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Nursing SLE NCLEX Review: Pathophysiology, Symptoms, Treatment
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive review of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an autoimmune disease causing inflammation that can damage organs, tissues, and joints. It explains the pathophysiology, highlighting defective cell apoptosis leading to autoantibody formation and immune complex deposition. The video covers key signs and symptoms across multiple systems, including skin rashes, joint pain, kidney issues, and neurological effects. Nursing roles are emphasized, focusing on monitoring labs, managing symptoms, patient education, and medication management. Mnemonics like LUPUS, LESS, and FLARE help nurses remember critical points about diagnostics, flare prevention, lifestyle, and early warning signs, supporting effective patient care.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation affecting organs, tissues, and joints, with periods of flare-ups and remission.
- 👩 Women, particularly Black, Latina, and Asian women of childbearing age, are at higher risk, suggesting hormones may influence disease onset.
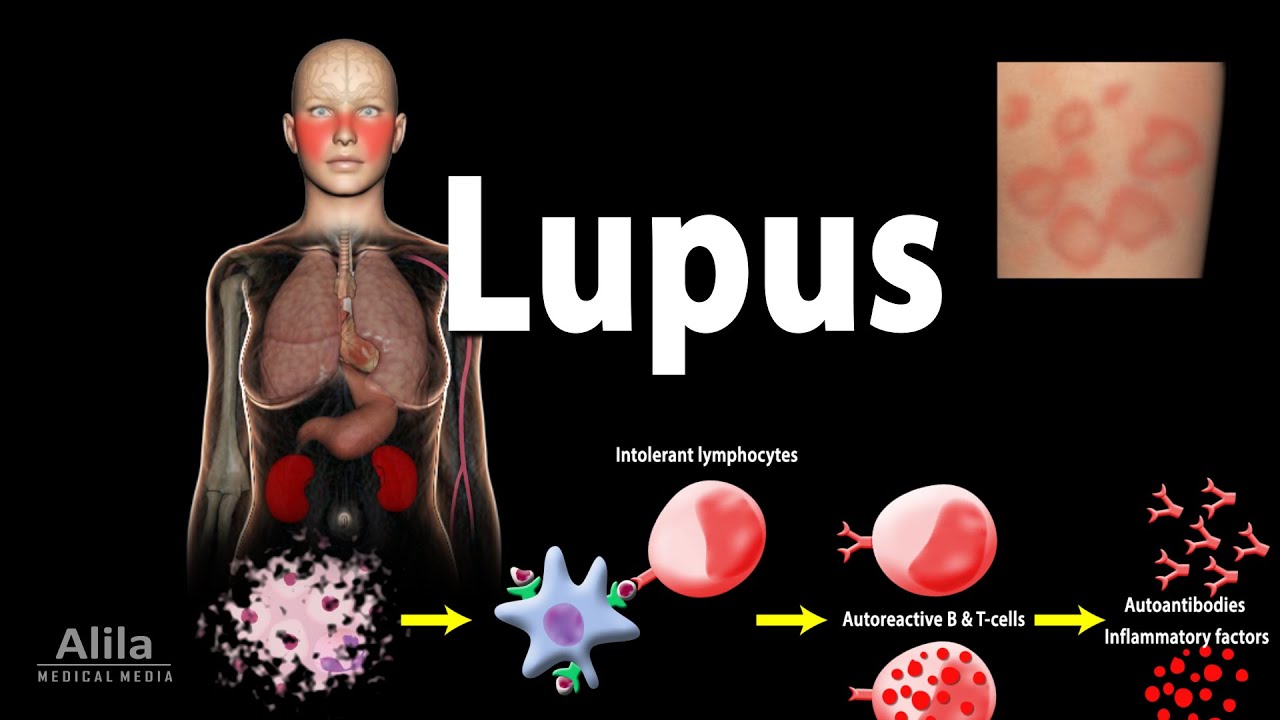
- 🔬 The pathophysiology involves defective apoptosis and ineffective clearance of cellular debris, leading to formation of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) and immune complexes that damage tissues.
- 👀 Lupus can affect multiple systems: eyes, skin, hair, brain, heart, lungs, kidneys, blood, joints, and the reproductive system, producing a wide range of symptoms.
- 💉 Diagnostic labs include ANA, anti-dsDNA, anti-Smith antibodies, ESR, CRP, complement proteins (C3, C4), CBC, and metabolic panels to monitor inflammation and organ function.
- 💊 Treatment options include steroids for acute inflammation, NSAIDs for pain, antimalarials like hydroxychloroquine for long-term disease control, immunosuppressants for severe cases, and biologics like belimumab to reduce B-cell activity.
- 👩⚕️ Nursing care involves system-specific monitoring, patient education on disease, medication adherence, pregnancy planning, and lifestyle modifications to reduce flare risk.
- ☀️ Lifestyle modifications for flare prevention include lowering stress, regular exercise, adequate sleep, sun protection, and tracking early signs of flares.
- 🤰 Pregnancy management requires disease remission for at least six months prior to conception and monitoring during pregnancy and postpartum due to flare and clotting risks.
- ⚠️ Patients on immunosuppressants or biologics are at increased infection risk; live vaccines should be avoided and mental health should be monitored for depression or suicidal thoughts.
- 📋 Early recognition of flare signs using the FLARE mnemonic (Fatigue, Low-grade fever, Achy joints, Rashes, Edema) helps patients manage symptoms proactively.
Q & A
What is systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and how does it affect the body?
-Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), commonly known as lupus, is an autoimmune condition that causes inflammation in various parts of the body, including organs, tissues, and joints. This inflammation can range from mild to severe and may result in permanent damage to affected structures.
What are the common organs and tissues affected by lupus?
-Lupus can affect the joints, skin, lungs, heart, kidneys, brain, and blood system. The specific areas affected can vary among patients, and the severity of the impact also differs.
How is lupus diagnosed, and what factors are considered?
-Diagnosing lupus can be challenging due to its fluctuating symptoms. Physicians consider factors such as family history, patient health history, presenting signs and symptoms, and laboratory results. Tests like the ANA (antinuclear antibody) can help confirm the diagnosis.
Is there a cure for lupus, and what treatments are available?
-There is currently no cure for lupus, but several treatments are available to manage symptoms, decrease flare-ups, and improve the patient's quality of life. These include steroids, immunosuppressants, NSAIDs, and anti-malarial drugs.
What role do hormones play in the onset and progression of lupus?
-Hormones, particularly in women, seem to play a significant role in the onset and worsening of lupus. It is more common in women of childbearing age, particularly among Black, Latina, and Asian women. Hormonal changes during menstruation, pregnancy, and the postpartum period can trigger flare-ups.
What is the pathophysiology behind lupus, particularly regarding cell death?
-In lupus, the process of apoptosis (programmed cell death) is disrupted. The body fails to properly clear apoptotic cell debris, leading to the leakage of cell contents. These fragments trigger an immune response, causing inflammation and immune complexes that damage tissues.
What are some common signs and symptoms of lupus?
-Common symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, memory loss, psychosis, photosensitivity (skin rashes), alopecia (hair loss), chest pain, and kidney issues. Some patients also experience seizures, pericarditis, and pleuritis.
How does lupus affect the kidneys, and what is lupus nephritis?
-Lupus nephritis refers to kidney inflammation caused by lupus, which can lead to impaired kidney function. It can result in proteinuria (protein in the urine), elevated blood pressure, and fluid retention, possibly requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant.
What are some strategies for managing lupus flare-ups?
-To prevent flare-ups, patients should avoid triggers like excessive sun exposure and stress, manage their medications carefully, and follow a healthy lifestyle. Regular monitoring of symptoms and lab results is essential.
What should a nurse consider when caring for a patient with lupus?
-Nurses need to tailor their care based on the systems affected by lupus. This includes monitoring kidney function, helping manage joint pain, educating patients on medications, managing stress, ensuring adequate sleep, and teaching sun protection strategies.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
Lupus: Symptoms, Risk factors, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatments.

Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) - causes, symptoms, diagnosis & pathology

Hipersensitivitas Tipe 3 (Immune complex-mediated Hypersensitivity), Immunology

Sudah Tahu Penyakit Lupus itu Penyakit Apa? Apakah Menular? Penyakit Lupus adalah Penyakit Autoimun

Immunology of the rheumatoid joint

Hipersensibilidade Tipo III - Doenças Mediadas por Imunocomplexos
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
