Project Management Resource Scheduling session 6
Summary
TLDRThis session delves into resource leveling and schedule compression in project management. It explains the concept of resource leveling to balance resource allocation and prevent inefficiencies, introducing schedule compression techniques like fast tracking and crashing. The instructor guides through a hands-on activity, assigns homework for practical application, and emphasizes the importance of understanding risks and probability in project completion. The session prepares participants for a deeper dive into project risk management in subsequent lectures.
Takeaways
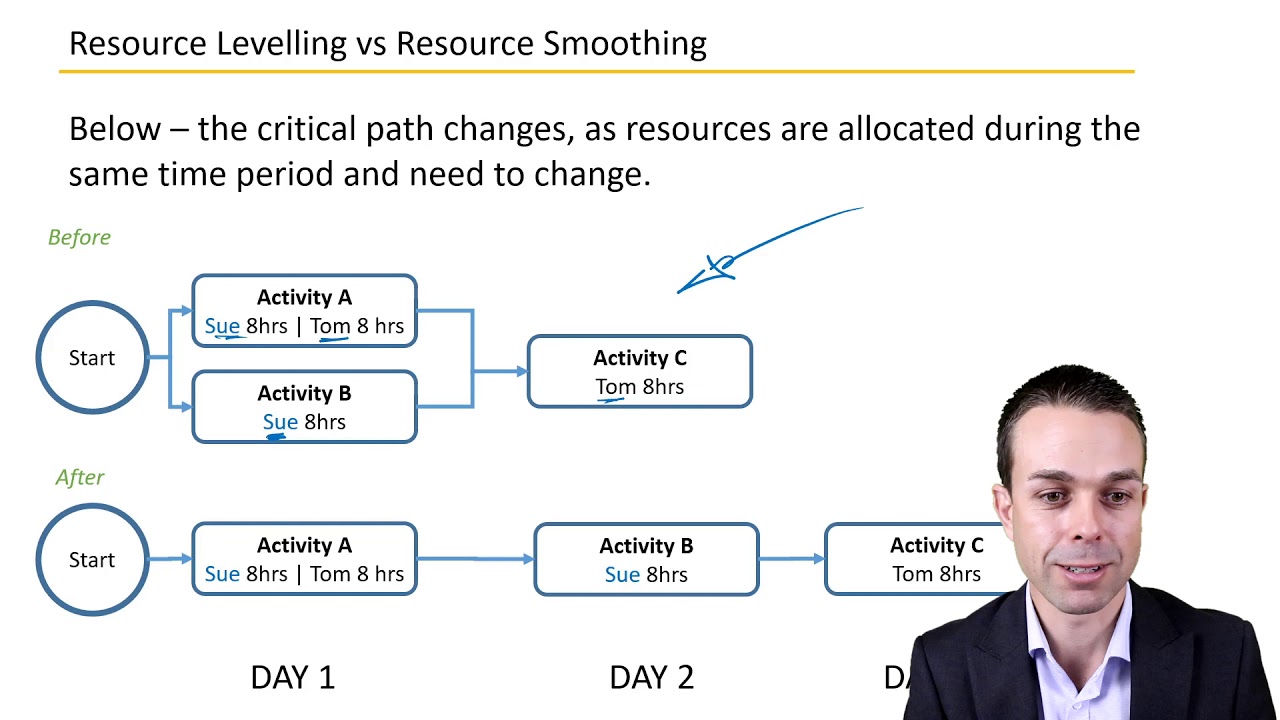
- 📈 Resource leveling is a technique used to balance resource allocation throughout a project to avoid peaks and valleys in usage, aiming to use resources more effectively without changing the project end date.
- 📊 Schedule compression includes two methods: fast tracking, which involves doing activities in parallel, and crashing, which is about reducing activity durations by applying more resources or changing the approach.
- 🔍 The critical path in a project is the sequence of activities with zero slack time that determines the project's overall duration, and managing it is crucial for resource leveling and schedule compression.
- 📚 Understanding the probability of completing a project within a certain timeframe is important for project managers, often requiring statistical knowledge to calculate variance, standard deviation, and confidence levels.
- 🛠 Tools like Excel can be used for resource leveling to help visualize and manage resource allocation over time.
- 🔑 Resource leveling can free up space for resources such as employees, machinery, or meeting rooms, allowing for more efficient use of available assets.
- 🚧 Risk management is an integral part of project management, and resource leveling and schedule compression can introduce new risks that need to be identified, prioritized, and mitigated.
- 💡 The concept of crashing a project involves increasing costs to reduce the project duration, but it must be analyzed carefully to ensure that the time saved justifies the additional expense.
- 📉 Crashing a project can lead to various risks, including decreased quality, increased errors, fatigue among workers, and potential safety issues.
- 📈 A crash cost graph is a useful tool for visualizing the relationship between the cost of crashing activities and the time saved, helping to make informed decisions about which activities to crash first.
- 🔑 The session also covered a hands-on activity and homework assignment to apply the concepts of resource leveling and schedule compression, reinforcing learning through practical application.
Q & A
What are the main topics covered in session six of the project management sessions?
-Session six focuses on resource leveling and schedule compression, including an introduction to resource leveling, different types of schedule compression such as fast tracking and crashing, a hands-on activity, and a homework assignment to apply the learned skills.
What is resource leveling and why might it be necessary?
-Resource leveling is the process of smoothing out the allocation of resources over time to eliminate peaks and valleys in resource usage, ensuring effective utilization without changing the project end date. It's necessary to manage resources efficiently and address issues like over-allocation or under-allocation of resources.
What is the critical path in a project network diagram?
-The critical path is the sequence of activities in a project network diagram that determines the longest possible duration of the project. It's called 'critical' because any delay in these activities will directly impact the project's overall completion time.
How can resource leveling be implemented using simple tools?
-Resource leveling can be implemented using simple tools like an Excel spreadsheet, which can help in visualizing and adjusting the allocation of resources over time to achieve a more balanced resource usage.
What is the purpose of schedule compression in project management?
-Schedule compression is used to shorten the project duration without reducing the project scope. It involves techniques like fast tracking and crashing to identify ways to perform activities in parallel or to reduce the duration of critical activities.
What are the potential risks associated with schedule compression?
-Risks associated with schedule compression include increased fatigue and reduced motivation among team members, potential for errors and quality issues, additional costs, and the possibility of needing to find additional resources, which can further impact the project timeline and budget.
What is the difference between fast tracking and crashing in schedule compression?
-Fast tracking involves performing activities in parallel that were originally planned sequentially, while crashing involves reducing the duration of critical activities by applying additional resources or changing the approach, which usually incurs additional costs.
How can the critical path method (CPM) help in determining the project duration and identifying risks?
-The critical path method helps in determining the project duration by calculating the longest path of activities through the network diagram. It identifies risks by highlighting activities that, if delayed, would impact the project's overall timeline, allowing for better risk management and mitigation strategies.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
Resource Leveling versus Resource Smoothing - Key Project Management Concepts from the PMBOK

Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM): Method, Scheduling & Example - AIMS Education

Critical Chain Project Management #2/4 - Project planning the Critical Chain way

Basic Practice Career Professionalism LO2 RESOURCES UTILIZATION AND MANAGEMENT 3.2.5

10 Knowledge Area Project Management

Project Management: Planning Process Group
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
