Python for Data Analysis: Pandas Data Frames
Summary
TLDRThis lesson introduces Pandas, a powerful Python library for data manipulation, focusing on Series and DataFrames. It begins with Pandas Series, a one-dimensional labeled array, explaining creation via lists or dictionaries, accessing elements, slicing, and performing mathematical operations. It then moves to DataFrames, two-dimensional tables capable of holding heterogeneous data, covering creation from dictionaries, adding or deleting columns, and accessing data using label-based, integer-based, or logical indexing. The video also demonstrates exploring datasets with functions like `.head()`, `.tail()`, `.describe()`, and `.info()`, using the Titanic dataset as an example, providing a foundation for efficient data analysis in Python.
Takeaways
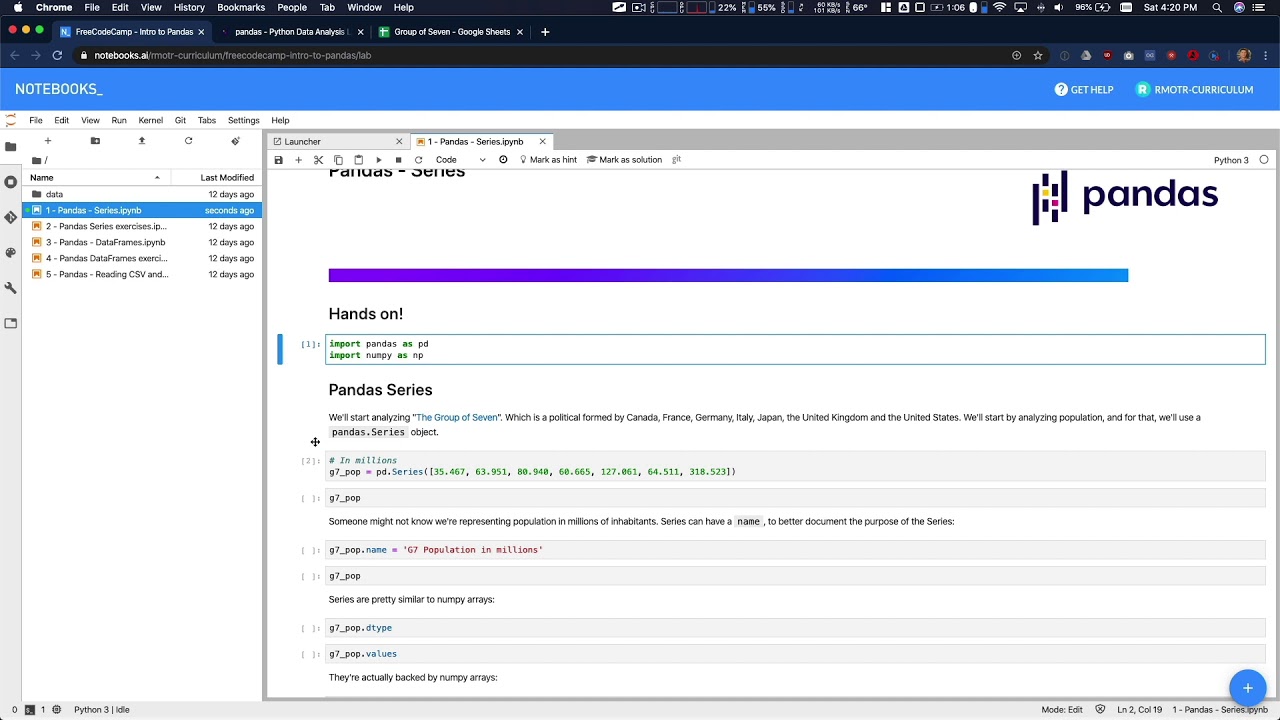
- 😀 Pandas Series are one-dimensional data structures that allow you to work with labeled data, similar to NumPy arrays but with customizable indices.
- 😀 Pandas Series can be created from a list, dictionary, or other sequence-like objects, allowing flexibility in how data is represented.
- 😀 You can access elements in a Pandas Series using either numeric indexing or custom labels, providing more control over data retrieval.
- 😀 Mathematical operations on Series are performed element-wise based on index labels, meaning matching labels are operated on together.
- 😀 If Series with mismatched indices are operated on, the result will contain 'NaN' (Not a Number) for the unmatched indices.
- 😀 A Pandas DataFrame is a two-dimensional, labeled data structure, essentially an equivalent of a table in an Excel workbook or SQL database.
- 😀 DataFrames can be created from various data sources, such as dictionaries, NumPy arrays, or Series, and columns can have different data types.
- 😀 You can add or delete columns in a DataFrame using standard dictionary-like operations, like using `del` for deletion or simple indexing to add new columns.
- 😀 The `.loc` and `.iloc` functions allow you to index DataFrames by label (`.loc`) or by position (`.iloc`), providing flexibility in data selection.
- 😀 The `.describe()` function provides summary statistics of numeric columns in a DataFrame, helping you understand the distribution of the data.
Q & A
What is the main difference between a pandas Series and a numpy array?
-The main difference is that a pandas Series allows you to assign labels (indices) to each element, whereas a numpy array only uses numerical indexing.
How can you create a pandas Series from a list?
-You can create a pandas Series by using the `pd.Series()` function and passing in a list of data. Optionally, you can also specify custom index labels using the `index` parameter.
What happens when you add two pandas Series with mismatched indices?
-When you add two pandas Series with mismatched indices, pandas will align the values by their index labels. If an index is not present in both Series, the result will contain NaN (Not a Number) for those indices.
How do mathematical operations work on pandas Series?
-Mathematical operations on pandas Series are element-wise and are based on the index labels. For example, if you add two Series, it will match elements with the same index labels and perform the operation accordingly.
What is the purpose of the `axis` parameter in functions like `np.mean()` when applied to pandas DataFrames?
-The `axis` parameter determines the direction of the operation. If `axis=0`, the operation is applied across columns. If `axis=1`, it operates across rows. For instance, `np.mean(df, axis=0)` will compute the mean of each column.
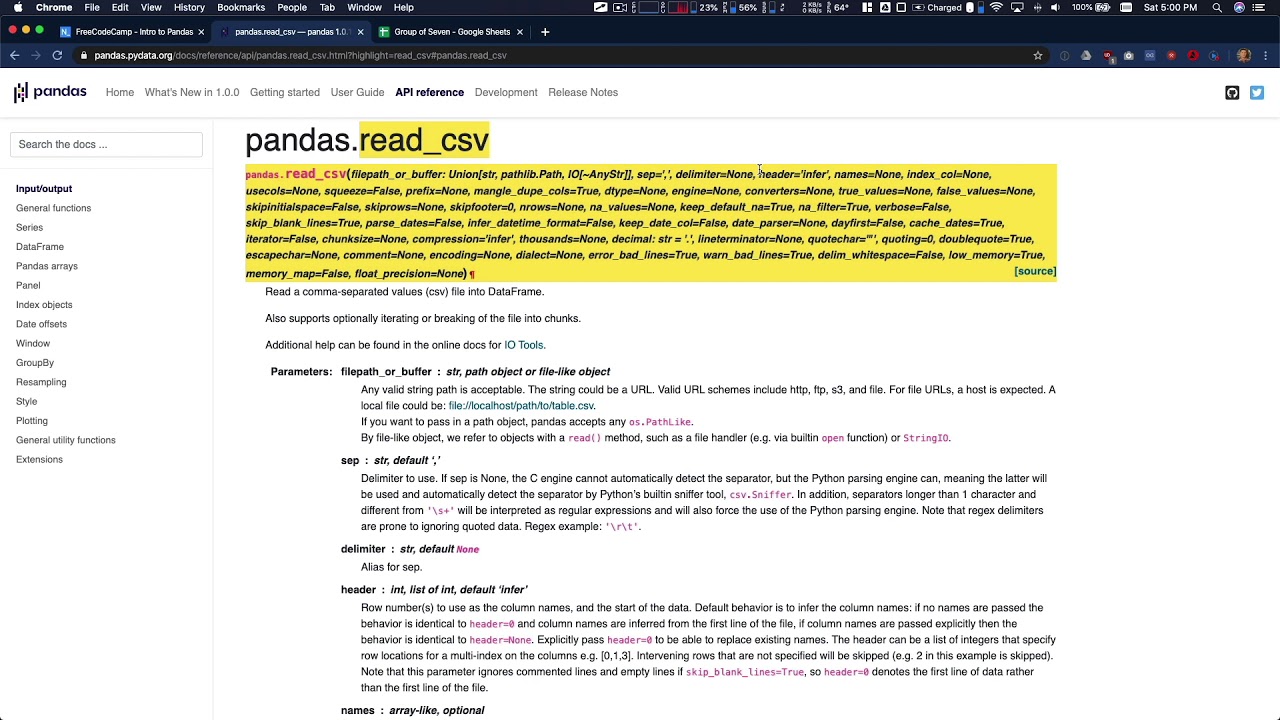
How can you create a pandas DataFrame from a dictionary?
-To create a pandas DataFrame from a dictionary, you can use the `pd.DataFrame()` function. The keys in the dictionary become the column names, and the values (which should be sequence-like structures) become the data for those columns.
What happens when you pass in a single value for a column in a pandas DataFrame?
-If you pass a single value for a column in a pandas DataFrame, pandas will fill the entire column with that value, replicating it for all rows in the DataFrame.
How can you access specific columns in a pandas DataFrame?
-You can access specific columns in a pandas DataFrame either by using the column name as a key (e.g., `df['column_name']`) or by using dot notation (e.g., `df.column_name`).
What is the purpose of `df.loc[]` and how is it different from `df.iloc[]`?
-`df.loc[]` is used for label-based indexing, where you specify row and column labels. `df.iloc[]`, on the other hand, is used for positional indexing, where you specify row and column indices (integer positions).
What is logical indexing in pandas, and how is it useful?
-Logical indexing in pandas involves creating a boolean series (True/False values) and using it to select rows from a DataFrame. It is useful for filtering data based on certain conditions, such as extracting rows where a column's value meets a specified criterion.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)