Woman Destroyed Her Kidneys (in 2 months) By Taking Common Vitamin
Summary
TLDRThis video script narrates a cautionary tale about the dangers of vitamin supplementation for kidney disease patients. It details the case of a 55-year-old woman whose kidney function rapidly deteriorated due to excessive vitamin C intake. The script warns against five specific vitamins (D, B12, E, A, and C) that, if not taken correctly, can cause severe harm. It emphasizes the importance of proper dosage and form of vitamins, especially for those with impaired kidney function, to avoid hospitalizations and further kidney damage.
Takeaways
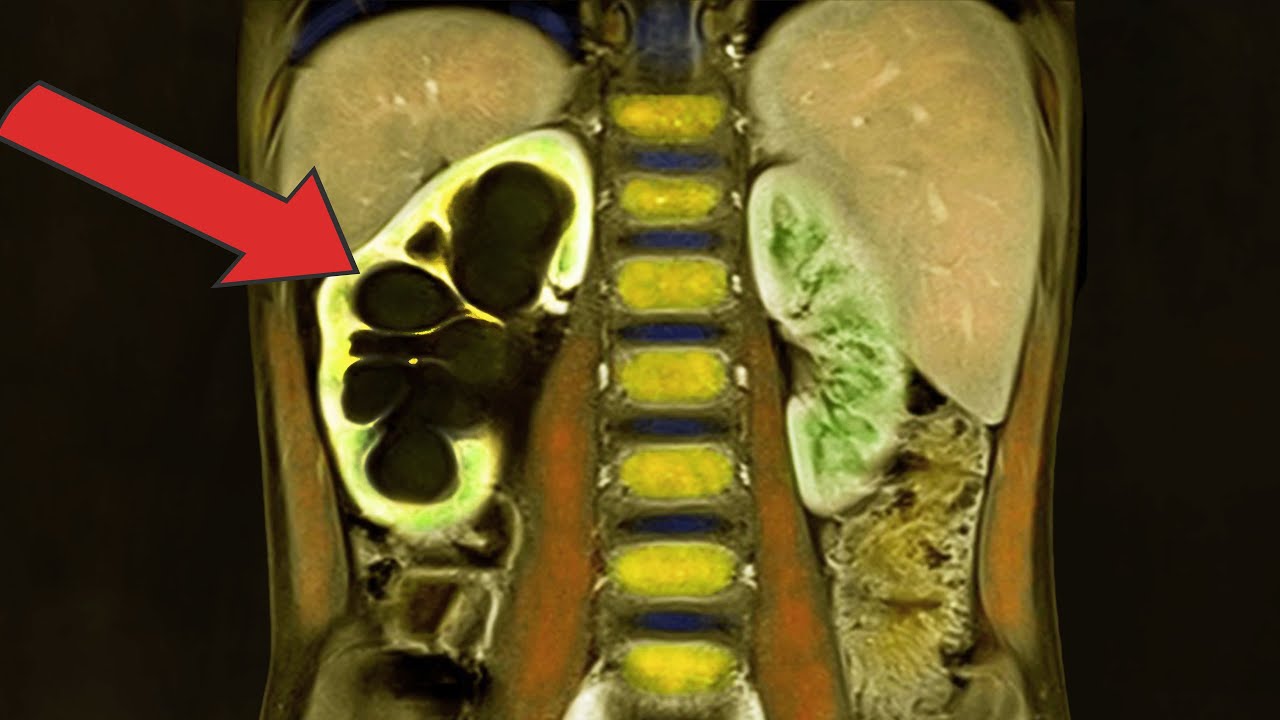
- 🚨 A 55-year-old woman with kidney disease experienced rapid kidney failure, which was later linked to vitamin supplementation.
- 🔍 Doctors initially suspected worsening kidney disease due to the patient's lethargy and severe symptoms, but found shockingly high creatinine levels indicating kidney failure.
- 🌡 The patient's body temperature was alarmingly low at 93°, a sign of severe medical distress.
- 🆘 Immediate transfer to the ICU and the start of dialysis were necessary due to the critical condition of the patient's kidneys.
- 🤔 The cause of the rapid kidney function loss was a common vitamin, highlighting the potential dangers of vitamin supplementation, especially for those with kidney disease.
- ⚠️ Five vitamins are flagged as potentially dangerous for individuals with kidney disease if not supplemented correctly: Vitamin D, B12 (cyanocobalamin form), E (alpha-tocopherol), A, and C.
- ☀️ Vitamin D, while important for kidney health, can be harmful in excess or if taken without proper balance of vitamin K2 and magnesium.
- 💊 Cyanocobalamin, the synthetic form of Vitamin B12, may lead to cyanide toxicity in individuals with impaired kidney function.
- 🌿 Synthetic vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) is prevalent in supplements and foods but may increase health risks, including kidney damage.
- 🚫 High doses of Vitamin A from supplements or certain foods can be toxic and cause kidney damage, especially for those with CKD.
- 🍊 The most commonly supplemented vitamin, Vitamin C, was the culprit in the case study, causing irreversible kidney damage due to oxalate crystal formation from excessive intake.
Q & A
What was the initial condition of the 55-year-old woman who presented to the emergency department in December 2022?
-The 55-year-old woman was lethargic, severely bradicardic, suffering from visible swelling, and had a body temperature of just 93°. She was also a kidney disease patient.
Why did the doctors immediately test the woman's creatinine levels?
-The doctors tested her creatinine levels immediately because they suspected the worsening of her kidney disease.
What shocking discovery did the doctors make regarding the woman's serum creatinine level?
-Her serum creatinine level was 3530 mg per dL, which was several times higher than what it was just 2 months prior, indicating her kidneys were failing.
What was the immediate medical intervention for the woman upon her transfer to the Intensive Care Unit?
-The woman was started on dialysis the same day of admission due to her kidney failure.
What was the cause of the woman's rapid loss of kidney function?
-The cause was later found to be a vitamin, which is normally considered safe but can be harmful when supplemented incorrectly.
What are the five vitamins that may be extremely dangerous for people with kidney disease if supplemented incorrectly?
-The five vitamins are Vitamin D, Cyanocobalamin (Vitamin B12), Alpha-Tocopherol (Vitamin E), Vitamin A, and Vitamin C.
Why is Vitamin D potentially dangerous for kidney disease patients?
-Vitamin D is fat-soluble and can accumulate if taken in excess, potentially leading to hyperphosphatemia and hypercalcemia, which can cause arterial calcification and acute kidney injury.
What is the recommended form of Vitamin B12 for kidney disease patients?
-Methylcobalamin is the recommended form for kidney disease patients, as opposed to Cyanocobalamin, which is the synthetic form that may lead to cyanide toxicity.
Why is Alpha-Tocopherol (the synthetic form of Vitamin E) dangerous for kidney disease patients?
-Alpha-Tocopherol has been linked to increased blood pressure, risk for stroke and cancer, bone loss, raised cholesterol levels, and kidney damage, especially in the synthetic form.
What is the main reason multivitamins are banned for people with CKD (Chronic Kidney Disease)?
-The main reason is the presence of Vitamin A, which can accumulate in the body and lead to toxicity, causing kidney damage and other health issues.
What was the vitamin that caused the hospitalization of the 55-year-old woman mentioned in the script?
-The woman was taking Vitamin C in high doses, which led to the formation of oxalate crystals in her kidneys and ultimately kidney damage.
What is the recommended daily dose of Vitamin C for kidney disease patients?
-The recommended daily dose of Vitamin C for kidney disease patients is usually around 100 milligrams, far less than the 1,000 milligrams that the woman was taking.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

A Man Ate 100 Zinc Vitamin C Gummies Everyday. This Is What Happened To His Spinal Cord.

I Was Wrong About Creatine?
A Man Inhaled Paint Thinner And It Ruined His Life

THE GOLDEN FRUIT - A Thought Provoking Story By Sandeep Maheshwari

PALASIK KUDUANG - KHW NUSANTARA SUMATERA BARAT

How to Stop Taking Blood Pressure Medication Safely | The Nutritarian Diet | Dr. Joel Fuhrman
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
