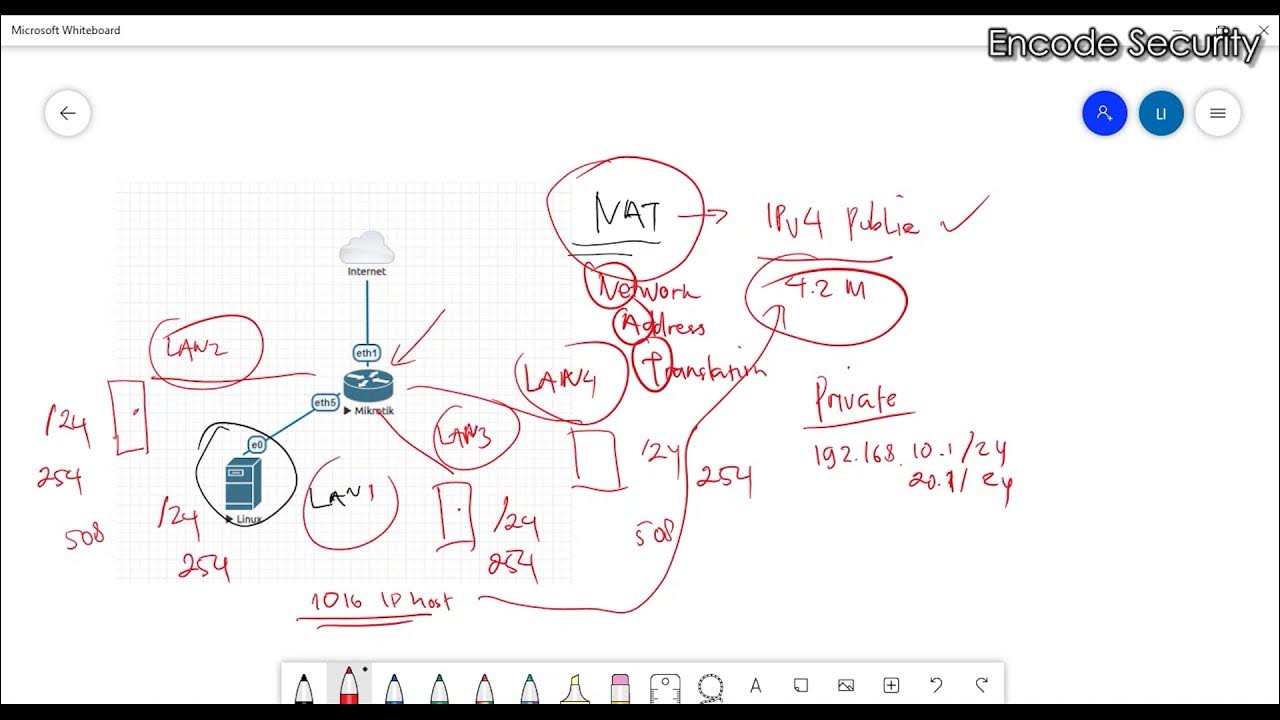
we’re out of IP Addresses….but this saved us (Private IP Addresses)
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the narrator explains how RFC 1918 and private IP addresses, combined with Network Address Translation (NAT), saved the internet by solving the problem of limited public IP addresses. Through a fun and engaging breakdown, viewers learn how private IPs are assigned within home networks and how NAT allows multiple devices to share a single public IP to access the internet. The video also touches on the shift to IPv6 and promotes secure password management using Dashlane. The narrator aims to make complex networking concepts approachable for anyone wanting to master subnetting and network configuration.
Takeaways
- 😀 RFC 1918 introduced private IP addresses, which saved the internet from running out of public IP addresses in 1996.
- 😀 Public IP addresses must be unique across the internet, while private IP addresses are not routable and can be reused by different networks.
- 😀 Without private IP addresses and NAT (Network Address Translation), devices in home networks wouldn't be able to connect to the internet.
- 😀 NAT allows multiple devices in a home network to share a single public IP address while still accessing the internet independently.
- 😀 The use of private IP addresses solves the problem of limited public IP address space by giving home devices a non-unique internal address.
- 😀 Every device in a home network is assigned a private IP, but all external communication from those devices uses the same public IP address provided by the ISP.
- 😀 The transition from IPv4 to IPv6 is happening to ensure enough IP addresses for all devices in the future, as IPv4 addresses are nearly exhausted.
- 😀 IPv6 is much larger and more complex than IPv4, allowing an immense number of addresses (2^128), which could accommodate every device with a unique public address.
- 😀 Private IP addresses are commonly used in homes and businesses, with routers using NAT to manage connections to the public internet through a single public IP.
- 😀 Despite IPv6's growing adoption, IPv4 remains critical for the foreseeable future, and subnetting skills are essential for understanding network configurations.
Q & A
What is RFC 1918 and why is it important for the internet?
-RFC 1918 is a standard that defines private IP address ranges, which are used within internal networks. It was crucial because it solved the problem of running out of public IP addresses by allowing multiple devices on different networks to share the same private IP range.
What are private IP addresses, and how do they differ from public IP addresses?
-Private IP addresses are reserved for internal use within local networks and cannot be accessed directly from the internet. In contrast, public IP addresses are unique and routable over the internet, allowing devices to communicate globally.
Why is it not possible for every device to have a public IP address?
-There aren't enough public IP addresses available to assign a unique one to every device. The sheer number of devices in homes and businesses exceeds the number of available IPv4 addresses.
How does NAT (Network Address Translation) work?
-NAT allows multiple devices on a local network to share a single public IP address. It translates the private IP addresses of devices on the internal network into a public IP when they need to access the internet, and vice versa for incoming traffic.
What is the role of a router in NAT?
-The router performs NAT by taking the private IP address of a device within the local network and translating it into the public IP address assigned by the ISP. It also tracks the communication to ensure that responses are directed to the correct internal device.
How does NAT help conserve public IP addresses?
-NAT enables multiple devices in a home or business to use a single public IP address for accessing the internet, which greatly reduces the number of public IP addresses needed.
What would happen if private IP addresses didn't exist?
-Without private IP addresses, every device on the internet would need a unique public IP address, which would quickly deplete the available IPv4 address space. This would result in a shortage of IP addresses for new devices.
Why did the internet run out of IPv4 addresses, and how was this problem addressed?
-IPv4 addresses were running out due to the rapid growth of devices requiring IP addresses. RFC 1918 and NAT addressed this by introducing private IP addresses and allowing multiple devices to share a single public IP address.
What is the difference between IPv4 and IPv6 addresses?
-IPv4 addresses are 32-bit and consist of four numbers separated by dots, providing approximately 4.3 billion unique addresses. IPv6 addresses are 128-bit and can accommodate a virtually unlimited number of devices due to their significantly larger address space.
What role does IPv6 play in the future of the internet?
-IPv6 solves the problem of IPv4 address exhaustion by providing an enormous address space, ensuring that the internet can continue to grow without running out of addresses. It is gradually being adopted, but IPv4 is still widely used.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)