(NETGEAR AV Level 1) Module 1: The OSI Model
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth explanation of the OSI model, breaking down its seven layers and their respective functions in data transmission. It covers the physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation, and application layers, emphasizing their roles in seamless communication between devices. The video explains how switches, routers, and protocols like TCP and UDP work together to ensure efficient data exchange. Additionally, it highlights the importance of encapsulation and decapsulation processes, as well as how data is transmitted and received across various networks, making complex networking concepts accessible and understandable.
Takeaways
- 😀 The OSI model, or Open Systems Interconnection model, describes how data moves from software applications through physical mediums to reach applications in other computers.
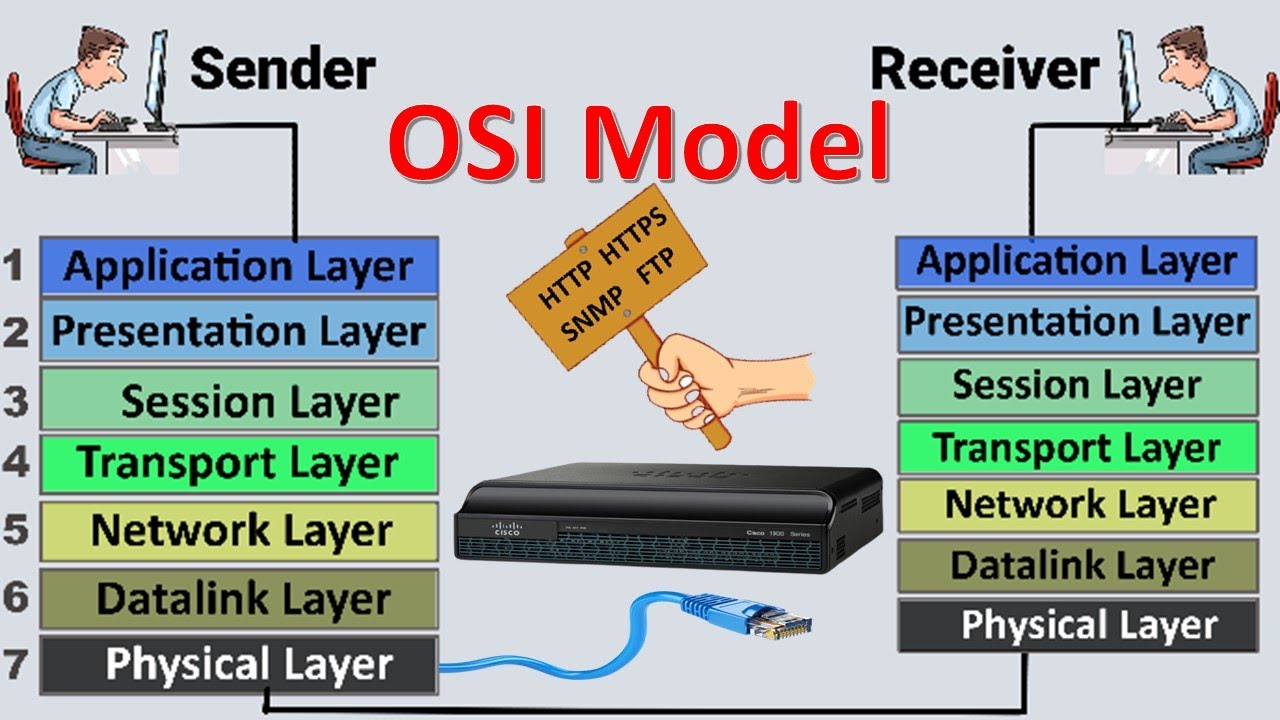
- 😀 The OSI model consists of seven layers, each with a specific function that facilitates seamless data exchange between devices.
- 😀 The seven layers of the OSI model can be remembered using the phrase: 'Please Do Not Throw Salami Pizza Away' (Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, Application).
- 😀 The OSI model is split into two sections: Hardware layers (Layers 1-4) and Software layers (Layers 5-7), with each focusing on different aspects of data handling and communication.
- 😀 The Physical Layer (Layer 1) deals with raw signals, turning digital data into bit streams transmitted through various physical media like cables or Wi-Fi.
- 😀 The Data Link Layer (Layer 2) ensures reliable data transfer between directly connected hosts and uses MAC addresses to identify devices on the same network.
- 😀 Layer 3, the Network Layer, handles packet routing across different networks using logical IP addresses, enabling communication between devices on separate networks.
- 😀 The Transport Layer (Layer 4) manages error detection, recovery, flow control, and data integrity. It uses protocols like TCP (reliable) and UDP (fast, but less reliable).
- 😀 Layers 5-7 (Session, Presentation, Application) are software layers that handle data representation, session control, and direct communication between networked applications.
- 😀 The OSI model's encapsulation and decapsulation processes ensure that data is properly packaged at each layer, with headers containing essential protocols to maintain communication across networks.
Q & A
What is the OSI model, and why is it important in networking?
-The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a conceptual framework that standardizes the functions of a communication system into seven layers. It is important in networking because it provides a universal way to understand how data moves across networks, ensuring interoperability between different network devices and technologies.
What are the seven layers of the OSI model?
-The seven layers of the OSI model are: 1. Physical, 2. Data Link, 3. Network, 4. Transport, 5. Session, 6. Presentation, and 7. Application.
How do the layers of the OSI model interact with each other?
-Each layer in the OSI model performs specific tasks and communicates with the layers above and below it. For example, the physical layer handles signal transmission, while the data link layer ensures error-free data transfer, and the network layer routes the data. As data moves through the layers, it is encapsulated with additional protocol information specific to each layer.
What is the role of the physical layer in the OSI model?
-The physical layer is responsible for transmitting raw bitstreams over physical media like copper cables, fiber optics, or radio frequencies. It defines the physical connection between devices and is crucial for converting digital data into signals suitable for transmission.
What is a MAC address, and what role does it play in networking?
-A MAC (Media Access Control) address is a 12-digit hexadecimal number that uniquely identifies a network device. It is used at the data link layer to ensure data packets reach the correct device on the same network.
How does the network layer function in the OSI model?
-The network layer is responsible for routing data packets across different networks using logical IP addresses. It ensures that data reaches the correct destination, even if it has to traverse multiple networks.
What are the differences between TCP and UDP in the transport layer?
-TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is connection-based, reliable, and ensures data packets are delivered in order. It requires acknowledgment for each packet. UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is connectionless and faster but less reliable, sending data packets without acknowledgment.
What function does the session layer serve in the OSI model?
-The session layer manages sessions or connections between devices. It establishes, maintains, and terminates connections, ensuring that data streams are properly synchronized. This is critical for applications that require continuous data flow, like video conferencing.
What is the purpose of the presentation layer in the OSI model?
-The presentation layer is responsible for translating, compressing, and encrypting data. It ensures that data sent from the application layer is readable by the receiving application, converting formats, and handling encryption for secure transmission.
What is the function of a managed switch compared to an unmanaged switch?
-An unmanaged switch operates at Layer 2 and forwards data based on MAC addresses without handling more complex tasks. A managed switch can operate at both Layer 2 and Layer 3, supporting additional functions like routing, dynamic IP assignment, and network management.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)