Pharmacodynamics - What the med does to your body - Quick Review - Pharmacology Lectures
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth look at pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics, with a focus on drug-receptor interactions, antagonism types, and drug tolerance. It explains the difference between competitive and non-competitive antagonists, using metaphors like a 'greedy capitalist' to clarify their effects on potency and efficacy. The lecture also touches on stereochemistry, tachyphylaxis, cross-tolerance, and inhaled anesthetics, emphasizing their clinical relevance and the importance of understanding drug behavior. The content is aimed at helping medical professionals master key concepts of pharmacology for effective patient care.
Takeaways
- 😀 Non-competitive antagonists, like 'Nancy the Karen', inhibit receptors without competing, leading to a decrease in efficacy but no change in potency.
- 😀 Competitive antagonists compete with the agonist for receptor binding, decreasing the agonist's potency but not affecting its efficacy. Potency can be restored by increasing the agonist dose.
- 😀 Stereoisomers (dextro vs. levo) can have vastly different pharmacodynamic effects, with examples like **Lidocaine** and **Bupivacaine** differing in their duration of action and side effects.
- 😀 Tachyphylaxis refers to the rapid development of tolerance to a drug with repeated exposure, and can be mitigated with drug-free intervals (e.g., nitrate holidays).
- 😀 Cross-tolerance occurs when tolerance to one drug leads to tolerance to similar drugs, even if the body has never encountered them before.
- 😀 Inhaled anesthetics, such as **halothane**, have properties like a minimal alveolar concentration and blood gas partition coefficient, which influence their use and side effects, such as cardiotoxicity.
- 😀 Inhaled anesthetics can be flammable when mixed with carbon dioxide, posing a risk of explosion.
- 😀 To effectively manage anesthesia, anesthesiologists must balance the partial pressures of the anesthetic in the lungs, arterial blood, and brain to maintain proper sedation.
- 😀 Drug elimination typically requires about five half-lives for a drug to be completely cleared from the body.
- 😀 When opioids and benzodiazepines are combined, they can create a **synergistic** or **additive** effect, which needs careful management due to the increased risk of respiratory depression and other side effects.
Q & A
What is the main difference between a competitive and a non-competitive antagonist?
-A competitive antagonist competes with the agonist for binding to the receptor, reducing the potency of the drug, but can be overcome by increasing the dose of the agonist. A non-competitive antagonist binds to a different site and decreases the efficacy of the drug, which cannot be overcome by increasing the dose of the agonist.
How does a non-competitive antagonist affect the dose-response curve?
-A non-competitive antagonist reduces the maximum effect (efficacy) of the agonist, shifting the curve down on the y-axis, while the potency (shift on the x-axis) remains the same.
What does 'potency' refer to in pharmacodynamics?
-Potency refers to the amount of drug needed to achieve a given effect. A decrease in potency shifts the dose-response curve to the right, meaning a higher dose is required to achieve the same effect.
What is tachyphylaxis and how does it relate to drug tolerance?
-Tachyphylaxis is a rapid and short-term development of drug tolerance, meaning a drug's effect diminishes quickly after repeated use. This phenomenon is seen with drugs like nitrates.
Why are nitrate-free intervals important in patients using nitrates?
-Nitrate-free intervals are important because they allow the body to regain sensitivity to nitrates, which prevents the rapid development of tolerance (tachyphylaxis) to the drug.
What is cross-tolerance in pharmacology?
-Cross-tolerance occurs when tolerance to one drug causes tolerance to other drugs that are chemically or pharmacologically similar, even if the new drug has never been used before.
How does stereochemistry affect the pharmacodynamics of drugs?
-Stereochemistry affects the pharmacodynamics of drugs by altering how different isomers of a drug interact with receptors in the body. For instance, the d- and l-forms of a drug can have significantly different effects and side effects.
What is the significance of the minimal alveolar concentration (MAC) in anesthesiology?
-The minimal alveolar concentration (MAC) is the concentration of an inhaled anesthetic required to prevent movement in 50% of patients exposed to a surgical stimulus. It helps in determining the potency of anesthetic agents.
What is the relationship between the partial pressure of an anesthetic in the alveoli, arterial blood, and brain?
-Anesthesiologists must balance the partial pressure of the anesthetic in the alveoli, arterial blood, and brain to achieve the desired level of anesthesia. Proper equilibrium is essential for effective and safe anesthesia.
What role does the half-life of a drug play in its elimination from the body?
-The half-life of a drug determines how long it takes for the drug to be reduced by half in the body. Typically, it takes about five half-lives for a drug to be completely eliminated from the system.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
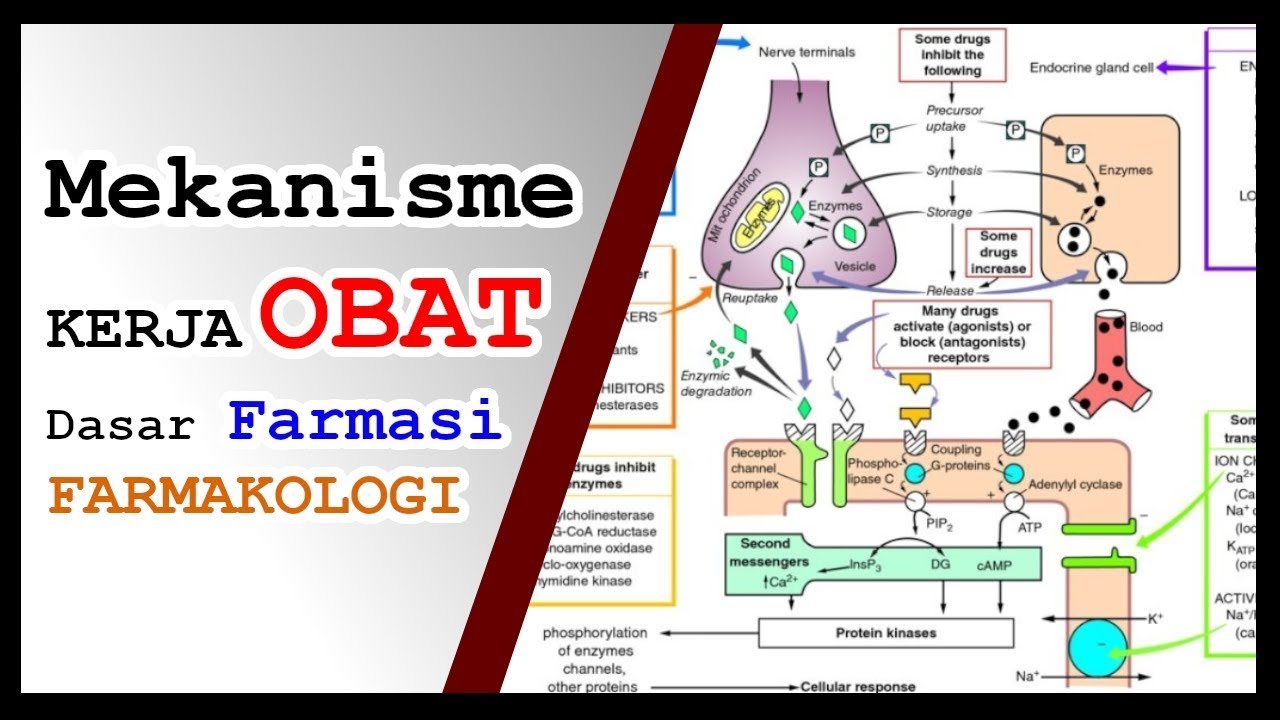
Farmakologi Medis - Mekanisme Kerja Obat Dasar Farmasi (1/5)
What Makes a Drug Work Well?

Farmakodinamik, Hubungan Dosis-Efek, Indeks Terapeutik Obat | Farmakologi 101

FARMACODINÂMICA COMPLETA (ENSINO SUPERIOR) - FARMACOLOGIA - MECANISMO DE AÇÃO DOS FÁRMACOS

Fase Kerja Toksik - Farmakodinamik - Interaksi Reseptor Obat

Farmacodinâmica | Aula 8 | Farmacologia rápida e fácil | Flavonoide
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
