Fase Kerja Toksik - Farmakodinamik - Interaksi Reseptor Obat
Summary
TLDRThe video explores the concepts of pharmacodynamics and toxicodynamics, focusing on drug-receptor interactions in the body. It delves into the mechanisms of reversible and irreversible interactions, the history of receptor theory, and the impact of chemical structures on drug activity. Key historical figures like Paul Ehrlich and John Langley are discussed, as well as modern understandings of how ligands interact with receptors to produce pharmacological effects. The video also illustrates various types of receptor interactions, including agonist and antagonist effects, and the significance of these processes in drug development and therapeutic applications.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video explains pharmacodynamics and toxicodynamics, focusing on the phases of drug interactions in the body, and how toxic effects are reversible or irreversible.
- 😀 Reversible interactions lead to functional changes that disappear once toxins are eliminated, while irreversible interactions cause lasting damage, such as chemical lesions.
- 😀 The historical concept of receptor interaction was introduced by Paul Ehrlich in 1897, who proposed that antibiotics neutralize bacterial toxins via side chains on antibodies.
- 😀 John Langley’s work in 1905 led to the development of the receptor concept, where toxins affect substances in muscles, not the contractile proteins themselves.
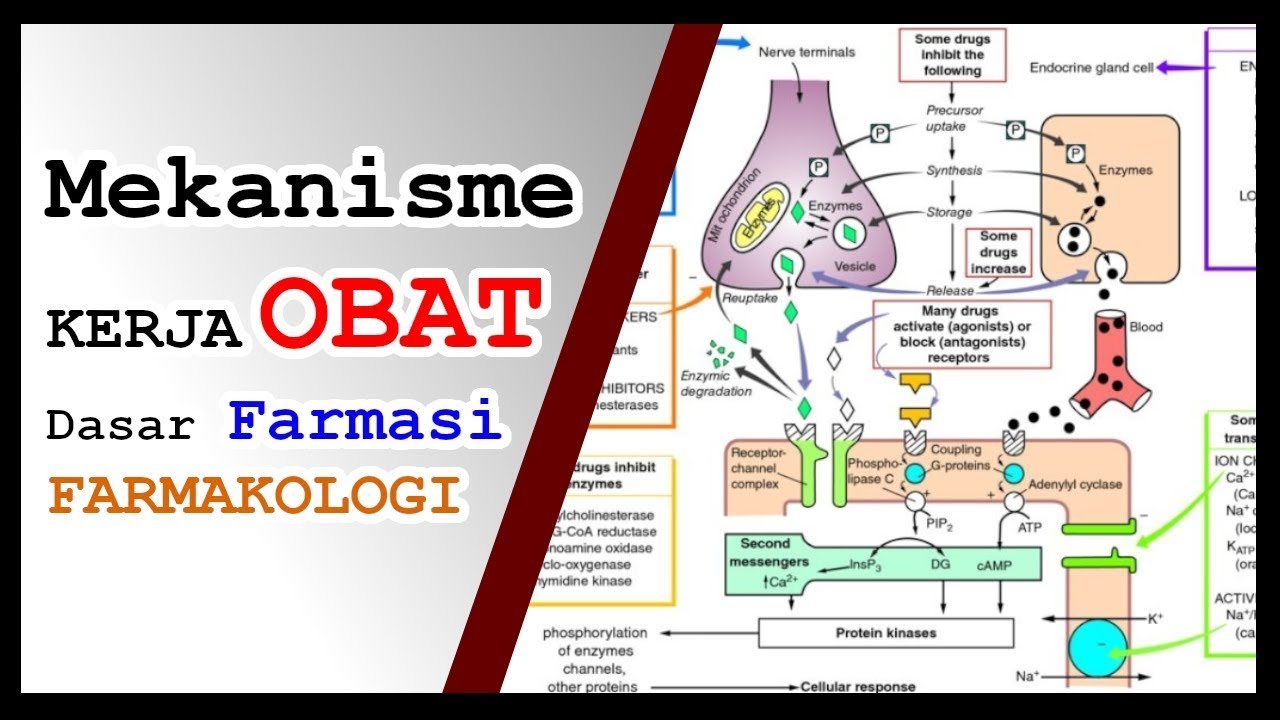
- 😀 Modern drug-receptor interactions are explained as binding between ligands (drugs) and proteins, which are large molecules made of amino acids that fold into specific shapes.
- 😀 Drug-protein interactions are influenced by physical and chemical properties like hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic forces, and steric hindrance.
- 😀 The mechanism of drug-receptor binding is compared to a key fitting into a lock, where the drug must match the receptor's structure to exert its effect.
- 😀 When a drug binds to a receptor, it causes intracellular signaling, influencing cellular functions such as enzyme activity and gene expression.
- 😀 Agonistic interactions occur when two ligands bind to the same or different receptors and produce similar effects, enhancing each other's actions.
- 😀 Antagonistic interactions occur when two substances bind to receptors and produce opposing effects, potentially canceling each other out.
- 😀 The video concludes by emphasizing the importance of understanding drug-receptor interactions for the development of drugs that specifically target receptors to achieve desired therapeutic effects.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the lecture?
-The main topic of the lecture is pharmacodynamics, specifically focusing on the interactions between drugs and receptors in the body.
What are the two types of drug-receptor interactions mentioned in the script?
-The two types of drug-receptor interactions mentioned are reversible and irreversible interactions. Reversible interactions are when the drug's effect disappears once the drug is eliminated, while irreversible interactions cause permanent changes, like chemical lesions.
What was the historical contribution of Foulcher Rich in pharmacology?
-Foulcher Rich, in 1897, theorized that antibiotics neutralize bacterial toxins through side chains that interact with specific toxins, preventing their harmful effects on organs.
What did John L'engle's research in 1905 contribute to the understanding of receptors?
-John L'engle's research demonstrated that toxins affect muscle contraction not by binding to contractile proteins but by interacting with other substances in the muscle, which are now understood as receptors.
How do proteins function as receptors in pharmacodynamics?
-Proteins function as receptors by forming large molecular structures composed of amino acids, which fold into specific shapes. Drugs (ligands) interact with these proteins by binding to specific sites, influencing the receptor's function and initiating a biological response.
What types of molecular interactions are involved in drug-receptor binding?
-Drug-receptor binding involves several molecular interactions, such as hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, ionic bonds, and steric effects, which depend on the chemical properties of both the drug and the receptor.
What is the 'key and lock' concept in drug-receptor interaction?
-The 'key and lock' concept describes how a drug (the key) fits into a specific receptor (the lock). If the drug fits the receptor properly, it triggers a biological response.
What is the role of receptor binding in cellular signaling?
-Receptor binding plays a critical role in cellular signaling by activating or inhibiting specific pathways inside the cell, which can lead to changes in cell function, such as enzyme activation or ion channel modulation.
What are the differences between agonists and antagonists in pharmacology?
-Agonists are drugs that bind to receptors and activate them, leading to a biological response, whereas antagonists bind to receptors but block their activation, preventing the biological effects of agonists.
How do receptor interactions affect pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics?
-Receptor interactions can influence both pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Pharmacodynamics refers to the drug's effects on the body, while pharmacokinetics involves how the body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes, and eliminates the drug. Receptor binding can alter both aspects, affecting drug efficacy and toxicity.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

FARMACODINÂMICA COMPLETA (ENSINO SUPERIOR) - FARMACOLOGIA - MECANISMO DE AÇÃO DOS FÁRMACOS
Farmakologi Medis - Mekanisme Kerja Obat Dasar Farmasi (1/5)

Farmakodinamik, Hubungan Dosis-Efek, Indeks Terapeutik Obat | Farmakologi 101

Interaksi Obat dengan Makanan: Konsep Dasar

Pharmacodynamics - What the med does to your body - Quick Review - Pharmacology Lectures

Pharmacodynamics - Part 1: How Drugs Act on the Body
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)