Tabela Periódica - Brasil Escola
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker breaks down the often-feared periodic table of elements, making it easier to understand and less intimidating. They explain the table’s structure, highlighting key divisions such as representative and transition elements, and how to interpret the groups and periods. The video covers important classifications like metals and non-metals, and discusses key features such as atomic numbers and electron configurations. With a focus on understanding, the speaker encourages students to view the periodic table as a helpful tool rather than a memorization challenge, making it more approachable for learners.
Takeaways
- 😀 The periodic table organizes elements in rows (periods) and columns (groups) to simplify understanding and identification.
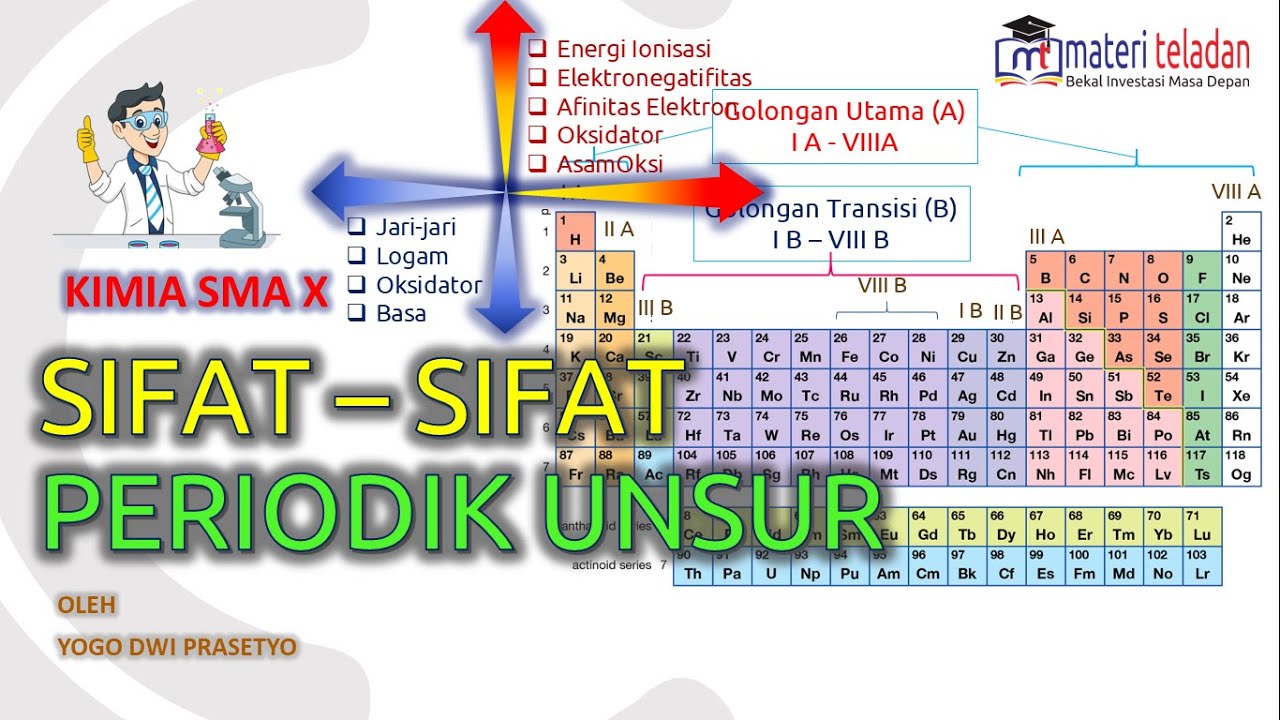
- 😀 There are 18 groups and 7 periods in the periodic table, totaling 118 elements recognized by IUPAC.
- 😀 The periodic table helps scientists find elements based on their properties and characteristics, making it easier to study chemistry.
- 😀 Group 1 and 2 elements are metals known as alkali metals and alkali earth metals, respectively, while groups 13-18 are representative elements with specific family names.
- 😀 Transition elements are found in groups 3-12, and they have different properties from the representative elements.
- 😀 Lanthanides and actinides are a special subset of transition elements, with their own characteristics, and are placed separately below the main table.
- 😀 Metals have distinct properties like shine, high conductivity, and malleability, while nonmetals lack these traits and are often brittle and poor conductors.
- 😀 Elements with atomic numbers greater than 92 are called transuranic elements, while those with atomic numbers below 92 are cisuranic.
- 😀 Each element has a symbol, atomic number, and atomic mass on the periodic table, which are essential for identifying and working with them.
- 😀 The periodic table also shows the electron configuration of elements, with specific sublevels (S, P, D, F) indicating the highest energy electron sublevel for each group.
Q & A
What is the purpose of the periodic table?
-The periodic table organizes chemical elements based on their properties and characteristics, making it easier for chemists to find and interpret information about elements.
How many groups and periods are there in the periodic table?
-The periodic table has 18 groups (columns) and 7 periods (rows).
What is the significance of the IUPAC in relation to the periodic table?
-The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recognizes and updates the periodic table, and currently acknowledges 118 elements.
What are representative elements in the periodic table?
-Representative elements are found in groups 1, 2, and 13 to 18. These elements have distinct families with specific characteristics, like alkali metals in group 1 and halogens in group 17.
What are transition elements, and how are they classified?
-Transition elements are found in groups 3 to 12. They are further classified into 'external transition elements' (from groups 3 to 12) and 'internal transition elements' (lanthanides and actinides, which are placed separately at the bottom of the table).
What distinguishes metals from non-metals in the periodic table?
-Metals have characteristics such as shine, high electrical and thermal conductivity, and malleability. Non-metals lack these properties and are generally poor conductors.
What are transuranic and cisuranic elements?
-Transuranic elements are those with atomic numbers greater than 92, beyond uranium. Cisuranic elements have atomic numbers less than 92.
How are the symbols of elements represented in the periodic table?
-Each element is represented by a symbol consisting of one uppercase letter, or one uppercase letter followed by a lowercase letter. The name of the element is displayed below its symbol.
What does the period of an element in the periodic table indicate?
-The period of an element corresponds to the number of electron shells it has. For example, elements in period 4 have four electron shells.
How is the electronic configuration of elements reflected in the periodic table?
-The periodic table is organized by atomic number and electron configuration. Elements in groups 1 and 2 have 'S' as their highest-energy orbital, groups 3 to 12 have 'D', groups 13 to 18 use 'P', and lanthanides and actinides use 'F'.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Tata Nama Senyawa Kimia • Part 2: Cara Mudah Mengingat Tabel Kation-Anion

Why Does the Periodic Table Look the Way It Does?

Sifat Keperiodikan Unsur | Kimia SMA | Tetty Afianti

KIMIA KELAS 10 | Sistem Periodik Unsur - Sifat Keperiodikan

Sifat Periodik Unsur | Jari jari Atom | Energi Ionisasi | Afinitas Elektron | Elektronegativitas
Sifat Keperiodikan Unsur Kelas X
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
