Fluida Dinamis • Part 4: Venturimeter / Pipa Venturi
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth explanation of Venturi tubes (Venturimeters), which are used to measure the flow rate of liquids. It covers two types: those without a manometer, using fluid dynamics principles like the continuity equation and Bernoulli’s principle, and those with a manometer that measures pressure differences. Through practical examples and calculations, the video demonstrates how fluid velocity changes in different pipe sections and how to compute these velocities using formulas. This informative guide is perfect for students learning about fluid dynamics and flow measurement techniques.
Takeaways
- 😀 Venturi pipe (or venturimeter) is used to measure the flow rate of liquids in pipes.
- 😀 Unlike Pitot tubes, which measure gas flow speed, venturimeters are designed for liquids.
- 😀 There are two types of venturimeters: one without a manometer and one with a manometer.
- 😀 In a venturi pipe without a manometer, the flow speed increases as the pipe narrows (based on the continuity equation).
- 😀 According to Bernoulli’s principle, the pressure at a narrower section of the pipe is lower than at a wider section.
- 😀 The flow velocity in the wider section of the pipe is slower than in the narrower section due to the continuity equation.
- 😀 To calculate flow velocity at different sections of the pipe, Bernoulli’s equation and the continuity equation are applied.
- 😀 The velocity at the wider section (V1) and narrower section (V2) can be calculated using formulas derived from Bernoulli’s law.
- 😀 In the venturi meter with a manometer, the pressure difference is determined by the height difference between two fluids (often mercury and water).
- 😀 Example calculations using given diameters, height differences, and fluid properties were explained to find the velocity at each section of the venturi meter.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of a Venturi tube or Venturimeter?
-The main purpose of a Venturi tube or Venturimeter is to measure the flow rate of a liquid within a pipe. It helps determine the velocity of the fluid by utilizing the principle of fluid dynamics.
What is the difference between a Venturi tube with and without a manometer?
-A Venturi tube without a manometer is an open system where the fluid flows freely through a narrowed pipe, while a Venturi tube with a manometer includes a pressure gauge to measure the pressure difference across the pipe's sections.
How does the principle of continuity apply to the Venturi tube?
-According to the principle of continuity, the product of the cross-sectional area and velocity of the fluid remains constant along the tube. This means that when the pipe narrows, the velocity of the fluid increases.
What does Bernoulli’s equation tell us about the relationship between fluid velocity and pressure in the Venturi tube?
-Bernoulli’s equation indicates that as the velocity of the fluid increases in the narrower section of the Venturi tube, the pressure decreases. This inverse relationship between velocity and pressure is essential for measuring the flow rate.
How do you calculate the flow velocity at different sections of the Venturi tube?
-To calculate the flow velocity at different sections of the Venturi tube, you can use the formula V1 = √(2gh / (A1^2 / A2^2 - 1)), where h is the height difference, g is the acceleration due to gravity, A1 and A2 are the cross-sectional areas at the two points, and V1 is the velocity at the larger cross-section.
What is the significance of the diameter differences in the Venturi tube?
-The diameter differences in the Venturi tube are crucial because the fluid velocity increases as the pipe narrows, leading to a decrease in pressure. This pressure difference is key to calculating the flow rate.
What role does the manometer play in a Venturimeter with a manometer?
-In a Venturimeter with a manometer, the manometer measures the pressure difference between the wider and narrower sections of the tube. This pressure difference helps in determining the flow velocity and the rate of fluid movement.
How does the height difference in the manometer relate to fluid pressure?
-The height difference in the manometer is directly related to the pressure difference between the two sections of the Venturi tube. A higher fluid level in the manometer indicates higher pressure at that section of the tube.
What is the formula used to calculate the velocity in a Venturimeter with a manometer?
-The formula to calculate the velocity in a Venturimeter with a manometer is derived from Bernoulli's equation, expressed as V1 = √(2gh * (ρ2 - ρ1) / (ρ1 * A1^2 / A2^2 - 1)), where ρ is the fluid density, h is the height difference in the manometer, and A1, A2 are the cross-sectional areas of the pipe.
In the example problem given, how is the velocity at the first section of the pipe (V1) calculated?
-In the example problem, the velocity at the first section (V1) is calculated using the formula V1 = √(2gh * (ρ2 - ρ1) / (ρ1 * A1^2 / A2^2 - 1)), by substituting the given values for gravitational acceleration (g), height difference (h), and fluid densities (ρ1 and ρ2), along with the cross-sectional areas (A1 and A2).
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

What is orifice plate & its types | Instrumentation Technician
Fluida Dinamis - Konsep Bernoulli - Simple Konsep - Fisika Kelas 11

Air Pollution Control by Wet Scrubbing
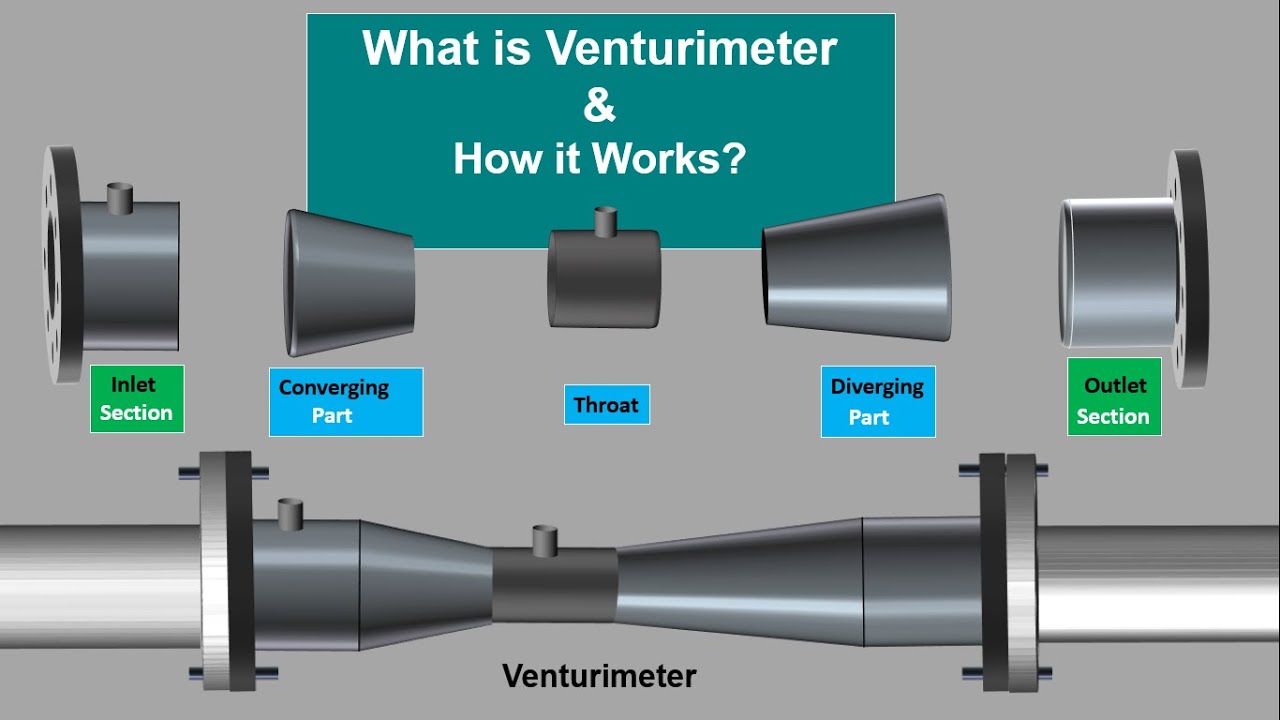
What is Venturimeter. How Venturimeter works. Working Principle of Venturimeter.Animation Video.

Cara Cepat Menghitung Debit Aliran Sungai Menggunakan Current Meter

Rotameter Working Explanation with 3d Animation
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
