Rotameter Working Explanation with 3d Animation
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the functioning of a rotameter, a flow meter used to measure the flow rate of fluids, typically gases or liquids. It consists of a tapered tube with a float that moves as the fluid flows through, with the position of the float indicating the flow rate. As fluid enters the tube, the float rises until buoyancy and gravity balance, providing an equilibrium height proportional to the flow rate. The device is simple, low-cost, and requires no external power source, making it easy to install and resistant to temperature, pressure, or viscosity changes.
Takeaways
- 😀 A rotameter is a type of flow meter used to measure the flow rate of fluids, such as gases or liquids.
- 😀 It consists of a tapered tube with a float inside that moves as the fluid flows through the tube.
- 😀 The position of the float is directly proportional to the fluid's flow rate.
- 😀 The flow rate can be read by observing the height of the float on the calibrated scale outside the tube.
- 😀 Fluid enters the tapered tube at the bottom, and the float rises with increasing flow rate.
- 😀 The float reaches equilibrium when the buoyancy force equals the gravitational force acting on it.
- 😀 The height at which the float stabilizes indicates the flow rate of the fluid.
- 😀 Rotameters are calibrated, and the scale is usually marked in units like liters per minute or gallons per hour.
- 😀 They are simple, low-cost, and easy to install without requiring an external power source.
- 😀 Rotameters are not significantly affected by changes in temperature, pressure, or fluid viscosity.
Q & A
What is a rotameter?
-A rotameter is a type of flow meter used to measure the flow rate of fluids, typically gases or liquids.
How does a rotameter work?
-A rotameter consists of a tapered tube with a float inside. As the fluid flows through the tube, the float moves up and down, and its position is proportional to the flow rate of the fluid.
What role does the float inside the rotameter play?
-The float moves within the tapered tube, and its position indicates the flow rate of the fluid. The height of the float is proportional to the flow rate.
What happens to the float when the flow rate increases?
-As the flow rate increases, the float rises upwards within the tapered tube.
How is the flow rate measured on a rotameter?
-The flow rate is measured by reading the height of the float against a calibrated scale on the outside of the tube, with units typically in volume per unit time (e.g., liters per minute or gallons per hour).
What is the principle behind the float's movement inside the rotameter?
-The float rises to a height where the buoyancy force acting on it equals the gravitational force. At this point, the float remains in equilibrium.
Why is the tube tapered in a rotameter?
-The tapered shape of the tube helps create a relationship between the height of the float and the flow rate, enabling accurate flow measurement.
What are the advantages of using a rotameter?
-Rotameters are simple, low-cost, easy to install, and do not require an external power source. They are also relatively unaffected by changes in temperature, pressure, or viscosity.
Can a rotameter measure both liquid and gas flow?
-Yes, rotameters can be used to measure the flow of both gases and liquids.
What are some limitations of a rotameter?
-While the script doesn't mention limitations, one common limitation is that rotameters may not be suitable for measuring very high or very low flow rates, and they can be sensitive to particle contamination in the fluid.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Types Of Flowmeters And Their Industrial Applications.

Cara Cepat Menghitung Debit Aliran Sungai Menggunakan Current Meter
Fluida Dinamis - Konsep Bernoulli - Simple Konsep - Fisika Kelas 11
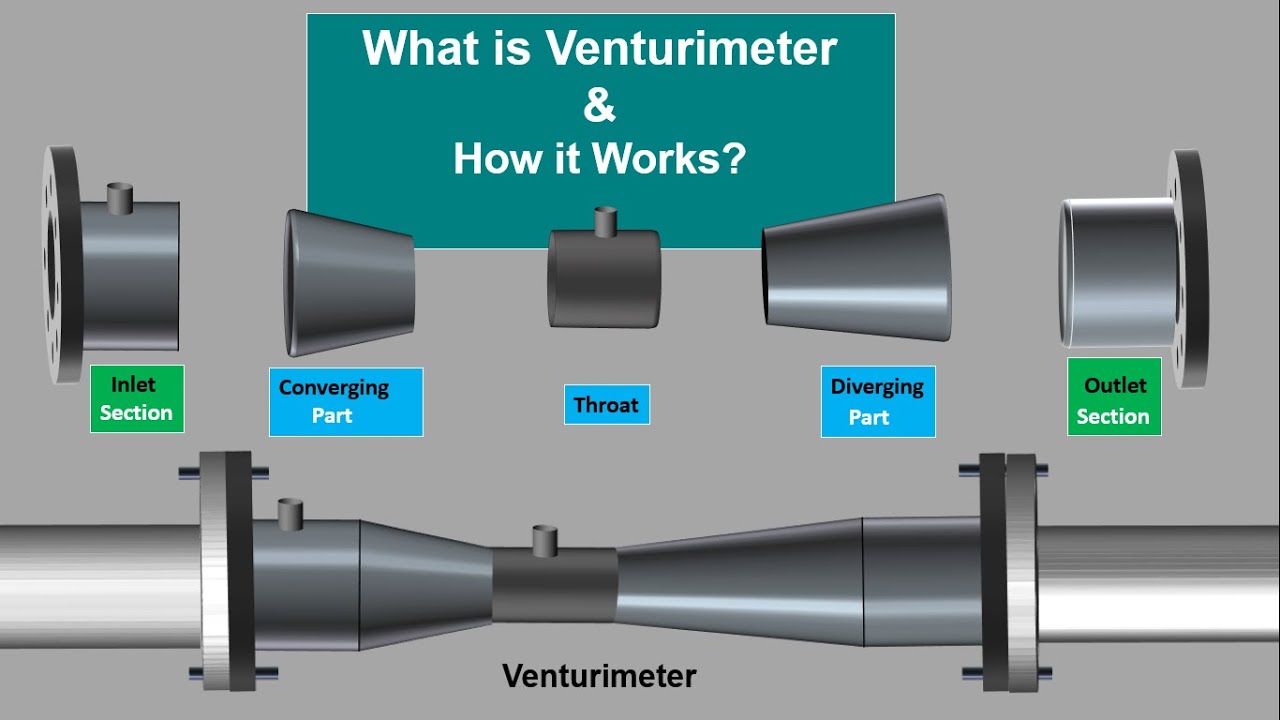
What is Venturimeter. How Venturimeter works. Working Principle of Venturimeter.Animation Video.

Bill Nye The Science Guy - S05E13 - Fluids - Best Quality

What is orifice plate & its types | Instrumentation Technician
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)