Tides: Crash Course Astronomy #8
Summary
TLDRThe video explores the concept of tides and their significance in the universe. It explains how tides, influenced by gravity, shape objects and create oceanic movements on Earth. The script delves into tidal forces, their impact on celestial bodies like the Moon and Earth, and the phenomena of tidal locking and spaghettification near black holes. The interaction between the Moon, Earth, and Sun's gravitational forces results in complex tidal patterns, such as spring and neap tides. Overall, tides play a crucial role in the dynamics of astronomical objects and their interactions.
Takeaways
- 🌊 Tides are not just about the ocean's daily ebb and flow but are a fundamental force in the universe that shapes celestial bodies.
- 🌌 Tidal forces originate from gravity, which weakens with distance and is measured from the center of mass of an object, not its surface.
- 🔍 The difference in gravitational pull on different parts of an object due to distance is what causes tidal forces, which stretch the object.
- 🌕 The Moon's gravity, though weaker than Earth's, significantly affects Earth due to Earth's size and the distance between them, causing tidal bulges.
- 🏞️ Earth experiences two high tides and two low tides daily because of its rotation and the tidal forces exerted by the Moon.
- 🌀 The Earth's rotation causes the tidal bulges to lag, slightly ahead of the Earth-Moon line, influencing the Moon's orbit and causing it to recede from Earth.
- 🌅 The Moon's gravity pulls on Earth's tidal bulge, which in turn affects the Moon's orbit and Earth's rotation, making days longer over time.
- 🌑 The Moon is tidally locked to Earth, showing only one face due to the synchronization of its spin with its orbit around Earth.
- ☀️ While the Sun has a stronger gravitational pull than the Moon, its greater distance means its tidal force on Earth is about half that of the Moon's.
- 🌐 Spring tides occur when the Sun and Moon's tidal forces align during new or full moons, causing higher high tides and lower low tides.
- 🌊 Neap tides happen when the Moon is at first quarter, with the Sun and Moon's tidal forces partially cancelling each other out, resulting in less pronounced tidal changes.
Q & A
What is the primary force responsible for tides in the universe?
-The primary force responsible for tides in the universe is gravity, which weakens with distance and acts on the center of mass of an object.
How does the difference in gravitational force experienced by different parts of an object create tidal forces?
-Tidal forces are created when the gravitational force on one end of an object is stronger than on the other, causing the object to stretch and deform.
Why does the Earth experience two high tides and two low tides each day?
-The Earth experiences two high tides and two low tides each day because of its rotation and the tidal bulges caused by the Moon's gravity, which are on opposite sides of the Earth.
How does the Earth's rotation affect the position of the tidal bulges?
-The Earth's rotation causes the tidal bulges to lag behind the Earth-Moon line, as the water cannot respond instantly to the tidal force, resulting in the bulges being slightly ahead of the direct line to the Moon.
What is the phenomenon where the Moon always shows one face to the Earth?
-The phenomenon where the Moon always shows one face to the Earth is called tidal locking, which occurs when the Moon's spin and orbital period match due to the tidal forces from the Earth.
Why is the Moon slowly moving away from the Earth?
-The Moon is slowly moving away from the Earth because the tidal bulge on Earth exerts a gravitational pull on the Moon, causing it to accelerate and move to a higher orbit.
What causes the variation in the height of tides, such as spring tides and neap tides?
-The variation in the height of tides is caused by the relative positions of the Earth, Moon, and Sun. Spring tides occur when the Sun and Moon's tidal forces align, while neap tides occur when they oppose each other.
How does the distance between two celestial bodies affect the strength of tidal forces between them?
-The strength of tidal forces between two celestial bodies decreases with the increase in distance between them, as the gravitational force weakens with distance.
What is the term used to describe the stretching effect of gravity near a black hole?
-The term used to describe the stretching effect of gravity near a black hole is spaghettification, where objects are pulled into long, thin strings.
How does the Earth's tidal bulge affect the Moon's orbit?
-The Earth's tidal bulge exerts a gravitational pull on the Moon, causing it to accelerate and move forward in its orbit, which in turn causes the Moon to gradually recede from the Earth.
What is the effect of tidal forces on the Earth's rotation and the Moon's orbit?
-Tidal forces have slowed the Earth's rotation, making the day slightly longer, and have also caused the Moon to move to a higher orbit, increasing its distance from the Earth.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

BUMI DAN ANTARIKSA part 1
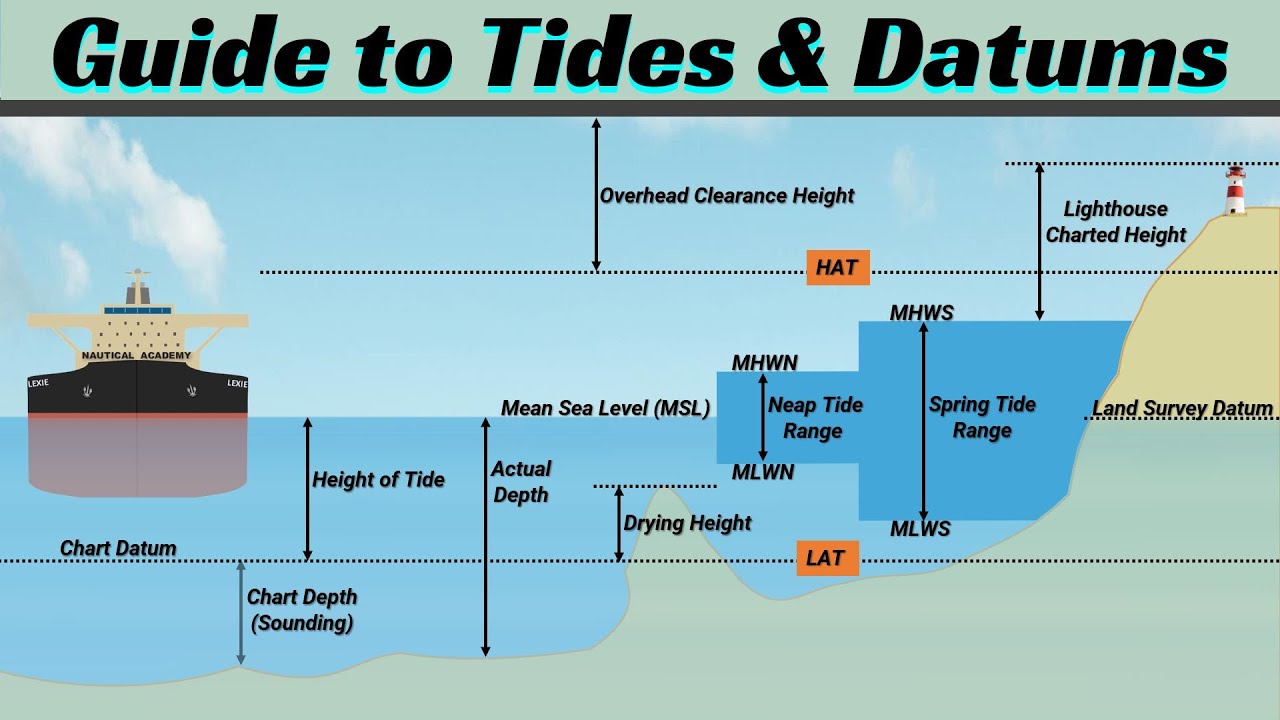
Understanding Tides and Datums: LAT, HAT, Mean Sea Level, MHWS, MLWS, MHWN, MLWN

Grade 7 - Natural Sciences - Tides and the Moon / WorksheetCloud Video Lesson

La influencia del Sol y la Luna sobre el espacio geográfico.

Geo X. 39. Dinamika Perairan Laut (Arus Laut, Gelombang dan Pasang Surut).

LAS 4 FUERZAS FUNDAMENTALES DE LA NATURALEZA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
