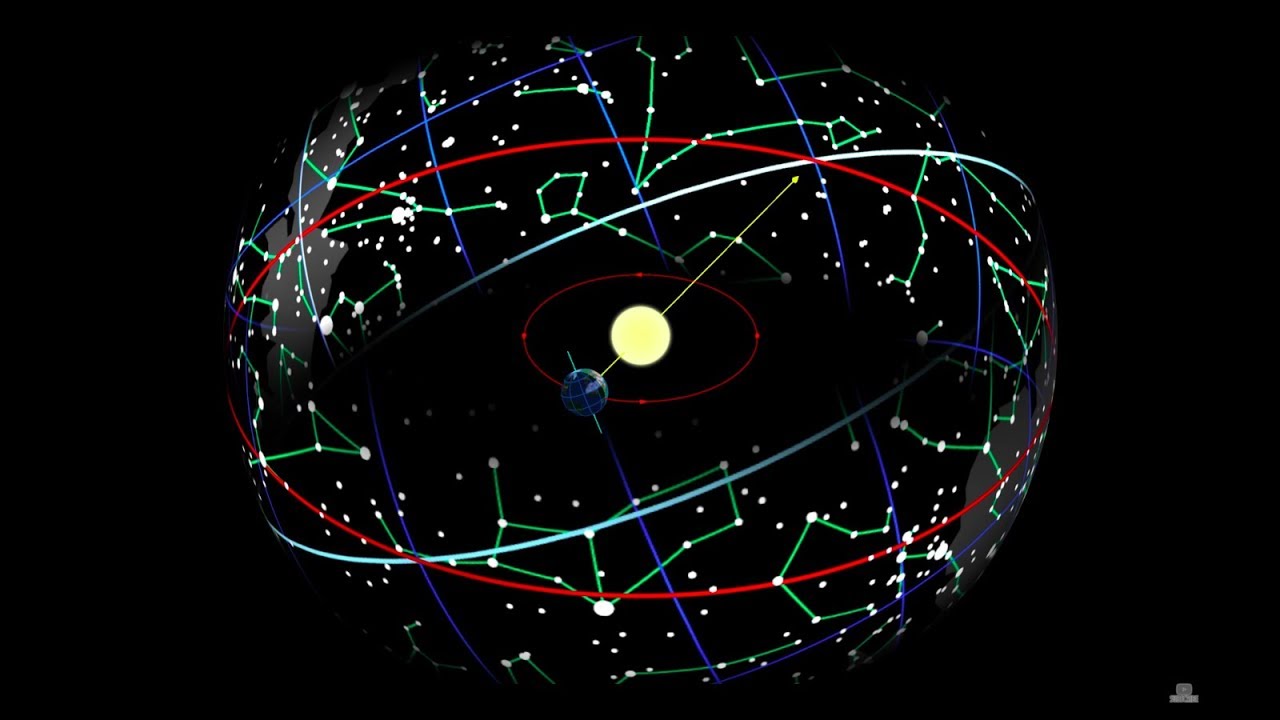
La influencia del Sol y la Luna sobre el espacio geográfico.
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the study of the universe, starting with early civilizations' reliance on celestial bodies like the sun and moon for agriculture and navigation. It delves into the scientific evolution of astronomy, the sun's structure and energy generation, and how its radiation impacts Earth. The moon's phases, its influence on tides, and its role in eclipses are also highlighted. The video explains key phenomena such as solar and lunar eclipses, Earth's movements, and their effects on seasons, day and night, and time zones. It emphasizes humanity's deep connection to nature and celestial events.
Takeaways
- 🌞 Ancient civilizations used the sun and moon cycles for agriculture and navigation.
- 🔭 The ancient Greeks were pioneers in trying to explain celestial movements using natural causes.
- 📡 Technological advancements in the 16th to 18th centuries laid the foundation for modern geography.
- 🌍 Despite our technological advancements, humanity is still deeply connected to and reliant on nature.
- 🌑 The sun's energy is generated through nuclear fusion, specifically the fusion of hydrogen atoms to form helium.
- ☀️ The sun's layers include the core, radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, and corona, each playing a role in energy production and radiation.
- 🌀 Solar radiation impacts Earth's water cycle, climate, photosynthesis, and even societal phenomena like communication systems.
- 🌕 The moon, a rocky body without atmosphere, regulates Earth's tides, seasons, and stabilizes its rotation.
- 🌗 Lunar phases—new moon, first quarter, full moon, and last quarter—are visible from Earth and impact various natural processes.
- 🌘 Eclipses occur when the sun, Earth, and moon align, with lunar eclipses happening more frequently than solar eclipses.
Q & A
What role did the cycles of the sun and moon play in ancient civilizations?
-Ancient civilizations used the solar cycles and lunar phases to guide agricultural activities and long-distance travel, as they observed that these cycles governed seasons and natural patterns.
How did the Greeks contribute to the study of astronomy?
-The ancient Greeks were the first to attempt to understand the movements of celestial bodies through natural explanations, laying the foundation for the scientific approach to astronomy.
What was Galileo's key observation about the sun?
-Galileo observed that sunspots moved across the surface of the sun, indicating that the sun rotates.
What is a sunspot, and why is it important?
-A sunspot is a cooler region on the sun's surface with strong magnetic activity. These spots help scientists understand the sun’s magnetic field and its effects on solar radiation.
How does the sun produce energy?
-The sun produces energy through nuclear fusion, where hydrogen atoms combine at high speed to form helium, releasing energy in the process.
What are the main layers of the sun, and which ones are visible from Earth?
-The main layers of the sun include the core, radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, and corona. The photosphere is the visible surface, while the chromosphere and corona can be seen during solar eclipses.
How does sunlight reach the Earth, and what percentage of it actually arrives?
-Sunlight is carried by photons, which take several days to escape the sun's surface. Once it travels to Earth, only about one-third of the sunlight reaches the surface due to atmospheric filtering.
What are some biological and physical effects of solar radiation on Earth?
-Solar radiation influences biological processes like photosynthesis and the production of vitamin D in humans, and physical phenomena like the water cycle and climate patterns.
How does the moon influence Earth’s natural phenomena?
-The moon’s gravitational pull affects the tides, its phases regulate certain biological cycles, and its orbit contributes to eclipses and the Earth’s rotational stability.
What causes a lunar and solar eclipse?
-A lunar eclipse occurs when Earth comes between the sun and the moon, blocking sunlight from reaching the moon. A solar eclipse happens when the moon positions itself between the Earth and the sun, obscuring the sun from view.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)