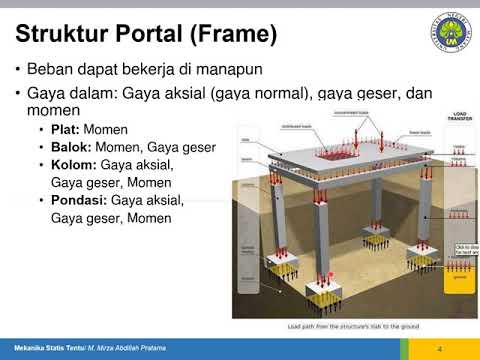
Teori Dasar Struktur Truss: Persamaan/Rumus, Reaksi Tumpuan, Gaya tarik atau tekan (T atau C)
Summary
TLDRThe transcript provides a detailed explanation of structural mechanics, focusing on static equilibrium principles applied to structures like beams, frames, and trusses. Key concepts include static balance equations (ΣF = 0, ΣM = 0), reactions at supports (e.g., roll, pin, and fixed supports), and the importance of analyzing forces on structural components. It covers how different types of supports influence the forces in the structure, including tension and compression. The text also discusses the modeling of trusses, including joint-based analysis, and emphasizes proper calculation methods to ensure structural stability in real-world applications like cranes and bridges.
Takeaways
- 😀 The core concept of static equilibrium is emphasized, where the sum of forces (ΣF = 0) and the sum of moments (ΣM = 0) must be satisfied for a structure in a static state.
- 😀 Different types of structural supports such as roll, rocker, pin, and fix are discussed, with their corresponding reaction forces and moments.
- 😀 The types of forces acting on a structure include tensile forces (T) and compressive forces (C), depending on whether the members are in tension or compression.
- 😀 The role of supports is crucial in determining the reaction forces that will ensure equilibrium, with specific calculations for each type of support.
- 😀 In truss analysis, the method of joints is used to determine forces in each member by considering the forces at the joints and solving for equilibrium conditions.
- 😀 The weight of the crane structure is converted into Newtons (force) using the formula: weight = mass × acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s²).
- 😀 A truss structure consists of members (rods or bars) that are connected by pin joints, which simplify the analysis of internal forces.
- 😀 The main load-bearing elements of a structure, such as the primary beams and trusses in a bridge or roof, are critical in maintaining the stability of the entire system.
- 😀 In bridge structures, additional elements like plates or covers are not considered load-bearing, and the primary structural components must be analyzed for load distribution.
- 😀 When analyzing a truss with the method of joints, forces acting on each joint are considered, and reactions are determined based on the static equilibrium conditions at each joint.
Q & A
What is the core principle used in static equilibrium for analyzing structures?
-The core principle is static equilibrium, which relies on the balance of forces and moments. The equations used are ΣF = 0 for forces and ΣM = 0 for moments, ensuring that the structure remains in equilibrium.
What are the types of supports commonly used in structural mechanics?
-The types of supports discussed include roll supports, rocker supports, short cable or short link supports, pin supports, and fixed supports. Each type offers different reaction forces based on the constraints they provide to the structure.
What happens at a pin support in terms of reaction forces?
-At a pin support, two reaction forces are generated: one along the x-axis (FX) and one along the y-axis (FY). No moment is generated at a pin support.
How does a fixed support differ from a pin support in terms of reaction forces?
-A fixed support provides three reactions: one force along the x-axis (FX), one force along the y-axis (FY), and one moment. This makes it more restrictive than a pin support, which only provides two reaction forces.
What is the significance of the force applied to a structure in Newton?
-For structural analysis, forces are calculated in Newtons, which is the standard unit of force in the International System of Units. For example, a mass in kilograms is converted to weight in Newtons by multiplying by 9.81 m/s², the acceleration due to gravity.
What is a truss structure and how does it work?
-A truss structure is composed of individual straight members connected by pins at the joints. The forces acting on the truss are either tension or compression, which means the members either pull apart (tension) or push together (compression) to carry the loads.
How does a truss distribute loads across its members?
-In a truss, each member is designed to either resist tension or compression, ensuring that the load is evenly distributed across the structure. By modeling the truss as a series of connected pins, the forces acting on the joints and members can be calculated.
What is the role of joints in a truss structure?
-Joints in a truss are the points where multiple members meet. The forces acting at these joints, whether in tension or compression, determine the behavior of the structure. Analyzing these forces at each joint is crucial for determining the internal forces in the truss.
What types of trusses are commonly used in bridge construction?
-Common truss types used in bridges include the Warren truss, Howe truss, and Pratt truss. These configurations vary in their internal structure and how they distribute loads, but all are designed to efficiently carry and distribute forces.
What is the importance of not considering non-structural elements in load-bearing calculations?
-In structural analysis, only the load-bearing components of a structure are considered for calculations. Non-structural elements, such as plates used for reinforcement, are not included in the load-bearing calculations since they do not directly carry the loads.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)