Myofibrils vs Myofilaments
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the structure of muscle fibers, specifically in cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscles. It highlights the role of **myofibrils**, which are composed of **sarcomeres** containing the contractile proteins **myosin** and **actin** (myofilaments) in cardiac and skeletal muscles. These myofibrils are highly organized, creating the characteristic light and dark bands. In contrast, smooth muscle lacks myofibrils but still relies on myofilaments for contraction. The video emphasizes the importance of these components for muscle function, distinguishing between the muscle types based on their structural organization.
Takeaways
- 😀 Myofibrils are rod-like structures found in cardiac and skeletal muscle.
- 😀 Myofibrils contain segments called sarcomeres, which are crucial for muscle contraction.
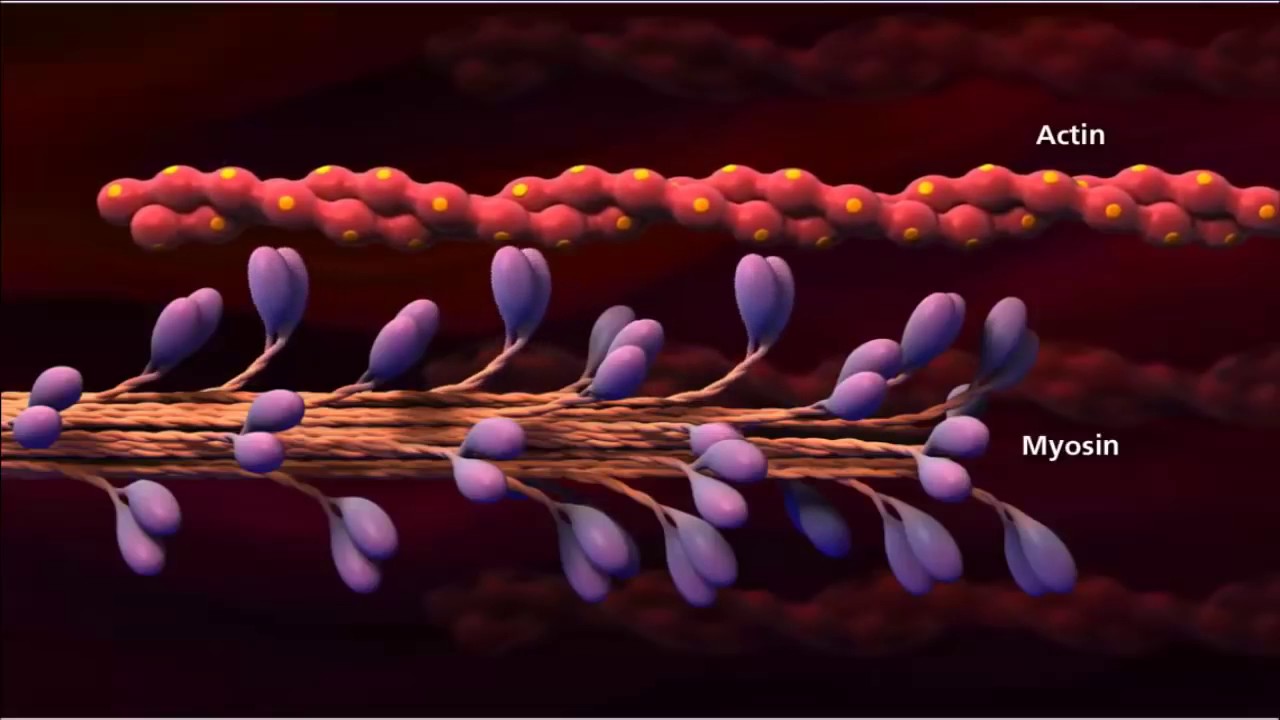
- 😀 Sarcomeres contain the myofilaments myosin and actin, which are responsible for muscle contraction.
- 😀 Myosin and actin are essential contractile proteins found in myofilaments.
- 😀 Smooth muscle does not contain myofibrils, unlike cardiac and skeletal muscle.
- 😀 The lack of myofibrils in smooth muscle means it lacks the highly organized structure seen in other muscle types.
- 😀 The highly organized myofibrils in cardiac and skeletal muscle create light and dark bands, visible under a microscope.
- 😀 Even though smooth muscle lacks myofibrils, it still contains myofilaments (myosin and actin).
- 😀 Actin and myosin are the myofilaments that allow muscle contraction to occur in all muscle types.
- 😀 Without myofilaments (actin and myosin), muscles would not be able to contract at all.
Q & A
What are myofibrils, and where are they found?
-Myofibrils are rod-like structures found in cardiac and skeletal muscle. They are composed of repeating segments called sarcomeres, which are responsible for muscle contraction.
What are sarcomeres, and what do they contain?
-Sarcomeres are segments within myofibrils, and they contain the contractile proteins myosin and actin, which are also known as myofilaments.
What are myosin and actin, and how do they relate to muscle contraction?
-Myosin and actin are contractile proteins known as myofilaments. They interact to facilitate muscle contraction by sliding past each other, which shortens the muscle fiber.
Why are myofibrils absent in smooth muscle?
-Myofibrils are absent in smooth muscle because smooth muscle doesn't exhibit the highly organized arrangement of actin and myosin found in cardiac and skeletal muscle. Smooth muscle lacks the structural organization necessary to form these rod-like structures.
What is the role of myofibrils in cardiac and skeletal muscle?
-In cardiac and skeletal muscle, myofibrils are crucial for organizing actin and myosin in a highly structured way, which creates the light and dark bands seen in these muscles and is essential for their contractile function.
Why do cardiac and skeletal muscles have light and dark bands?
-The light and dark bands in cardiac and skeletal muscles are due to the highly organized arrangement of myofilaments (actin and myosin) within myofibrils. This organization creates the alternating bands that are visible under a microscope.
Does smooth muscle contain myofilaments?
-Yes, smooth muscle contains myofilaments, including actin and myosin. While it doesn't have myofibrils, these myofilaments are still essential for the contraction of smooth muscle.
What would happen if there were no myofilaments in muscle tissue?
-Without myofilaments (actin and myosin), muscle tissue would not be able to contract, as these proteins are essential for the contraction mechanism in all muscle types.
How do smooth muscles contract without myofibrils?
-Smooth muscles contract without myofibrils by relying on a less organized arrangement of myofilaments (actin and myosin). This allows contraction to occur, but without the banding patterns seen in cardiac and skeletal muscles.
What makes cardiac and skeletal muscle contraction different from smooth muscle?
-Cardiac and skeletal muscle contractions are highly organized, involving myofibrils and the distinct banding patterns due to the precise arrangement of actin and myosin. In contrast, smooth muscle contraction is less organized and occurs without the visible banding.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)