Sifat-sifat Gelombang Bunyi
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the key properties of sound waves, including reflection, refraction, diffraction, interference, beats, and the Doppler Effect. It covers how sound waves interact with different mediums, how they can be amplified or diminished, and how they behave in various environments. For example, sound reflection creates echoes, while refraction makes thunder sound louder at night. Diffraction allows sound to travel through openings, and interference can create varying sound intensities. The Doppler Effect explains the change in pitch as a sound source moves toward or away from a listener. Understanding these properties is essential for exploring acoustics and sound behavior.
Takeaways
- 😀 Sound waves are mechanical waves that require a medium to travel through and are classified as longitudinal waves.
- 😀 Reflection occurs when sound waves hit a hard surface and bounce back, creating echoes, such as when shouting near a cliff.
- 😀 Refraction happens when sound waves enter a different medium, bending the waves, like thunder sounding louder at night due to denser air near the ground.
- 😀 Diffraction is the bending of sound waves around obstacles or through small openings, allowing you to hear sounds from another room.
- 😀 Interference is the interaction between two sound waves, which can be constructive (amplifying sound) or destructive (weakening sound).
- 😀 Constructive interference happens when sound waves align to make the sound louder, while destructive interference occurs when they cancel each other out.
- 😀 Beat frequency occurs when two sound waves with slightly different frequencies interfere, creating a fluctuating sound, like an ambulance siren.
- 😀 The Doppler Effect is the change in pitch or frequency of a sound as the source moves relative to the listener, such as when an ambulance passes by.
- 😀 When sound moves toward you, its frequency increases, and when it moves away, its frequency decreases, creating the Doppler Effect.
- 😀 Sound in enclosed spaces, like rooms, can reflect off walls, causing the reflected sound to merge with the original sound, making it louder or clearer depending on the setup.
Q & A
What is the primary characteristic of sound waves?
-Sound waves are mechanical longitudinal waves that require a medium to travel through, such as air, water, or solids.
How does sound reflection occur?
-Sound reflection happens when sound waves hit a hard surface and bounce back to the source, such as when shouting near a cliff and hearing an echo.
What is the difference between echo and reverberation?
-Echo occurs when sound reflects off a distant surface, taking longer to return to the listener. Reverberation happens in closed spaces where sound reflects off nearby surfaces, making it sound louder and more continuous.
Why does thunder sound louder at night?
-Thunder sounds louder at night because the lower air layers are denser, causing the sound waves to bend (refraction) towards the ground, making them more intense.
What is diffraction in sound waves?
-Diffraction is the bending of sound waves around obstacles or through small openings. For example, you can hear someone talking in an adjacent room due to sound wave diffraction.
What is interference in sound waves?
-Interference occurs when two sound waves interact within the same medium, either amplifying each other (constructive interference) or canceling each other out (destructive interference).
What is the difference between constructive and destructive interference?
-Constructive interference happens when two waves are in phase and reinforce each other, while destructive interference occurs when two waves are out of phase and cancel each other out.
How do beats occur in sound waves?
-Beats occur when two sound waves of slightly different frequencies interfere, creating a fluctuation in loudness. For example, hearing varying intensity in two overlapping musical notes.
How does the Doppler Effect affect sound?
-The Doppler Effect causes a change in sound frequency or pitch due to the relative movement of the source and observer. When the sound source approaches, the pitch increases, and when it moves away, the pitch decreases.
Can you give an example of the Doppler Effect?
-An example of the Doppler Effect is the changing pitch of an ambulance siren as it approaches and then moves away from a listener. The sound becomes higher in pitch as it approaches and lower when it moves away.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Fisika kelas 11 | Gelombang Bunyi part 2

Fenômenos ondulatórios - reflexão, refração, difração, interferência e ressonância

Gelombang Bunyi • Part 1: Sifat, Klasifikasi, dan Cepat Rambat Gelombang Bunyi

Peristiwa Pemantulan, Pembiasan, Interferensi dan Difraksi Gelombang Pada Tangki Riak
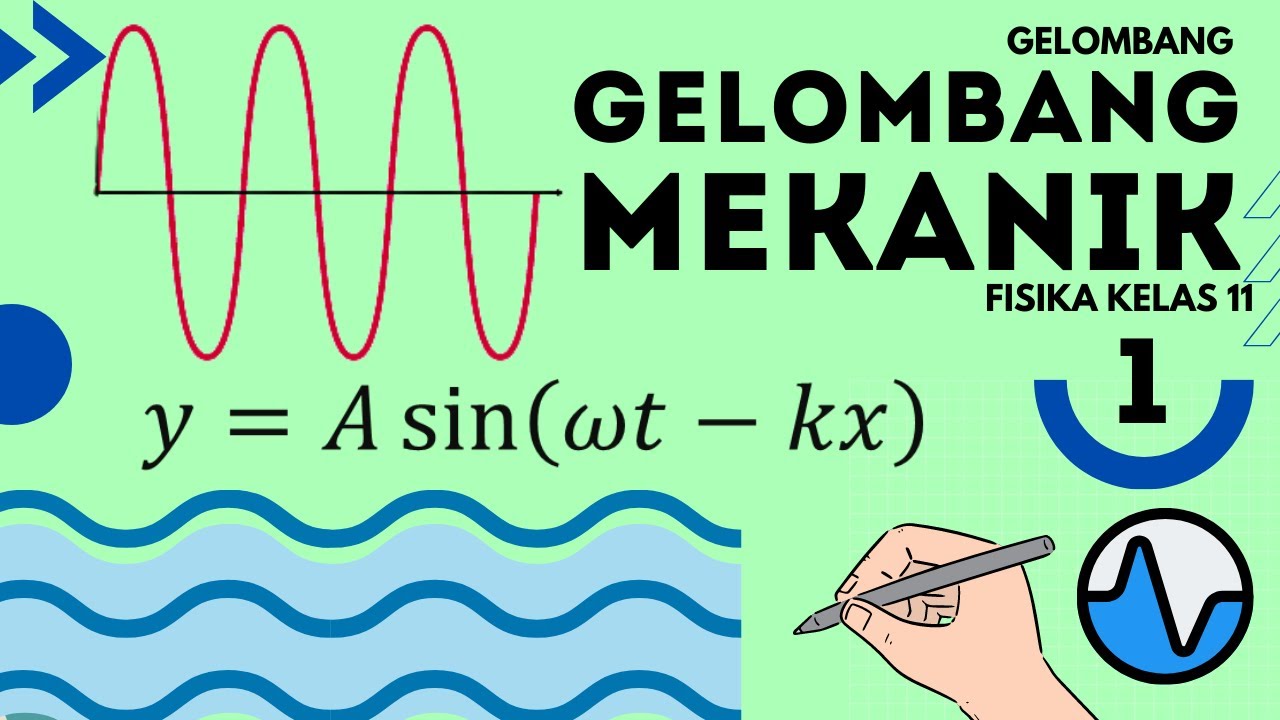
Gelombang Mekanik Fisika Kelas 11- Part 1 : Konsep Gelombang Mekanik

All of WAVES in 15 mins - AS & A-level Physics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
