KIMIA TANAH
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses the composition and functions of soil, highlighting its essential role for plant life and other organisms. It covers the different types of soil, such as solid and organic, and explains their characteristics, including mineral and organic content. The impact of pollution, especially acid rain, on soil quality is explored, as well as the importance of proper land use and farming practices. The script also explains nutrient exchange in soil, the role of microorganisms, and the need for fertilizers to maintain plant health. Overall, it emphasizes the critical relationship between soil health and environmental sustainability.
Takeaways
- 😀 Soil is a thin layer on the Earth's surface and serves as a vital resource for both humans and other living organisms.
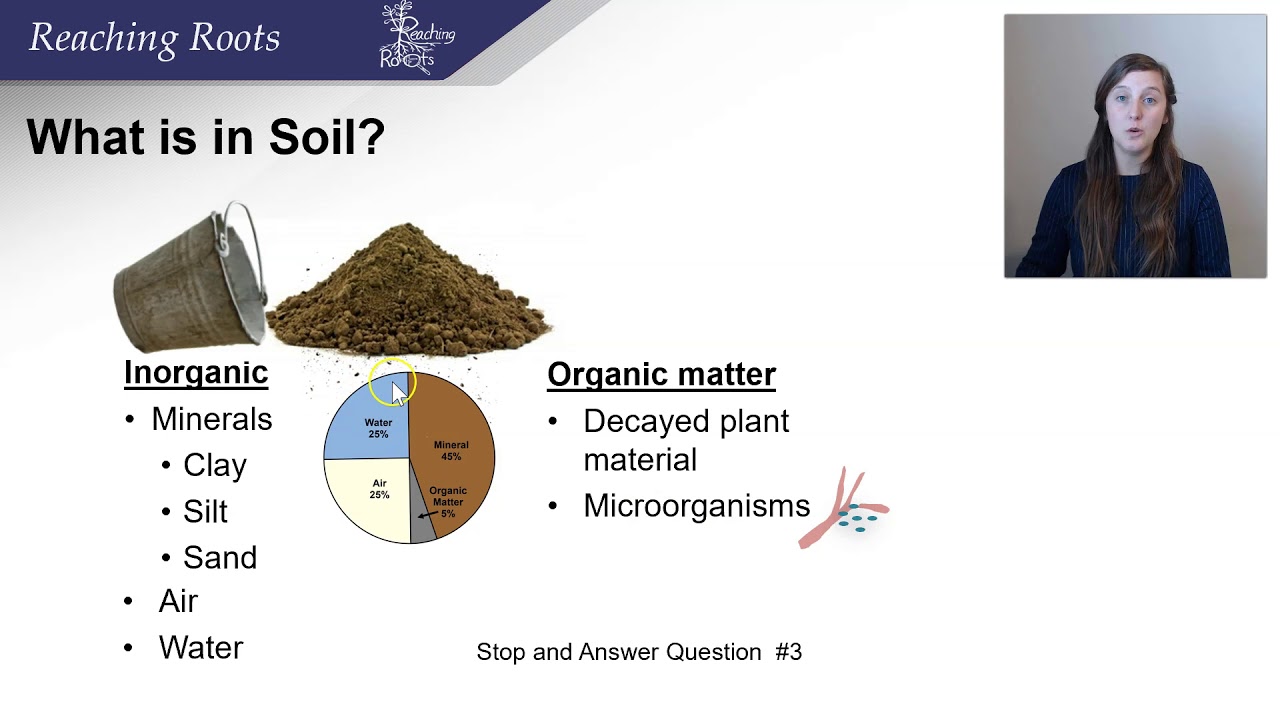
- 😀 Soil composition consists of minerals, organic material, and water, with two main types: compact soil and porous soil.
- 😀 Porous soil with larger pores allows water to pass through more easily compared to soil with smaller pores.
- 😀 Solid soil typically contains 95% inorganic substances, whereas peat soil is rich in organic material, up to 90%. Peat soil retains a lot of water and supports the growth of plants like shrubs.
- 😀 Soil quality can be negatively impacted by pollution, such as acid rain, which is caused by industrial emissions reacting with water vapor in the atmosphere.
- 😀 Acid rain can lower soil pH, causing nutrient deficiencies in plants, and over time, it can make the soil infertile.
- 😀 Improper farming practices on sloped land can lead to soil erosion, which can be seen in the color of river water as it becomes muddy.
- 😀 The rising population and urban development often lead to construction in water retention areas, increasing the risk of flooding during rainy seasons.
- 😀 Air and water within the soil play critical roles in delivering nutrients to plants and maintaining soil health through processes like transpiration.
- 😀 The organic material in soil, known as humus, is resistant to water and decomposition and is essential for providing nutrients to microorganisms in the soil.
- 😀 Essential plant nutrients include nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are obtained from organic matter and animal decomposition, and are absorbed by plants through ion exchange.
Q & A
What is the primary function of soil according to the script?
-The primary function of soil is to act as a resource for sustaining life, providing essential nutrients for plants, animals, and humans.
What are the main components of soil?
-Soil is made up of a mixture of minerals, organic materials, and water.
What are the two types of soil structures mentioned?
-The two types of soil structures are compact soil with small pores and loose soil with larger pores.
How does soil with large pores compare to compact soil in terms of water movement?
-Soil with large pores allows water to pass through more easily compared to compact soil with smaller pores.
What is peat soil, and what is its composition?
-Peat soil has a high organic compound content, with 90% organic material and only 5% inorganic material.
What impact does industrial pollution have on soil quality?
-Industrial pollution can lead to acid rain, which can lower the pH of soil, depleting essential nutrients and making it less fertile.
What is acid rain and how does it affect soil?
-Acid rain occurs when pollutants in the atmosphere combine with water vapor, forming acidic compounds that lower the soil's pH and deplete nutrients needed for plant growth.
How does improper agricultural practice contribute to soil erosion?
-Improper agricultural practices on steep land can lead to soil erosion, visible through muddy river water, resulting in the loss of fertile soil.
What are the key nutrients required by plants from the soil?
-Key nutrients for plants include nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are necessary for plant growth and development.
What is the process of ion exchange in soil, and how does it relate to nutrient absorption by plants?
-Ion exchange is a process where plants release hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil, allowing them to absorb essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

TANAH DAN KEBERLANGSUNGAN KEHIDUPAN - IPA KELAS 9 SMP #biology

Types of Soil (Quiz Edition)
Soil Science Introduction

How to Grow Amazing Plants with Compost Tea - Masterclass with Dr. Elaine Ingham (Part 1 of 5)

PERAN TANAH | TANAH DAN KEBERLASUNGAN KEHIDUPAN

Tanah dan Kehidupan: Komponen Penyusun Tanah - SMP Kelas 9 | Part 3
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
