EKG 3
Summary
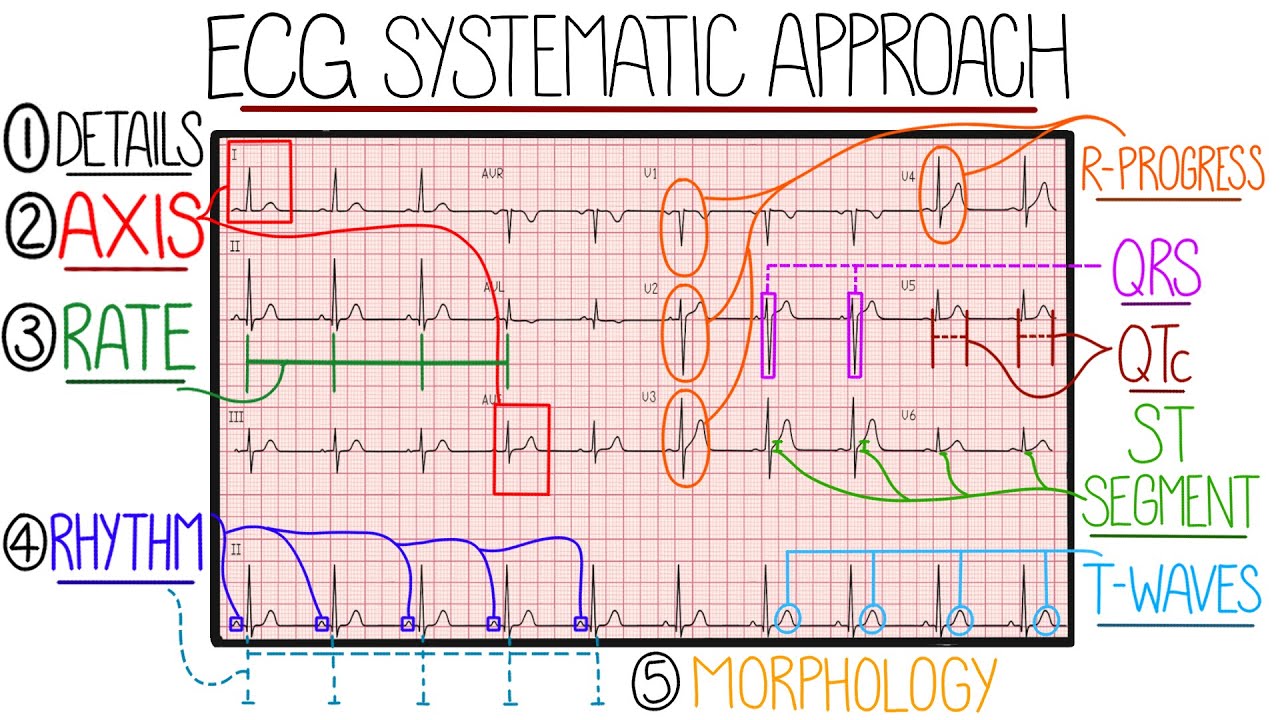
TLDRThis presentation covers the different types of ECG morphology and their clinical significance. It discusses normal ECG features, as well as conditions like sinus bradycardia, sinus tachycardia, myocardial ischemia, and myocardial infarction. Key ECG findings such as ST segment depression and elevation are highlighted, helping to distinguish between ischemia and infarction. The script emphasizes the importance of ECG in diagnosing these cardiovascular conditions, offering insight into treatment options like atropine, cardioversion, and angioplasty. Understanding ECG morphology is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management of heart-related disorders.
Takeaways
- 😀 Sinus bradycardia is characterized by a heart rate less than 60 bpm, and while the ECG may appear normal, it can lead to decreased cardiac output and hypotension if untreated.
- 😀 Atropine is the first-line treatment for symptomatic sinus bradycardia, as it increases heart rate by enhancing sympathetic activity.
- 😀 Sinus tachycardia occurs when the heart rate exceeds 100 bpm, often as a compensatory response to conditions like fever, anxiety, or shock.
- 😀 Cardioversion and medications like adenosine are used to manage tachycardia when the heart rate exceeds 150 bpm.
- 😀 Common causes of tachycardia include anemia, respiratory distress, pulmonary embolism, sepsis, and hyperthyroidism, all of which increase the body's demand for oxygen.
- 😀 Myocardial ischemia results from a lack of oxygen supply to the cardiac muscle, and ECG findings such as ST depression can help identify it.
- 😀 Myocardial infarction (MI) occurs when myocardial ischemia leads to permanent cell death, and ECG findings of ST elevation indicate infarction.
- 😀 MRI and CT scans are crucial tools for diagnosing myocardial ischemia and infarction, as they help assess myocardial damage and detect blockages.
- 😀 In myocardial ischemia, the ST segment typically shows depression, while in infarction, it shows elevation, marking the progression of the condition.
- 😀 Myocardial infarction can be classified as Type 1 (due to blood clot rupture) or Type 2 (due to vessel spasm or oxygen supply-demand imbalance).
Q & A
What does the P wave represent in an ECG?
-The P wave represents atrial depolarization, which is the electrical activity that triggers the contraction of the atria.
What is the significance of the QRS complex in an ECG?
-The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization, which initiates the contraction of the ventricles in the heart.
How is sinus bradycardia defined and what are its typical ECG findings?
-Sinus bradycardia is defined as a heart rate of less than 60 beats per minute. In the ECG, the rhythm is regular with normal P waves, PR interval, and QRS duration, but with a slower heart rate.
What treatment is recommended if sinus bradycardia leads to symptoms such as hypotension?
-If sinus bradycardia causes symptoms like hypotension, atropine is the first-line treatment. Atropine increases sympathetic activity in the heart and raises the heart rate.
What is the typical heart rate in sinus tachycardia and what does the ECG show?
-Sinus tachycardia is characterized by a heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute. The ECG shows a regular rhythm with normal P waves and QRS complexes, but the heart rate is increased.
How do conditions like anemia or hyperthyroidism affect heart rate?
-In conditions like anemia and hyperthyroidism, the body’s oxygen demand increases, prompting the heart to beat faster, leading to tachycardia.
What is myocardial ischemia and how is it identified on an ECG?
-Myocardial ischemia is a condition where the heart muscle does not receive sufficient oxygen, often due to coronary artery blockage. On an ECG, it typically presents as ST depression.
What distinguishes myocardial infarction from myocardial ischemia in terms of ECG findings?
-In myocardial infarction, the ECG shows ST elevation and the presence of pathological Q waves, indicating permanent damage to the heart muscle. In contrast, myocardial ischemia is marked by ST depression without permanent damage.
What are the main causes of myocardial infarction?
-Myocardial infarction is commonly caused by atherosclerosis, vasospasm, blood clot formation, or supply-demand imbalances in oxygen delivery to the heart muscle.
How are myocardial infarction types 1 and 2 different?
-Type 1 myocardial infarction is caused by the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque leading to blood clot formation, while Type 2 is caused by supply-demand imbalance, often due to conditions like vasospasm or fixed atherosclerosis.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)