Pengolahan Sinyal Digital: 11 Tipe dan Karakteristik Filter
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an introduction to digital signal processing, focusing on filter types and their characteristics. It covers four main filter types: low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, and band-reject, explaining their function in terms of frequency response. The video highlights the importance of frequency response measurement on a logarithmic scale and discusses practical filter designs, such as Butterworth and Chebyshev filters. The limitations of ideal filters are also addressed, stressing why they are impractical for real-world applications due to the undesirable effects of sharp cutoffs. The video wraps up by explaining the smoother, more usable transitions in real filters.
Takeaways
- 😀 Filters in digital signal processing are crucial for manipulating signals by selectively passing or blocking certain frequencies.
- 😀 There are four main types of filters: low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, and band-stop filters.
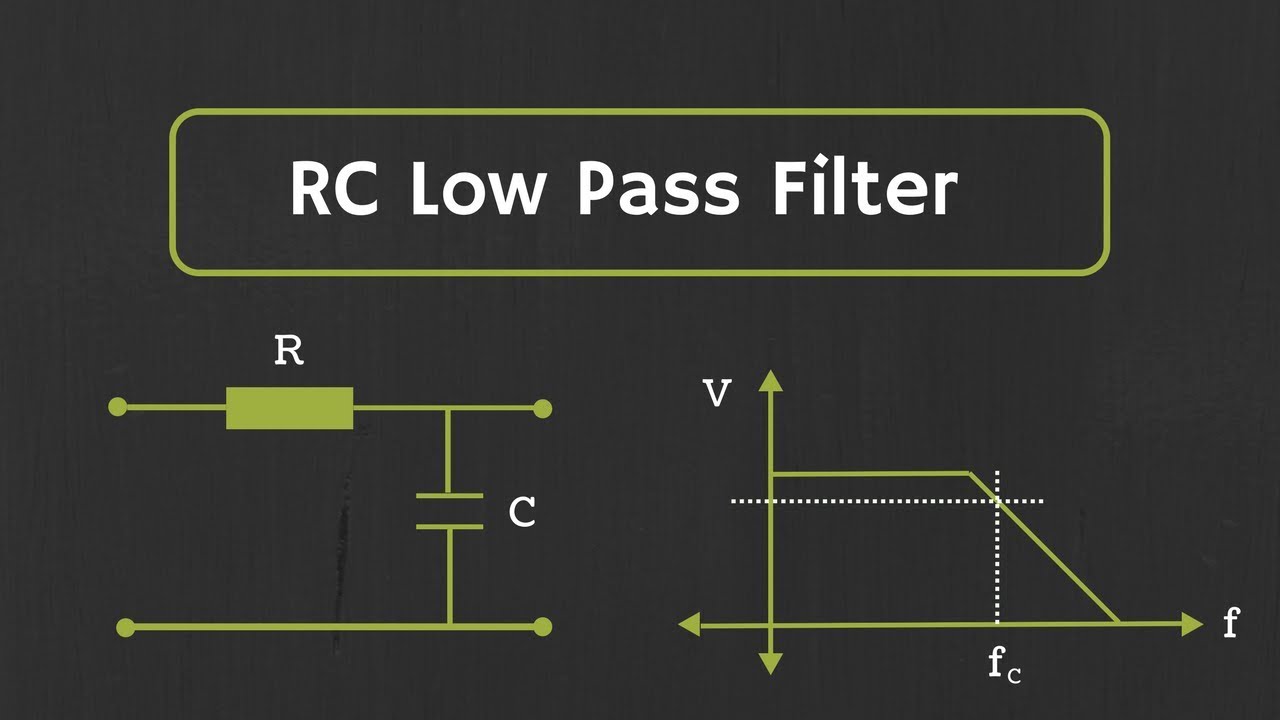
- 😀 A low-pass filter allows low frequencies to pass and attenuates higher frequencies.
- 😀 A high-pass filter allows high frequencies to pass and attenuates lower frequencies.
- 😀 A band-pass filter allows a specific range of frequencies to pass and blocks others outside that range.
- 😀 A band-stop filter (or band-reject filter) blocks frequencies within a specific range and allows others to pass.
- 😀 Ideal filters are mathematically perfect but impractical due to sharp frequency cutoffs that cause distortion in the signal.
- 😀 In real-world applications, filters must have smoother transitions between passband and stopband to avoid unwanted artifacts.
- 😀 The frequency response of filters is often analyzed using decibels (dB), which presents a logarithmic scale of signal attenuation.
- 😀 Common filters include Butterworth filters (flat passband, slower roll-off) and Chebyshev filters (steeper roll-off but with ripple).
- 😀 Despite the theoretical appeal of ideal filters, practical filters are preferred to avoid undesirable effects like noise or distortion.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the lecture in the provided script?
-The main topic of the lecture is digital signal processing, specifically focusing on filtering techniques, filter types, and their characteristics.
What are the four main types of filters discussed in the lecture?
-The four main types of filters discussed are low-pass filters, high-pass filters, band-pass filters, and band-stop filters.
What is the purpose of a low-pass filter?
-A low-pass filter allows low frequencies to pass through while blocking higher frequencies, typically used to retain the low-frequency components of a signal.
How does a high-pass filter differ from a low-pass filter?
-A high-pass filter allows higher frequencies to pass through while blocking lower frequencies, in contrast to the low-pass filter which does the opposite.
What is a band-pass filter used for?
-A band-pass filter allows only a specific range of frequencies to pass through while blocking frequencies outside that range.
What is the function of a band-stop filter?
-A band-stop filter (or notch filter) blocks a narrow band of frequencies while allowing all other frequencies to pass through.
What does the frequency response of a filter indicate?
-The frequency response of a filter shows how different frequencies are either passed or blocked. It is usually represented on a logarithmic scale (in decibels).
Why are ideal filters not used in practical applications?
-Ideal filters are not used in practice because their sharp transitions between passband and stopband can introduce unwanted artifacts, such as ringing or distortion, into the signal.
What is a Butterworth filter, and what are its characteristics?
-A Butterworth filter is a type of filter known for having a flat passband. It is commonly used in applications where a smooth response is desired, though its transition from passband to stopband is slower compared to other filters.
How does the order of a filter affect its performance?
-The order of a filter affects its steepness and frequency response. Higher-order filters can achieve sharper transitions between passband and stopband, but they also introduce more complexity and potential for signal distortion.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)