Understanding Sepsis (Sepsis Explained Clearly)
Summary
TLDRSepsis is a life-threatening condition where the body’s response to an infection causes organ dysfunction and failure. It results from a disregulated immune response, leading to reduced blood circulation and oxygen delivery to tissues. Sepsis can be caused by various infections, including bacterial, viral, or fungal. Early detection is key, with a focus on identifying organ dysfunction using criteria like the SOFA score. Treatment includes blood cultures, antibiotics, fluids, and oxygen. Timely management is crucial to prevent septic shock, a severe form of sepsis with persistent hypotension and high mortality rates.
Takeaways
- 😀 Sepsis is a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a disregulated host response to an infection.
- 😀 Not all infections lead to sepsis, but any infection has the potential to develop into sepsis.
- 😀 Sepsis leads to organ dysfunction through increased metabolic demands and insufficient circulation.
- 😀 In sepsis, the immune response is disregulated, impairing normal body function and causing systemic vasodilation.
- 😀 Reduced cardiac output in sepsis results from vasodilation, lowered blood volume, and impaired heart contractility.
- 😀 Septic shock is defined as sepsis with severe hypotension requiring vasopressors to maintain mean arterial pressure.
- 😀 Nitric oxide release in sepsis causes vasodilation and reduced blood flow, impairing organ perfusion.
- 😀 Sepsis increases vessel permeability, causing fluid loss and coagulopathy, which further impairs blood flow.
- 😀 Common sources of sepsis include bacterial infections like pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and abdominal infections.
- 😀 The SOFA score is used to assess organ dysfunction in sepsis, with a score of 10 or higher indicating high mortality risk.
- 😀 Early treatment of suspected sepsis includes blood cultures, lactate level measurement, intravenous antibiotics, and fluids.
Q & A
What is the definition of sepsis?
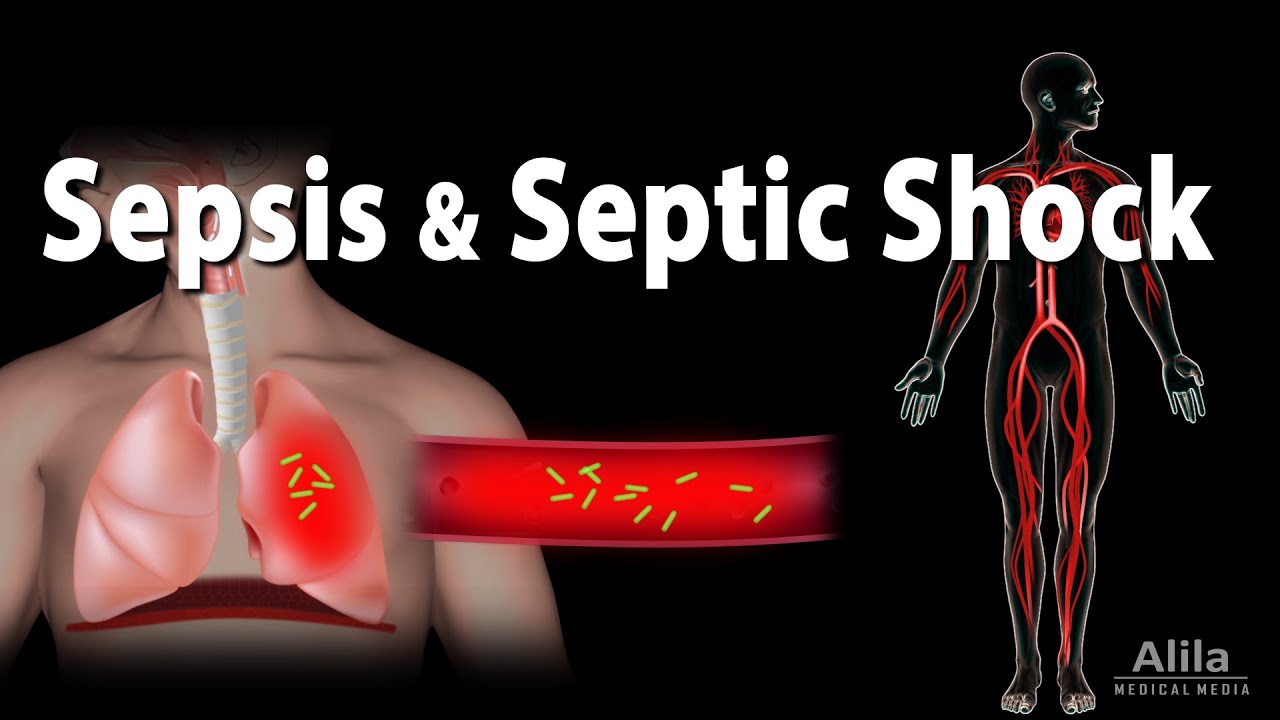
-Sepsis is a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a disregulated host response to an infection. The body's response to the infection ends up damaging organs, eventually leading to organ failure and death.
What causes organ dysfunction in sepsis?
-The organ dysfunction in sepsis results from increased metabolic demands combined with insufficient circulation, meaning there's an increased demand for oxygen and nutrients, but a reduced supply due to impaired circulation.
How does the immune response differ in sepsis compared to a normal infection?
-In a normal infection, the immune response is localized and includes the release of cytokines and recruitment of cells like neutrophils and macrophages. In sepsis, this immune response becomes disregulated, impairing normal body functions, though it doesn't necessarily mean it is excessive.
What role does nitric oxide play in sepsis?
-In sepsis, nitric oxide is released as a vasodilator, causing systemic vasodilation. This leads to reduced venous return (preload), a decreased stroke volume, and thus a reduced cardiac output. This can cause low blood pressure, impaired circulation, and ultimately reduced perfusion to organs.
What is septic shock, and how does it relate to sepsis?
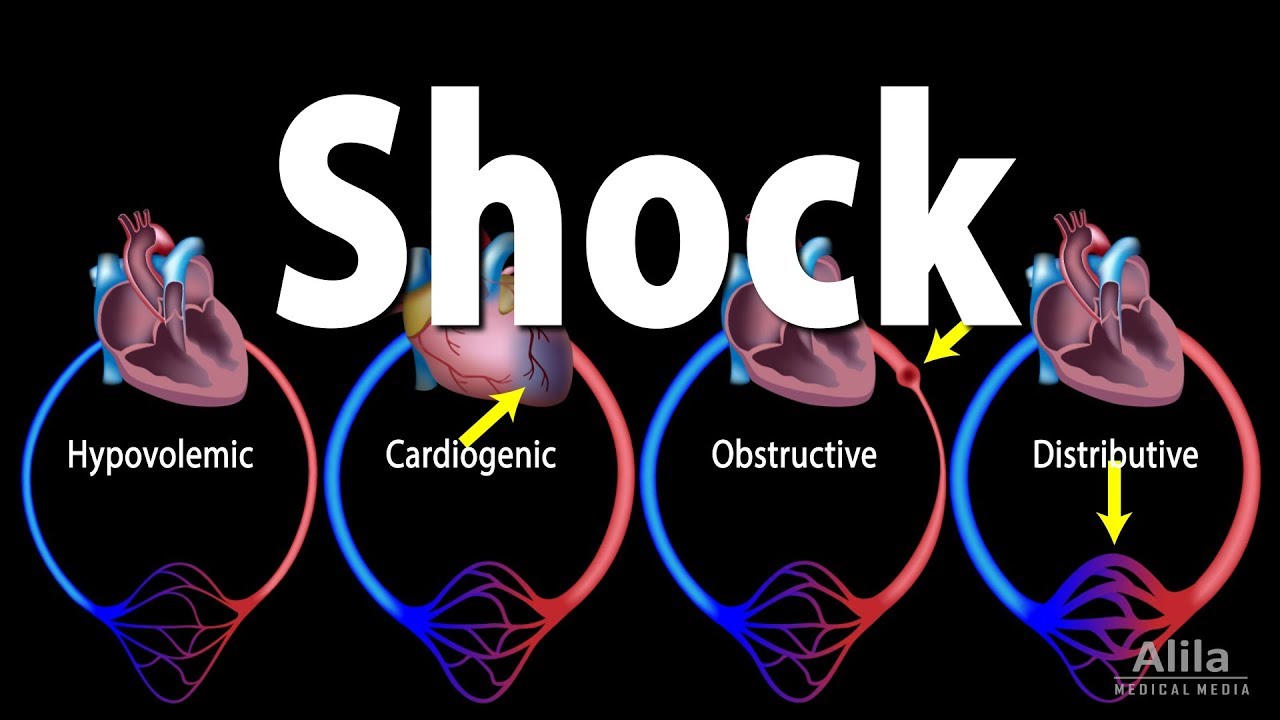
-Septic shock is a severe form of sepsis characterized by persistent hypotension (low blood pressure) that requires vasopressors to maintain a mean arterial pressure above 65 mmHg, and a serum lactate level above 2. It is a type of distributive shock resulting from sepsis.
What are the common causes of sepsis?
-Bacterial infections, such as those caused by *Staphylococcus aureus*, *Pseudomonas aeruginosa*, and *E. coli*, are the most common sources of sepsis. However, sepsis can also be caused by viruses, fungi, and parasites. Lower respiratory tract infections like pneumonia are the most frequent primary source.
Which populations are at higher risk for sepsis?
-Certain factors increase the risk of sepsis, such as older age (above 65), very young children, immunocompromised states (e.g., cancer treatment, steroid use), recent surgery, indwelling catheters, diabetes, alcohol or drug use, and pregnancy.
How is sepsis diagnosed clinically?
-Sepsis is diagnosed based on the presence of infection and organ dysfunction. The SOFA (Sequential Organ Failure Assessment) score is often used in ICU settings to assess the degree of organ failure. A score of 2 or more indicates organ dysfunction and defines sepsis.
What is the difference between the SOFA score and the SIRS criteria in diagnosing sepsis?
-The SIRS (Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome) criteria were previously used to diagnose sepsis, focusing on indicators like temperature, heart rate, and white blood cell count. The SOFA score, however, is now preferred as it assesses organ failure across six parameters and is more accurate for determining sepsis severity.
What are the initial steps in managing suspected sepsis?
-The initial management of suspected sepsis follows the 'sepsis six' protocol, which includes three things to give: blood cultures, intravenous antibiotics, and intravenous fluids; and three things to take: blood tests (including lactate level), urine output measurements, and oxygen administration.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)