micro:bit compass
Summary
TLDRA digital compass is a sensor that detects magnetic fields, particularly the Earth's magnetic field, to determine magnetic North. It is often integrated into smartphones and devices like the BBC micro:bit, enabling navigation and direction-finding features. The micro:bit’s compass requires calibration for accurate results, which happens automatically when first used. Users can detect magnetic fields, like the presence of a magnet, without calibration. Once calibrated, the compass can be applied in various projects, such as creating alarms or weather vanes to detect changes like the opening of a door or wind direction.
Takeaways
- 😀 A digital compass is an input sensor that detects magnetic fields, especially the Earth's magnetic field, to find magnetic North.
- 😀 Digital compasses are often called magnetometers because they measure magnetic fields.
- 😀 Smartphones typically have a digital compass that helps users determine which direction they are heading when using maps.
- 😀 The compass in a smartphone can automatically rotate maps to reflect the direction you are pointing, aiding in navigation.
- 😀 The BBC micro:bit includes an inbuilt compass that detects the Earth's magnetic field, helping users know which direction it is facing.
- 😀 The micro:bit compass requires calibration to ensure accurate results, which occurs the first time you use the compass in a program.
- 😀 Calibration of the micro:bit compass involves tilting the device in every direction to fill the screen, ensuring it works properly.
- 😀 The micro:bit can detect strong magnetic fields without needing calibration, which is useful for identifying nearby magnets.
- 😀 With calibration complete, the compass can be used in various projects, such as navigation or magnetic field detection.
- 😀 One example of using the micro:bit compass is to create an alarm that senses when a door has opened.
- 😀 Another creative project is building a micro:bit weather vane to measure wind direction by programming the compass.
Q & A
What is a digital compass?
-A digital compass is an input sensor that detects magnetic fields, especially the Earth's magnetic field, to find magnetic North.
Why is a digital compass sometimes called a magnetometer?
-It is called a magnetometer because it detects magnetic fields, which is the same principle used by magnetometers to measure magnetic field strength.
How do smartphones use digital compasses?
-Smartphones use digital compasses to detect the direction the phone is facing, allowing map applications to auto-rotate and reflect the user's heading, making navigation easier.
What is the role of the compass in the BBC micro:bit?
-The compass in the BBC micro:bit detects the Earth's magnetic field, allowing it to determine the direction the micro:bit is facing.
Why does the compass in the micro:bit need calibration?
-The compass in the micro:bit needs calibration to ensure the readings are accurate, and this happens automatically the first time it is used.
What happens during the calibration of the micro:bit's compass?
-During calibration, the micro:bit scrolls the message 'tilt to fill screen,' and you must tilt the device in every direction to ensure the compass is properly calibrated.
Can you use the micro:bit's compass without calibration?
-Yes, you can use the compass without calibration to detect strong magnetic fields, such as the presence of a magnet, but the readings won't be as precise.
How can you use the micro:bit to detect a nearby magnet?
-You can program the micro:bit to light up its LEDs when it detects a nearby magnet, even without calibrating the compass.
What are some examples of projects you can create with the micro:bit's compass?
-Examples include creating an alarm to sense when a door is opened or making a weather vane to measure the wind's direction.
What does calibrating the compass on the micro:bit ensure?
-Calibrating the compass ensures that the device gives accurate readings of the Earth's magnetic field, which is essential for determining precise directions.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
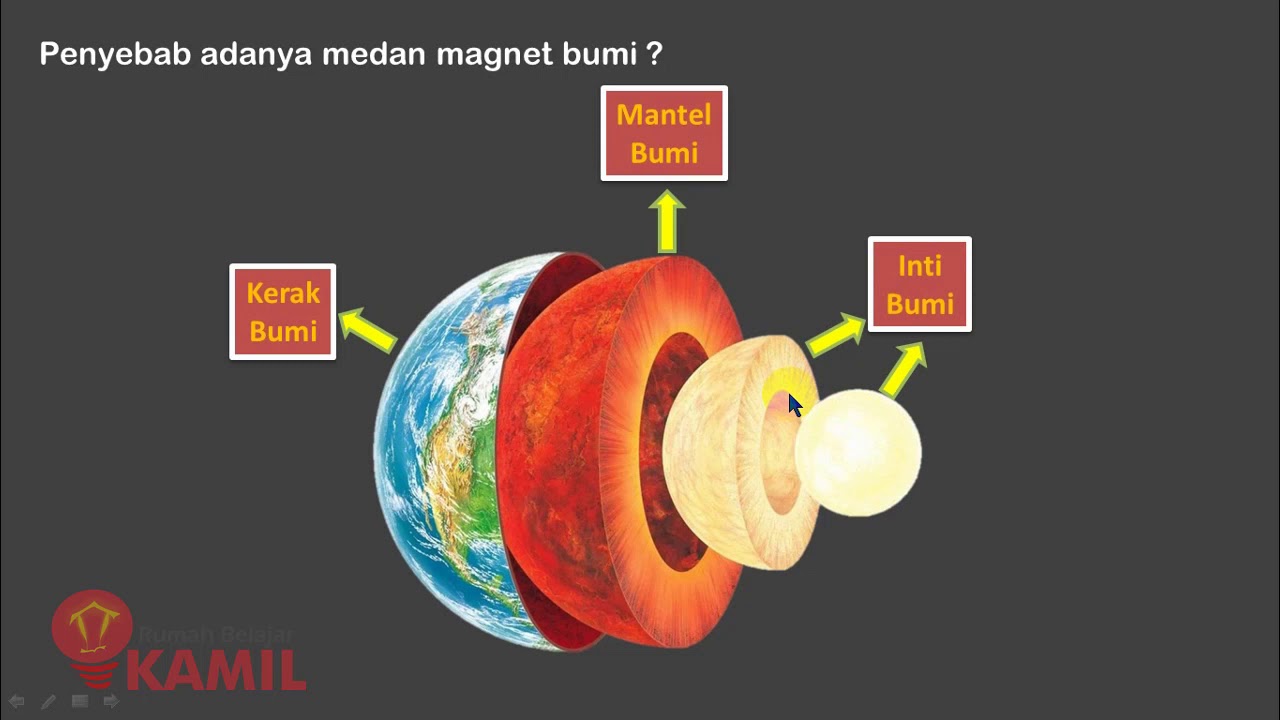
IPA Kelas 9 Semester 2 : Kemagnetan (Part 2 : Medan Magnet dan Magnet pada Bumi)
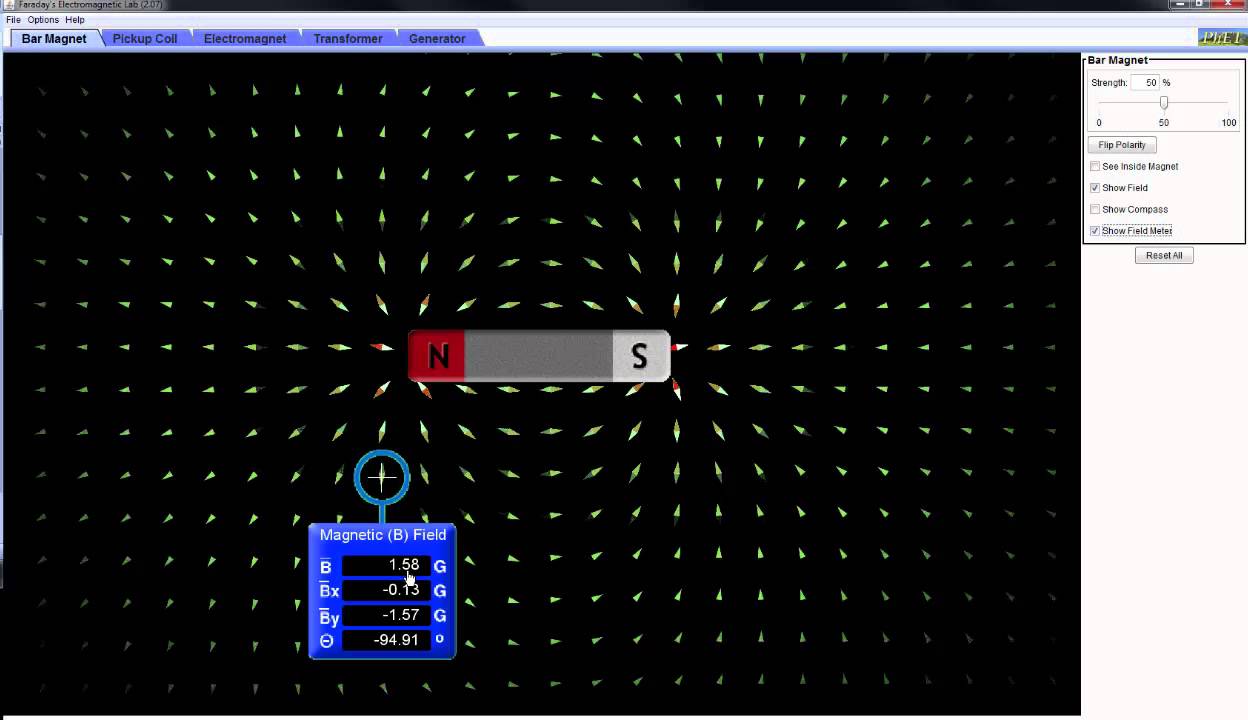
Phet Simulation: Faraday's Lab on the Bar Magnet

Teori Kemagnetan Bumi Kelas 9 Semester Genap
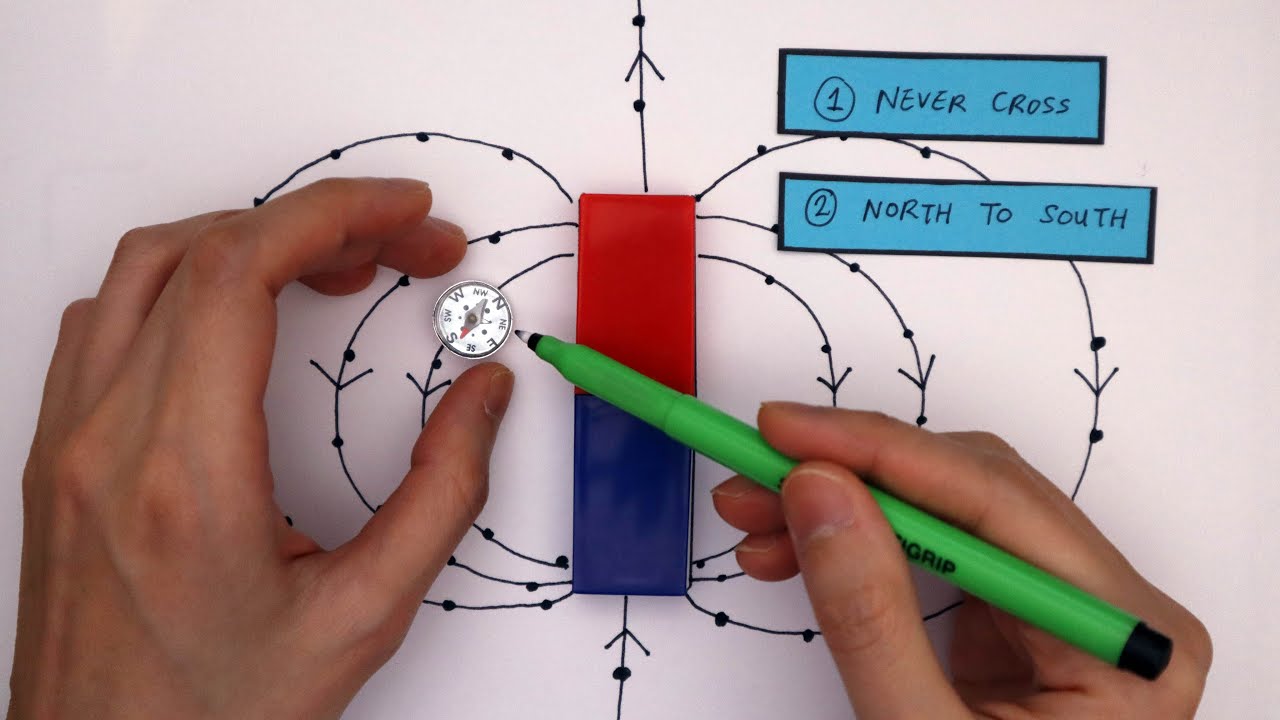
Plotting Magnetic Field Lines GCSE Physics Required Practical

Medan Magnet pada Solenoida dan Toroida: di Tengah dan Ujung Solenoida, di Dalam Toroida

Tangent Galvanometer - Amrita University
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
