Kenali Talasemia Sebelum Menikah
Summary
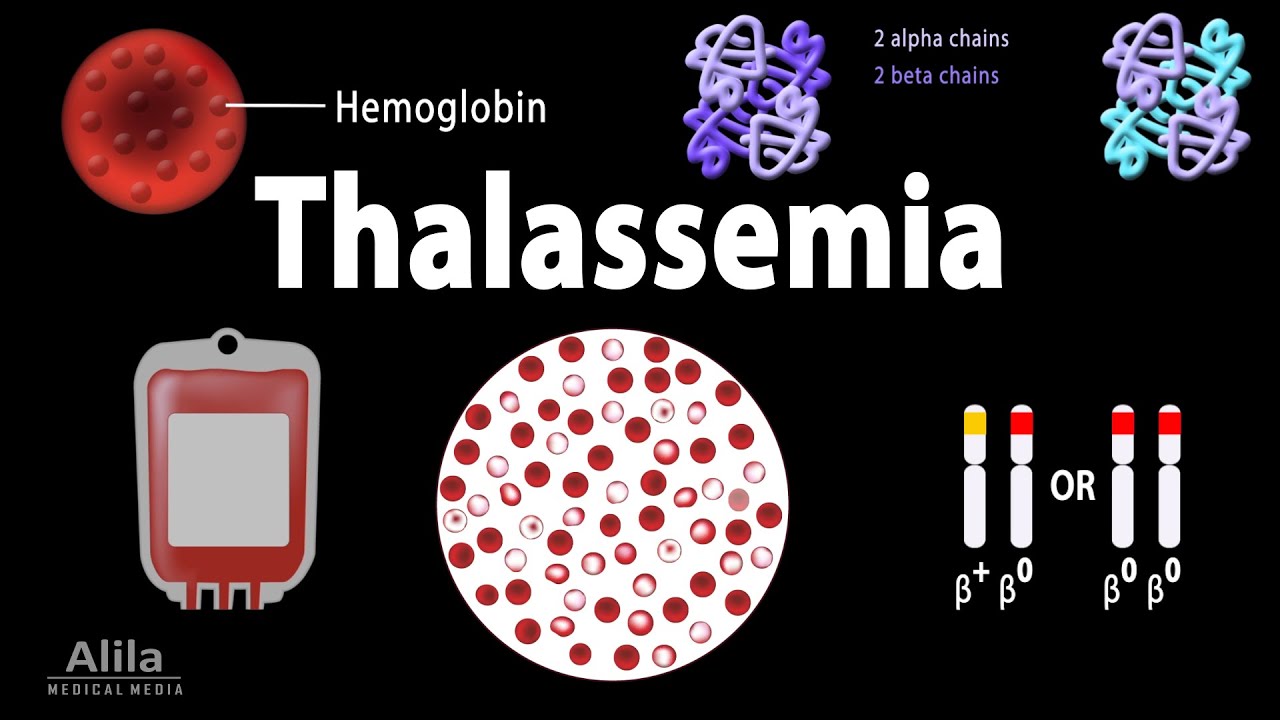
TLDRThis video explains thalassemia, a genetic blood disorder that reduces or stops the production of hemoglobin, leading to anemia. It discusses the different types of thalassemia: Major, Intermedia, and Minor, with a focus on the severe form, Thalassemia Major, which requires lifelong blood transfusions and iron chelation therapy. Early detection through blood screening is crucial for preventing thalassemia in newborns. The video also highlights the importance of genetic counseling and prenatal screening to manage and prevent thalassemia in future generations.
Takeaways
- 😀 Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder that reduces or stops the production of hemoglobin, causing anemia.
- 😀 There are three types of thalassemia: Major, Intermedia, and Minor, each with varying severity.
- 😀 Thalassemia Major is the most severe form, requiring lifelong blood transfusions and iron chelation therapy.
- 😀 The early symptoms of Thalassemia Major include pale skin, jaundice, slow growth, and enlarged liver and spleen.
- 😀 Thalassemia Intermedia is milder and symptoms usually appear in adolescence or adulthood, with occasional blood transfusions needed.
- 😀 Thalassemia Minor, or being a carrier, has no significant symptoms but can be passed to children.
- 😀 Thalassemia is inherited from parents through genes, and if both parents are carriers, there’s a 25% chance the child will have Thalassemia Major.
- 😀 Iron overload is a common complication in Thalassemia Major, requiring iron chelation therapy to prevent organ damage.
- 😀 Bone marrow transplants are the only curative treatment for Thalassemia Major but are not widely available in all countries.
- 😀 Early screening, including blood tests, is essential to detect Thalassemia carriers and diagnose the condition early, ideally before marriage or during school years.
Q & A
What is thalassemia?
-Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder that reduces or stops the production of hemoglobin, causing red blood cells to break apart easily, leading to anemia.
How is thalassemia inherited?
-Thalassemia is inherited through genes from both parents. If both parents are carriers of the thalassemia trait, there is a 50% chance their child will also be a carrier, and a 25% chance the child will have thalassemia major.
What are the three types of thalassemia?
-The three types of thalassemia are thalassemia major, thalassemia intermedia, and thalassemia minor. Thalassemia major is the most severe form, while thalassemia minor is a carrier state with no symptoms.
What are the symptoms of thalassemia major?
-Symptoms of thalassemia major include pallor, yellowing of the skin, lethargy, poor weight gain, and enlargement of the liver and spleen.
When is thalassemia intermedia typically diagnosed?
-Thalassemia intermedia is typically diagnosed during adolescence or adulthood, often showing mild symptoms compared to thalassemia major.
What treatment is required for thalassemia major?
-Treatment for thalassemia major includes regular blood transfusions, medication to reduce iron levels in the body, and potentially a bone marrow transplant, although the latter is not yet available in Indonesia.
Why do patients with thalassemia major need blood transfusions?
-Patients with thalassemia major require blood transfusions to manage their anemia since their bodies are unable to produce enough healthy red blood cells.
What complications can arise from blood transfusions in thalassemia patients?
-Blood transfusions can lead to an excess of iron in the body, which may cause organ damage. This is managed by taking medications that help reduce the excess iron.
How can thalassemia be prevented?
-Thalassemia can be prevented by early screening, especially before marriage or during school-age years, to identify carriers of the thalassemia trait.
What is thalassemia screening?
-Thalassemia screening involves blood tests, including a complete blood count and hemoglobin analysis, to detect whether an individual is normal, a carrier, or affected by thalassemia.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Thalassemia (Problema sa dugo): Types, Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
Thalassemia: Alpha & Beta-Thalassemias, Genetics, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis & Treatment, Animation

Beta-thalassemia - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, pathology

Materi Keperawatan Anak : Asuhan Keperawatan Thalasemia

#PDKT Anemia | Ep.2 Hipokromik Mikrositer

Promosi Kesehatan "Anemia"
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
