BAB 2 Bilangan Bentuk Pecahan | Matematika Dasar | Alternatifa
Summary
TLDRThis video focuses on teaching the fundamental operations of fractions, from understanding proper fractions to performing addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. It explains how to simplify fractions, convert improper fractions to mixed numbers, and adjust denominators for easy addition or subtraction. The video also covers practical examples, such as visualizing fraction operations with pizzas and applying rules for multiplying and dividing fractions. The emphasis is on making fraction concepts easy to understand with logical steps and practical applications, helping learners master these essential math skills.
Takeaways
- 😀 Proper fractions occur when the numerator is smaller than the denominator, like 1/2.
- 😀 Improper fractions occur when the numerator is larger than the denominator, like 17/4.
- 😀 Improper fractions can be converted to mixed fractions, for example, 17/4 becomes 4 1/4.
- 😀 To simplify fractions, find the greatest common divisor (GCD) and divide both the numerator and denominator by it.
- 😀 For example, 4/6 simplifies to 2/3 and 6/10 simplifies to 3/5 by dividing both by 2.
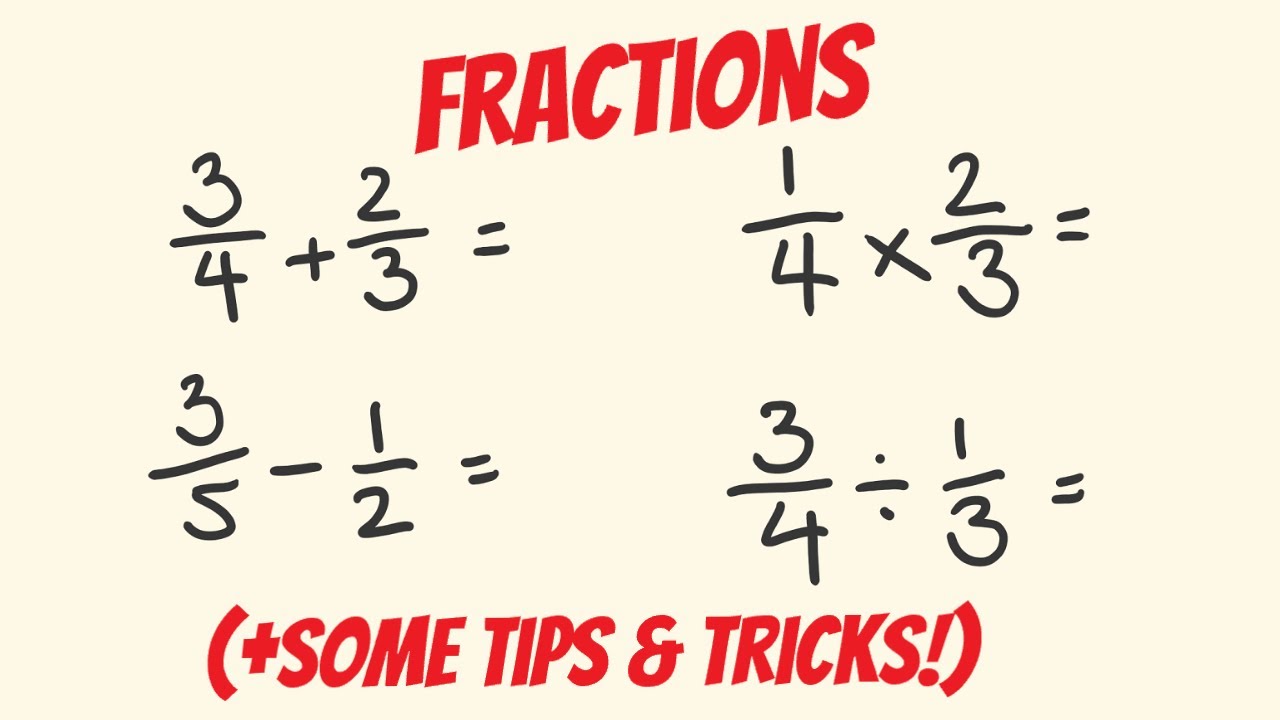
- 😀 Adding or subtracting fractions requires a common denominator to be found first.
- 😀 Example: To add 1/2 + 1/3, the common denominator is 6, resulting in 5/6.
- 😀 Multiplying fractions involves multiplying the numerators and the denominators. For example, 3/5 * 10/12 = 30/60 = 1/2.
- 😀 Dividing fractions involves multiplying by the reciprocal of the second fraction. For example, 3/5 ÷ 7/6 = 3/5 * 6/7 = 18/35.
- 😀 Converting improper fractions to mixed fractions is done by dividing the numerator by the denominator and writing the remainder as a fraction.
- 😀 For example, 10/7 becomes 1 3/7 when converted to a mixed fraction after division.
Q & A
What is a proper fraction?
-A proper fraction is one where the numerator (the number above the fraction line) is smaller than the denominator (the number below the fraction line). This makes it easier to interpret and understand, for example, 1/2.
How do you convert an improper fraction into a mixed fraction?
-To convert an improper fraction into a mixed fraction, divide the numerator by the denominator. For example, 17/4 is divided to get 4 whole parts, with a remainder of 1, so it becomes 4 1/4.
What is the process for simplifying fractions?
-To simplify a fraction, find a common divisor for both the numerator and denominator. For example, for 4/6, both 4 and 6 can be divided by 2, simplifying it to 2/3.
What is the rule for adding fractions with different denominators?
-When adding fractions with different denominators, you first need to find a common denominator. Then, adjust the numerators accordingly before adding the fractions together.
Why is it important to have the same denominator when adding or subtracting fractions?
-Having the same denominator makes it possible to directly compare the fractional parts. It ensures the fractions are in equivalent terms, allowing for easier addition or subtraction.
How do you add fractions like 1/2 and 1/3?
-To add fractions like 1/2 and 1/3, find the least common denominator, which in this case is 6. Adjust the fractions to have the same denominator: 1/2 becomes 3/6 and 1/3 becomes 2/6. Then add the numerators, resulting in 5/6.
How do you multiply fractions?
-To multiply fractions, simply multiply the numerators and denominators. For example, to multiply 3/5 by 10/12, multiply 3 by 10 and 5 by 12, resulting in 30/60, which simplifies to 1/2.
What is the method for dividing fractions?
-To divide fractions, multiply the first fraction by the reciprocal (inverse) of the second fraction. For example, 3/5 divided by 7/6 becomes 3/5 multiplied by 6/7, resulting in 18/35.
How do you handle division of fractions when the denominator is also a fraction?
-When dividing by a fraction, multiply by the reciprocal of that fraction. For example, 10/3 divided by 7/3 becomes 10/3 multiplied by 3/7, simplifying to 10/7.
What is a mixed fraction and when is it used?
-A mixed fraction is a whole number combined with a proper fraction, used when the numerator is greater than the denominator. For example, 10/7 becomes the mixed fraction 1 3/7, which is easier to interpret.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Learn Fractions In 7 min ( Fast Review on How To Deal With Fractions)

Fractions & Decimals - Chapter 2 - Introduction - Class 7
Elementary Mathematics: Module 1(5) - Fractions

MATEMATIKA DASAR ke -3 untuk SD, SMP, SMA

Le quattro operazioni fondamentali con le frazioni
How to Calculate ANY Fraction Easily!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
