What is Total Productive Maintenance | 8 Pillars of TPM | 6 Big Losses | Type of Maintenance
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive guide to Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), explaining its importance in achieving zero unscheduled downtime. It covers the history of TPM, the six major losses in production, and the eight pillars essential for successful TPM implementation. Additionally, it distinguishes TPM from Total Quality Management (TQM) and outlines various maintenance strategies like corrective, preventive, and condition-based maintenance. The video offers practical tips for implementing TPM effectively, emphasizing the importance of expert guidance, adequate resources, and a focused approach on one machine at a time for optimal results.
Takeaways
- 😀 TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) aims to achieve zero unscheduled downtime by focusing on preventive maintenance and ensuring equipment runs when needed.
- 😀 The history of TPM dates back to Japan post-WWII, evolving from an emphasis on preventive maintenance to incorporating autonomous maintenance by line operators.
- 😀 The six big losses that reduce equipment efficiency include equipment failure, setup and adjustments, idling and minor stops, reduced speed, process defects, and startup losses.
- 😀 The eight pillars of TPM provide a structured approach to improvement, including autonomous maintenance, focused improvement, and quality maintenance.
- 😀 TPM and Total Quality Management (TQM) are different approaches; while TQM focuses on product quality, TPM aims to eliminate losses in equipment to ensure efficiency.
- 😀 Four types of maintenance are commonly recognized: corrective, preventive, risk-based, and condition-based maintenance, each targeting different stages of equipment performance.
- 😀 Autonomous maintenance is a key concept where operators take responsibility for daily maintenance tasks, freeing up maintenance workers for more complex tasks.
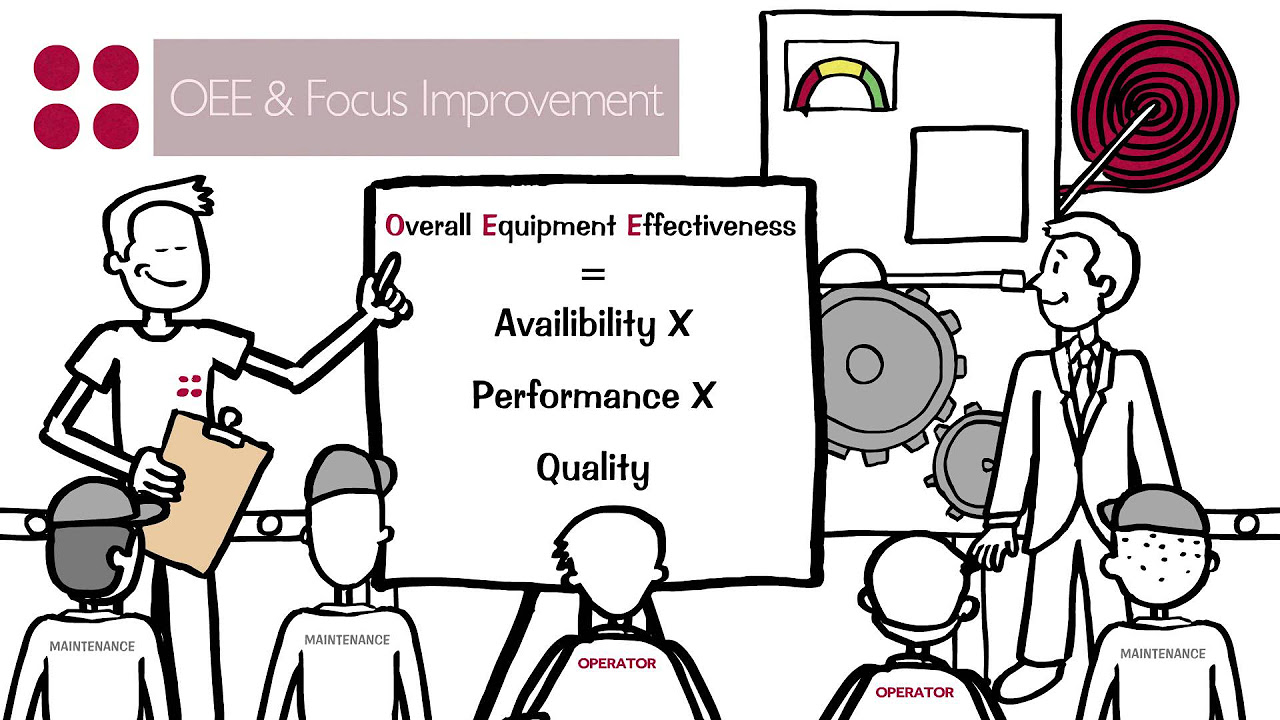
- 😀 The nine-step process for implementing autonomous maintenance includes equipment history analysis, defining OEE, setting priorities, and developing best practices and standards.
- 😀 Practical tips for TPM include being guided by an expert, starting with a single machine, and ensuring adequate resources for maintenance tasks to achieve lasting results.
- 😀 Investing in a comprehensive TPM program can lead to significant economic returns for companies by improving machine productivity and reducing downtime.
Q & A
What is Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)?
-TPM is a methodology aimed at achieving zero unscheduled downtime by ensuring that maintenance is planned, such as preventive maintenance, to keep equipment running efficiently.
Why is TPM important for a company?
-TPM is important because it maximizes production capacity, minimizes unexpected downtime, and ensures that machinery operates effectively, helping to increase overall company profitability.
How does the history of TPM relate to its current practices?
-TPM originated in post-WWII Japan, influenced by American quality management principles. Initially focused on preventive maintenance, it evolved with the introduction of autonomous maintenance and now aims to integrate all aspects of production.
What are the six big losses in TPM?
-The six big losses are: equipment failure, setup and adjustments, idling and minor stops, reduced speed, process defects, and startup losses. These losses must be identified and addressed to improve efficiency.
What is the relationship between TPM and TQM?
-While Total Quality Management (TQM) focuses on improving product quality and customer satisfaction, TPM focuses on eliminating equipment-related losses to improve production efficiency. TPM can support TQM objectives by ensuring that equipment is reliable.
What are the key pillars of TPM?
-The eight pillars of TPM are: autonomous maintenance, focused improvement, planned maintenance, education and training, early management, quality maintenance, safety, health and environment, and office TPM.
What are the different types of maintenance in TPM?
-The four types of maintenance are corrective maintenance (fixing problems as they arise), preventive maintenance (scheduled maintenance to avoid failures), risk-based maintenance (based on risk analysis), and condition-based maintenance (triggered by equipment monitoring).
What is the nine-step process for implementing autonomous maintenance?
-The nine-step process includes: collecting equipment history, defining OEE, assessing six big losses, performing critical assessments, cleaning and inspecting, planning refurbishments, developing asset care routines, creating best practices, and focusing on problem prevention.
How can an organization ensure success when starting TPM?
-Success can be ensured by starting small, focusing on one machine, setting clear goals for OEE, and gradually expanding to other machines after achieving improvements.
What practical tips can help implement TPM effectively?
-Practical tips include being guided by an expert, starting with one machine, planning adequate resources for maintenance, and joining the Lean Community for expert support.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

What is TPM -Total Productive Maintenance ? | 8 TPM pillars Total Productive Maintenance
Four Principles TPM

Four Principles – Lean Manufacturing & TPM

How 7 Companies Mastered TPM (Total Productive Maintenance)

Interview Questions for Maintenance Engineers

#22 Free Lean Six Sigma Green Belt | Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
