LIPOPROTEÍNAS - QUILOMÍCRONS, VLDL, LDL E HDL
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into lipoproteins, explaining their role in transporting and regulating lipid metabolism. It describes the various types of lipoproteins, including VLDL, LDL, and HDL, focusing on their density and function. The script covers how lipoproteins interact with lipids, including triglycerides, cholesterol, and fat-soluble vitamins, and how they impact cardiovascular health. It emphasizes the significance of cholesterol, the process of lipoprotein metabolism, and the risks of excess LDL, which can contribute to atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, it highlights the protective role of HDL in reversing cholesterol buildup in the arteries.
Takeaways
- 😀 Lipoproteins are complexes of proteins and lipids that help transport and regulate lipid metabolism in the body.
- 😀 Cholesterol is 10-30% exogenous (from diet) and 70-90% endogenous (produced by the liver).
- 😀 Lipoproteins transport not only cholesterol but also triglycerides and cholesterol esters.
- 😀 Lipids are non-polar, so they need to be covered by hydrophilic substances (phospholipids and proteins) to be transported in the blood.
- 😀 Lipoproteins are classified by their density: the more lipids they contain, the lower their density.
- 😀 HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) has a high protein-to-lipid ratio and is known for its protective cardiovascular role, helping remove cholesterol from peripheral tissues.
- 😀 VLDL (Very Low-Density Lipoprotein) and LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) both transport cholesterol and lipids, but with different densities and functions.
- 😀 VLDL transforms into LDL after it loses fat, and LDL has a lower lipid content and a higher cholesterol content.
- 😀 LDL is often referred to as 'bad cholesterol' because its excess in the blood can lead to plaque formation in blood vessels, causing atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases.
- 😀 HDL is called 'good cholesterol' because it helps reverse cholesterol transport, removing excess cholesterol from tissues and transporting it back to the liver.
- 😀 Atherosclerosis occurs when LDL accumulates in the arterial walls, forming plaques that lead to inflammation and calcification, potentially causing heart attacks or strokes.
Q & A
What are lipoproteins and what role do they play in the body?
-Lipoproteins are complexes of proteins that help transport and regulate lipid metabolism in the body. They are composed of triglycerides, cholesterol, and cholesterol esters, and sometimes include fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamins A, D, E, and K.
What is the origin of cholesterol in the body?
-Cholesterol comes from both endogenous and exogenous sources. Around 10-30% of cholesterol comes from the diet (exogenous), while 70-90% is produced by the liver (endogenous).
Why are lipoproteins necessary for transporting lipids in the blood?
-Lipoproteins are essential because lipids, being mostly nonpolar, cannot dissolve in water. If lipids were placed directly into the blood, they would aggregate and block blood vessels. Lipoproteins, which have a hydrophilic outer layer of phospholipids and proteins, allow lipids to be transported through the bloodstream without aggregation.
How are lipoproteins classified based on density?
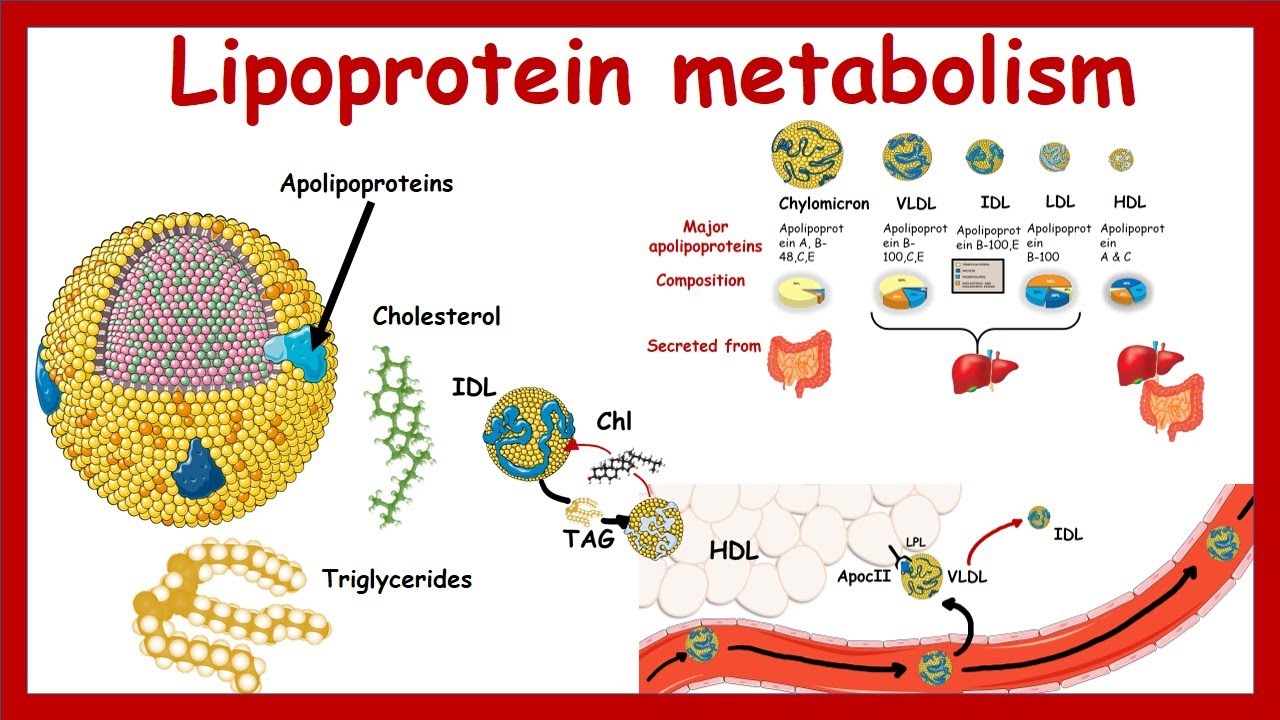
-Lipoproteins are classified based on their density. Those with higher lipid content and lower protein content have lower density, while those with higher protein content and lower lipid content have higher density. For example, VLDL has low density, while HDL has high density.
What is the difference between VLDL and HDL in terms of lipid content?
-VLDL (Very Low-Density Lipoprotein) has a high lipid content and low protein content, whereas HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) has a high protein content and low lipid content, making HDL denser.
What happens to VLDL as it loses lipids?
-As VLDL loses lipids, it transforms into IDL (Intermediate-Density Lipoprotein) and then eventually into LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein). The loss of lipids increases the density of these lipoproteins.
Why is LDL referred to as 'bad cholesterol'?
-LDL is often referred to as 'bad cholesterol' because when it accumulates in excess, it can adhere to the walls of blood vessels, forming plaque and causing inflammation, which can lead to atherosclerosis and increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
What is the function of HDL in the body?
-HDL is referred to as 'good cholesterol' because it helps remove cholesterol from peripheral tissues and transports it back to the liver, thus reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. It essentially slows the formation of plaque in blood vessels.
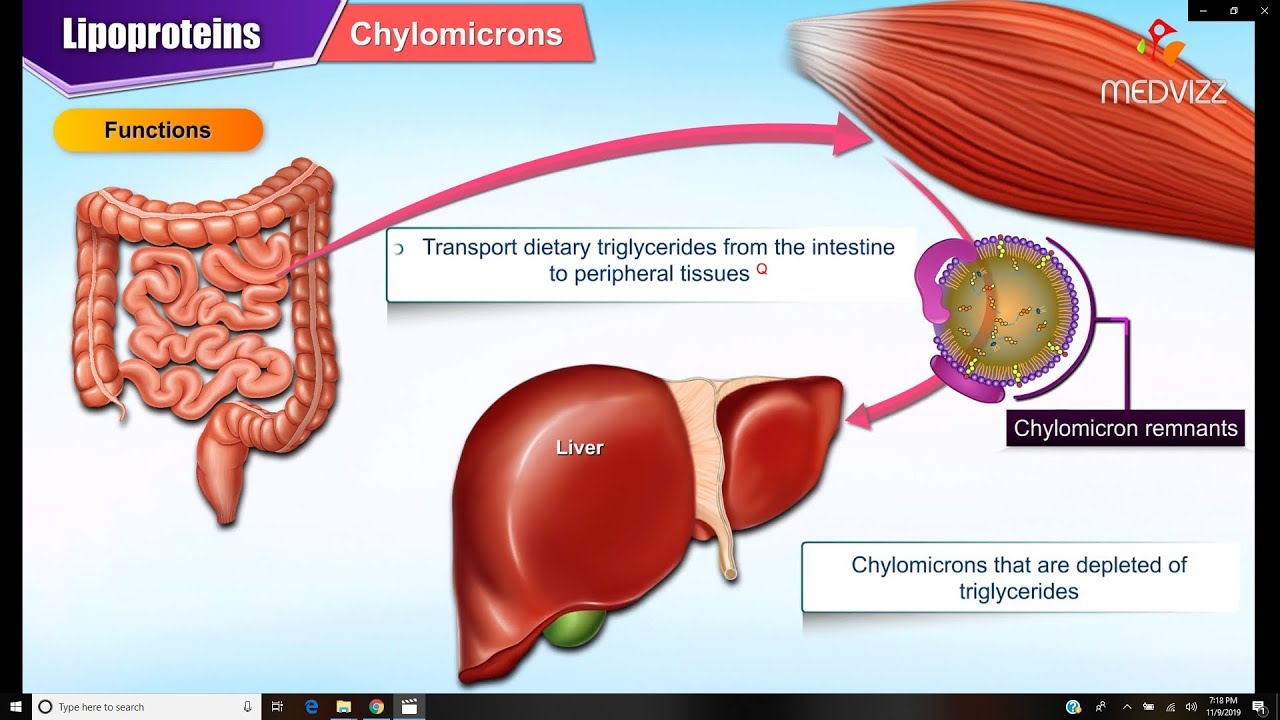
What happens to lipids in the body when we consume fatty foods?
-When we consume fatty foods, the lipids are absorbed in the intestine and transported by chylomicrons to peripheral tissues (like muscle and adipose tissue) for energy storage or use. The lipids in these foods can later be processed by VLDL, which transports them to other tissues.
What is the relationship between dietary fats, cholesterol, and the development of cardiovascular diseases?
-Excessive intake of saturated fats and trans fats can lead to increased LDL levels in the blood. High LDL levels can result in plaque formation in blood vessels, which can lead to atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases like heart attacks and strokes.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Lipids Part 1

22: VLDL, LDL Metabolism | Lipid metabolism | Biochemistry | N'JOY Biochemistry
Lipoprotein metabolism and transport | Chylomicron, VLDL,IDL, LDL,HDL | Metabolism | Biochemistry
Lipoproteins and Apolipoproteins - Structure , function and metabolism : Medical Biochemistry

Kimia Klinik: Analisis Lipid dan Lipoprotein

Konsep Dasar Lipid(Lemak) : Kolesterol, Trigliserida, Fosfolipid
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
