Human Factors Engineering (Ergonomics)
Summary
TLDRHuman factors and ergonomics are two interrelated disciplines that focus on improving the interaction between people and their environments. While ergonomics emphasizes physical stresses and the design of workspaces to match human capacities, human factors takes a broader approach, including psychology and engineering to reduce human error and enhance performance. Originating in World War II, both fields have expanded to improve user-centered design in various industries. Key concepts include intuitive design, affordances, cognitive ability, and the psychological impact of work environments. By applying these principles, we can create systems that improve efficiency, reduce fatigue, and enhance safety.
Takeaways
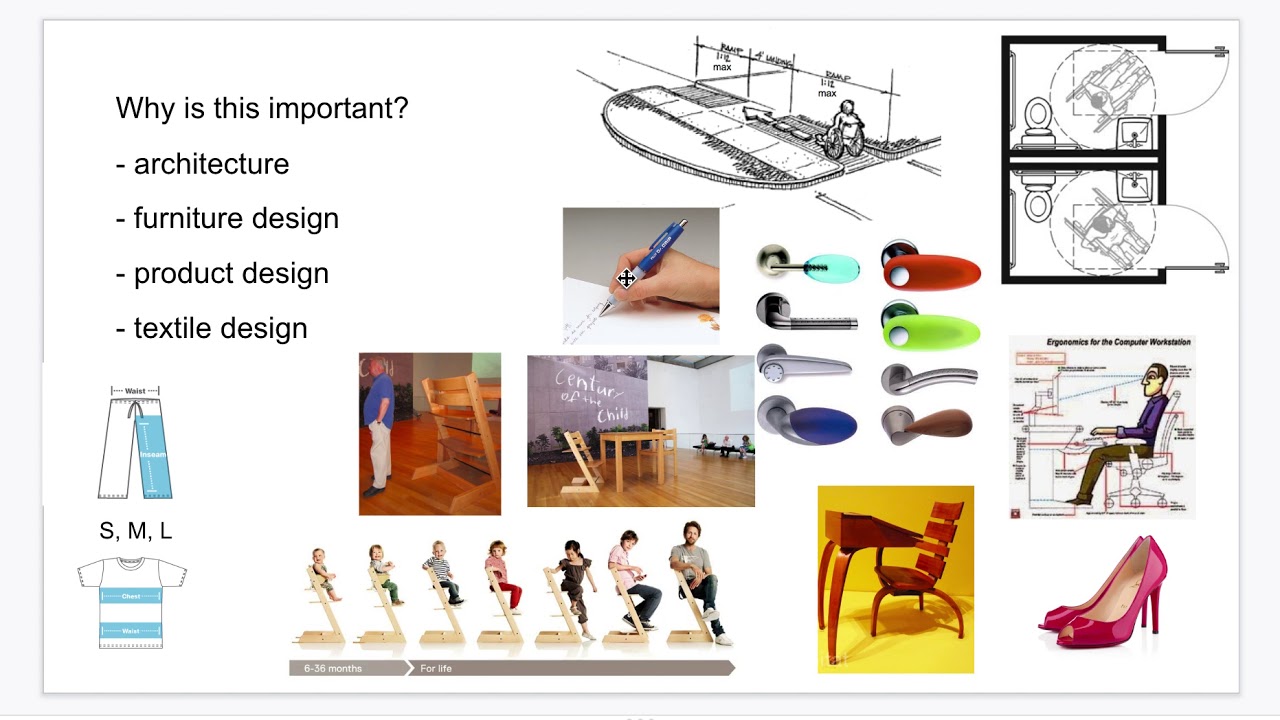
- 😀 Ergonomics focuses on how work affects people, considering physical stresses, environmental factors, and task design.
- 😀 Human factors, while similar to ergonomics, primarily deals with the interaction between humans and machines, focusing on human error reduction and psychological impacts.
- 😀 Ergonomics emphasizes biomechanics and the physiological effects of work, while human factors are more about psychology, decision-making, and perception.
- 😀 The human factors discipline emerged during WWII to improve machine interfaces, particularly in high-stress environments like aircraft controls.
- 😀 Human factors design seeks to reduce human error by creating intuitive and user-friendly interfaces, such as color-coded buttons or clear signage.
- 😀 User-centered design improves usability by adapting systems to fit human needs, which can reduce training time and human errors.
- 😀 Examples of human-centered design can be seen in everyday life, such as websites, parking signs, and online gaming interfaces.
- 😀 Affordances are cues that help users understand how to interact with objects, and incorrect affordances can cause confusion or errors.
- 😀 False affordances are perceived actions that don’t actually function, like placebo buttons in elevators that give the illusion of control.
- 😀 Stimulus-response compatibility and cognitive abilities are key to designing effective user interfaces that align with human expectations and mental capacities.
Q & A
What is the difference between ergonomics and human factors?
-Ergonomics focuses on the interaction between people and their work environments, looking at bodily stresses, work capacities, and physical design to improve comfort and safety. Human factors, on the other hand, focuses more on human behavior in interaction with equipment, psychological and emotional stresses, and aims to reduce human error, often integrating psychology and engineering concepts.
How did human factors emerge as a discipline?
-Human factors emerged during World War II, as countries needed to design machinery that could be operated effectively under stressful conditions. Initially, the focus was on improving productivity and physiological performance. Over time, the discipline expanded to address non-military needs, such as safer work environments and improved quality of life.
What is the key concept of user-centered design?
-The key concept of user-centered design is that systems and interfaces are designed to fit the needs, abilities, and expectations of the user, reducing training time, minimizing human error, and enhancing comfort, safety, and productivity.
Can you provide an example of a well-designed user interface?
-A good example of a user-centered design is the parking signs in Los Angeles, which were simplified into a single sign with clear visual cues (green and red) for parking times, a legend, and a QR code for additional information. This design reduced confusion and made the information more accessible.
How does human factors engineering impact industries like gaming and e-sports?
-In gaming, human factors engineering focuses on designing user interfaces that prioritize the most relevant information, keeping distractions minimal. Effective designs improve gameplay by ensuring players can focus on important data without feeling overwhelmed by excessive or scattered information.
What are some common activities in human factors work?
-Human factors activities include accident investigation, simulation and virtual reality training, occupational and public health and safety research, and the design of consumer products. For example, police training using driving simulations allows officers to practice dangerous scenarios without real-world risk.
What is an affordance in human factors design?
-An affordance is a feature of an object or environment that suggests its intended use. For example, a push bar on a door clearly indicates that the door should be pushed open. It helps users understand how to interact with the object without confusion.
What is a false affordance, and can you give an example?
-A false affordance occurs when an object appears to have a function but doesn't actually perform the intended action. An example is a placebo button, like the 'close door' button in older elevators, which gives the illusion of control but doesn't actually speed up the process.
Why are user stereotypes and expectancies important in human factors design?
-User stereotypes and expectancies influence how people interact with objects based on past experiences. These prior experiences help users anticipate how things should work, improving their efficiency. However, mismatched expectations can lead to errors or confusion if the design doesn't align with users' cognitive assumptions.
How does cognitive ability affect human factors design?
-Cognitive ability affects a person's capacity to multitask, make decisions, and process stimuli. As people age, or when they are under stress, their cognitive abilities can decline, making it harder to perform tasks. Human factors design aims to minimize decision-making demands and accommodate cognitive limitations, especially in high-stress situations.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
T1 Human Factors and Ergonomics - Introduction

[TEKNIK INDUSTRI - EPSK1 - 1] PENGANTAR ERGONOMI DAN FAKTOR MANUSIA

The difference between Urban Planning and Urban Design explained in 100 seconds

ANTHROPOMETRY & ERGONOMICS

PENGENALAN KONSEP INTERAKSI MANUSIA DAN KOMPUTER

Art vs Architecture: Same or Different? (2024)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
