Inside Electric Vehicle Powertrains: A Comprehensive Guide for Engineers
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive exploration of Electric Vehicle (EV) Powertrain Systems, detailing the key components that drive the future of transportation. Hosted by Aliakbar, the journey covers the roles of batteries, electric motors, power electronics, and transmissions, highlighting their design, optimization, and contributions to performance and sustainability. It delves into battery technologies, motor types, regenerative braking, and power flow management. Additionally, the video introduces the Scholars Club, an academic platform that connects students with tutors. The session concludes with an insightful reflection on the evolving landscape of electric vehicles.
Takeaways
- 😀 Electric vehicles (EVs) rely heavily on the efficiency and performance of their powertrain systems, which include the battery, electric motor, power electronics, and transmission.
- 🔋 The battery pack is the heart of an EV, with lithium-ion batteries being the most common due to their high energy density and rechargeability. Solid-state batteries are emerging as a promising alternative.
- 🧠 The Battery Management System (BMS) ensures optimal battery performance by balancing cells, monitoring state of charge (SOC), and managing thermal conditions for safety and efficiency.
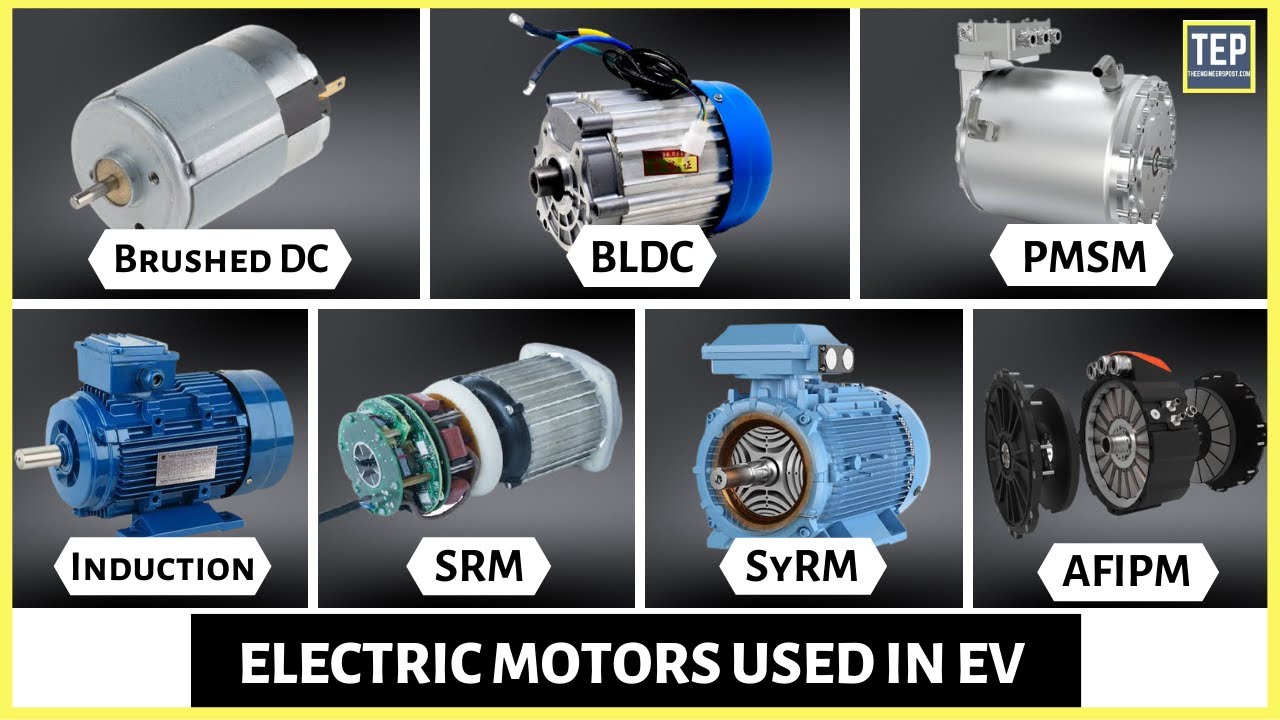
- ⚡ Electric motors in EVs come in different types, such as AC induction motors, permanent magnet motors, and synchronous reluctance motors, each with distinct advantages depending on efficiency, cost, and performance.
- ⚙️ Motor control algorithms manage torque delivery, ensuring smooth acceleration and deceleration, while regenerative braking recovers energy during braking to extend driving range.
- 🔌 Power electronics and inverters convert and control electrical energy between the battery and the motor, optimizing efficiency and performance. Inverters also regulate motor speed and torque.
- 🔄 The DC-DC converter manages different voltage levels in the EV, ensuring that auxiliary systems like lights and air conditioning receive the appropriate power, improving overall efficiency.
- 🚗 EVs commonly use single-speed transmissions, which provide smooth, efficient acceleration. Some performance models use multi-speed transmissions to optimize energy consumption across a wider speed range.
- 🚙 Drivetrain configurations like front-wheel drive (FWD), rear-wheel drive (RWD), and all-wheel drive (AWD) offer distinct advantages in terms of traction, handling, and performance for different driving conditions.
- 🎓 The Scholars Club is a platform designed to help students optimize their academic journey by connecting them with ideal tutors based on their academic needs, using advanced machine learning technology.
Q & A
What are the key components of an electric vehicle's powertrain?
-The key components of an electric vehicle's powertrain include the battery, electric motor, power electronics, and transmission (if applicable). These components work together to create an efficient and seamless electric driving experience.
Why is the Battery Management System (BMS) crucial for electric vehicles?
-The BMS is responsible for monitoring and controlling various parameters of the battery, ensuring its optimum functionality. It balances the battery cells, monitors the state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH), manages thermal conditions, and provides safety features to prevent overcharging, overheating, and other potential hazards.
What are the advantages of solid-state batteries over traditional lithium-ion batteries?
-Solid-state batteries offer increased energy density, faster charging times, and improved safety compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. They are seen as a promising solution to overcome some of the limitations of lithium-ion technology.
How do electric motors in vehicles contribute to performance?
-Electric motors provide precise torque delivery and enable regenerative braking. They come in different types, including AC Induction, Permanent Magnet, and Synchronous Reluctance Motors, each offering unique advantages like higher power density, efficiency, and performance at varying speeds.
What is regenerative braking, and how does it benefit electric vehicles?
-Regenerative braking is a process where the electric motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy into electrical energy during braking. This energy is stored back in the battery, improving overall efficiency and extending the vehicle's driving range.
What role do motor control algorithms play in electric vehicles?
-Motor control algorithms manage the flow of electrical current to the motors, ensuring smooth and precise torque delivery for acceleration. They also regulate energy recovery during regenerative braking and optimize driving modes for performance or efficiency.
How do power electronics and inverters contribute to an electric vehicle's powertrain?
-Power electronics, particularly inverters, convert direct current (DC) from the battery into alternating current (AC) for the electric motor. They control the motor's speed and torque, ensuring efficient energy delivery. Inverters also play a key role in optimizing energy flow during regenerative braking.
What is the function of the DC-DC converter in electric vehicles?
-The DC-DC converter adjusts voltage levels within the vehicle's electrical system, converting high-voltage DC from the battery into lower-voltage DC needed for auxiliary systems like lights, infotainment, and air conditioning. This ensures optimal power distribution and enhances energy efficiency.
What are the different types of transmission systems used in electric vehicles?
-Electric vehicles commonly use single-speed transmissions, which are simple and reduce mechanical losses. Some performance-oriented vehicles use multi-speed transmissions, which offer better power distribution and improved efficiency across a broader range of speeds.
What are the different drivetrain configurations in electric vehicles, and how do they differ?
-The three primary drivetrain configurations in electric vehicles are Front-Wheel Drive (FWD), Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD), and All-Wheel Drive (AWD). FWD is commonly used for urban driving, RWD is favored for performance due to improved handling, and AWD provides superior traction and stability, particularly in challenging conditions.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Electric Heavy-Duty Truck Design: Which E-Powertrain is Better – Direct Motor or Electric Axle? #ev

Electric Vehicles In India: The Complete Breakdown
Types of Motors used in EV | Single, Dual, Three & Four Motor Configuration in EV

EV Electrical Systems BASICS!

World's First Electric Road: Charging EVs While Driving

Latest Advancements in Electric Vehicle Technology Explained And Future EV Technology
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
