Bio 251 Ch 2B
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the four essential organic compounds that make up living organisms: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. These compounds are polymers formed by monomers through dehydration synthesis and broken down by hydrolysis. The video details their structures, functions, and key roles in cellular processes. Carbohydrates provide short-term energy, lipids make up cell membranes and store long-term energy, proteins perform diverse functions, and nucleic acids store genetic information and aid in protein synthesis. The importance of enzymes, protein folding, and denaturation is also highlighted.
Takeaways
- 😀 Carbohydrates are essential for short-term energy storage (e.g., glycogen) and structural support (e.g., cellulose).
- 😀 Dehydration synthesis forms polymers by removing water, while hydrolysis breaks them down by adding water.
- 😀 Lipids, including triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids, play crucial roles in energy storage, cell membrane structure, and hormone production.
- 😀 Phospholipids are amphipathic, having hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads, essential for fluid cell membrane formation.
- 😀 Proteins are made up of amino acids, and their shape determines their function in the body, with four structural levels: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary.
- 😀 Denaturation of proteins, caused by changes in temperature or pH, can lead to loss of function, and can be reversible or irreversible.
- 😀 Enzymes act as catalysts, lowering activation energy to speed up chemical reactions without being consumed in the process.
- 😀 Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, are essential for genetic information storage and protein synthesis, with ATP and GTP also playing a role in energy transfer.
- 😀 DNA is double-stranded and contains thymine, while RNA is single-stranded and contains uracil instead of thymine.
- 😀 The structure and function of proteins are highly dependent on the sequence of amino acids, with even a single incorrect amino acid altering the protein's function (e.g., sickle cell anemia).
Q & A
What are the four main types of organic compounds that make up cells?
-The four main types of organic compounds are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
What is the process through which polymers are formed and broken down?
-Polymers are formed through dehydration synthesis, where a molecule of water is removed, and they are broken down by hydrolysis, where water is added to break the bond.
What is the main function of carbohydrates in the human body?
-Carbohydrates primarily serve as short-term energy storage, with glycogen being the main energy storage molecule in the body.
How do saturated and unsaturated fats differ in terms of their molecular structure?
-Saturated fats have a molecule structure where all carbon atoms are fully saturated with hydrogen, making the chain straight. Unsaturated fats have at least one double bond, which causes a kink in the chain.
Why is the structure of a phospholipid important for cell membranes?
-Phospholipids have hydrophobic tails and a hydrophilic head, which makes them amphipathic. This property is essential for forming the fluid structure of cell membranes, allowing selective permeability.
What are the monomers of proteins, and what is their role in protein function?
-The monomers of proteins are amino acids. They are linked together by peptide bonds, and their specific sequence determines the protein’s structure and function.
What is the significance of the primary structure of a protein?
-The primary structure of a protein refers to the specific sequence of amino acids. This sequence is crucial because a single change in the amino acid sequence can drastically affect the protein’s function, such as in diseases like sickle cell anemia.
What is the role of enzymes in chemical reactions, and how do they function?
-Enzymes act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to proceed. They are not consumed in the reaction and are highly specific for their substrates.
What distinguishes DNA from RNA in terms of structure and function?
-DNA is double-stranded and stores genetic information, while RNA is single-stranded and plays a role in protein synthesis. Additionally, RNA contains uracil instead of thymine, which is found in DNA.
How does denaturation affect protein function, and is it always reversible?
-Denaturation involves the loss of a protein’s 3D structure, which affects its function. It can be reversible under some conditions, but in many cases, such as with egg whites, it is irreversible and the protein will not regain its functional shape.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
Organic Compounds | Grade 9 Science Quarter 2 WEEK 6 | DepEd MELC-based

S9Q2W6 | ORGANIC COMPOUNDS: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins & Nucleic Acid

Beginners Guide to MACROMOLECULES

Overview of Organic Compounds

Βιολογία Γ΄ Γυμνασίου | 1.1 Τα μόρια της ζωής| Μαθαίνω πώς να Μαθαίνω | ⭐ 1o Βήμα
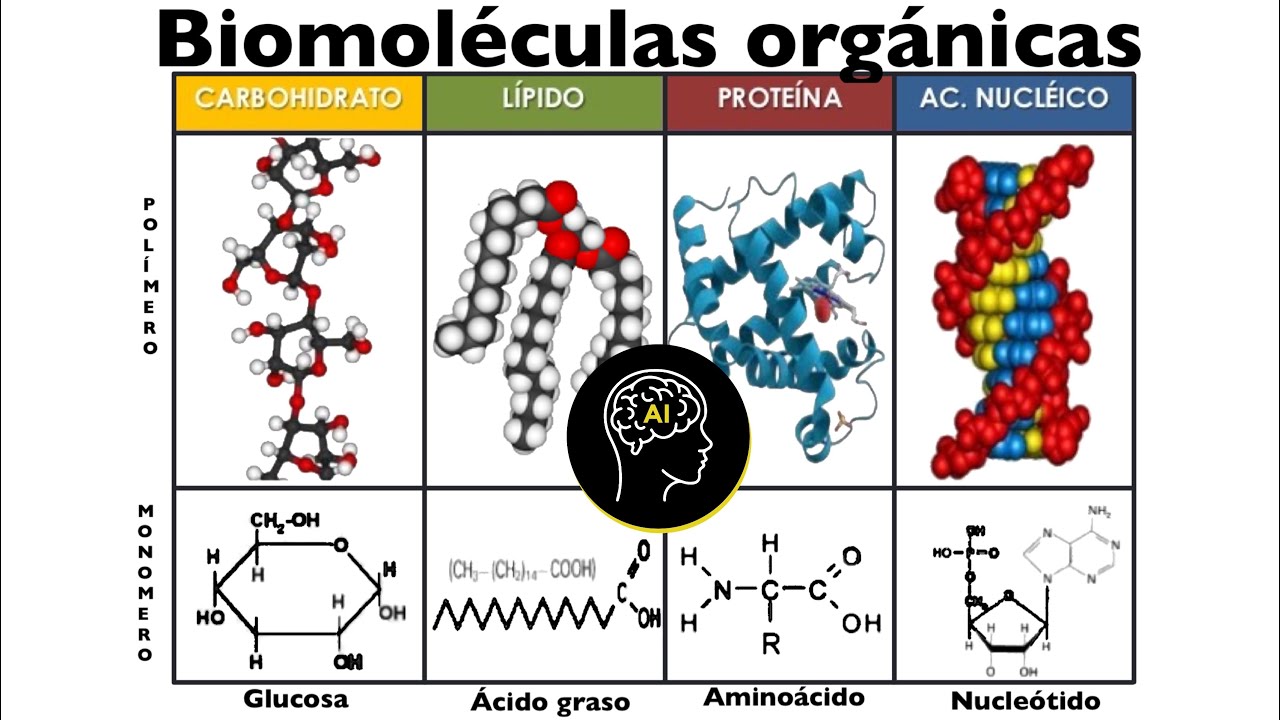
Biomoléculas presentes en células (orgánicas): carbohidratos, lípidos, proteínas y ácidos nucleicos
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
