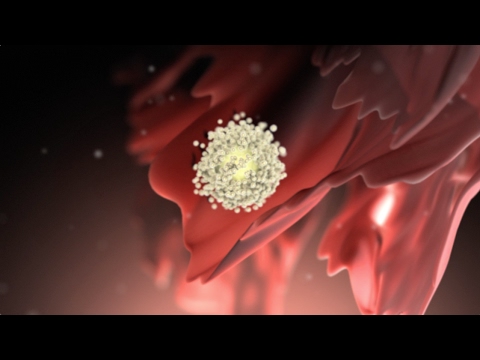
Ovulation
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the menstrual cycle, starting with ovulation when a mature egg is released from the ovary. The process begins with several follicles growing and producing estrogen, which prepares the uterus for pregnancy. Only one follicle becomes dominant and continues to grow, secreting more estrogen, which triggers a surge of luteinizing hormone from the pituitary gland. This causes the follicle to burst open, releasing the egg into the fallopian tube. If fertilization doesn’t occur, the egg disintegrates and is shed with the uterine lining during menstruation, marking the start of a new cycle.
Takeaways
- 😀 Ovulation marks the release of a ripe egg from the ovary, starting the reproductive cycle.
- 😀 The ovary contains hundreds of thousands of follicles, each housing an immature egg.
- 😀 The 28-day menstrual cycle begins with the first day of menstrual bleeding.
- 😀 During the first 7 days of the cycle, a few follicles start growing and release estrogen to prepare the uterus for pregnancy.
- 😀 By Day 7, all follicles except one stop growing, and the dominant follicle continues to grow and nourish the egg.
- 😀 On Day 12, the dominant follicle secretes a surge of estrogen, triggering the pituitary gland to release luteinizing hormone.
- 😀 Luteinizing hormone causes the dominant follicle to undergo a growth spurt around Day 14.
- 😀 Just before ovulation, the egg detaches from the follicle, and the follicle bursts open, releasing the ovum into the abdominal cavity.
- 😀 The fallopian tube's fimbriae sweep across the ovulation site, capturing the ovum and guiding it toward the uterus.
- 😀 The ovum can be fertilized within 12-24 hours after ovulation; if not fertilized, it disintegrates and is shed during menstruation.
Q & A
What is ovulation and how does it occur?
-Ovulation is the release of a mature egg, or ovum, from the ovary. It occurs when a dominant follicle in the ovary undergoes a sudden growth spurt due to the release of luteinizing hormone, causing the follicle to burst open and release the egg.
What happens during the first 7 days of the menstrual cycle?
-During the first 7 days of the menstrual cycle, a few follicles in the ovaries start to grow. These growing follicles secrete estrogen, which helps prepare the uterine lining for a possible pregnancy.
Why do most follicles stop growing during the menstrual cycle?
-Around Day 7 of the cycle, most of the follicles stop growing and begin to degenerate, except for one dominant follicle. This dominant follicle continues to grow and nourish the developing egg inside.
How does estrogen influence the menstrual cycle?
-Estrogen, produced by the growing follicles, is released into the bloodstream to prepare the uterus for pregnancy. Around Day 12, a surge in estrogen signals the pituitary gland to release luteinizing hormone, triggering the final stages of follicle maturation.
What role does luteinizing hormone (LH) play in ovulation?
-Luteinizing hormone (LH) causes the dominant follicle to undergo a growth spurt around Day 14, leading to the rupture of the follicle and the release of the egg during ovulation.
What is the function of the fimbriae during ovulation?
-The fimbriae, tiny finger-like projections at the end of the fallopian tube, move in closer to the ovulation site and help capture the released egg. They guide the egg into the fallopian tube through microscopic cilia.
How does the egg travel to the uterus after ovulation?
-After ovulation, the egg is guided by the fimbriae into the fallopian tube, where muscular contractions gently propel it toward the uterus.
How long can an egg survive after ovulation?
-The egg survives for 12-24 hours after ovulation, during which fertilization may occur if sperm is present.
What happens if the egg is not fertilized?
-If the egg is not fertilized within 12-24 hours, it disintegrates and is shed along with the uterine lining during menstruation, marking the end of one reproductive cycle and the beginning of another.
How does the menstrual cycle begin?
-The menstrual cycle begins on the first day of menstrual bleeding, signaling the start of a new cycle where ovulation and other reproductive processes will take place.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)