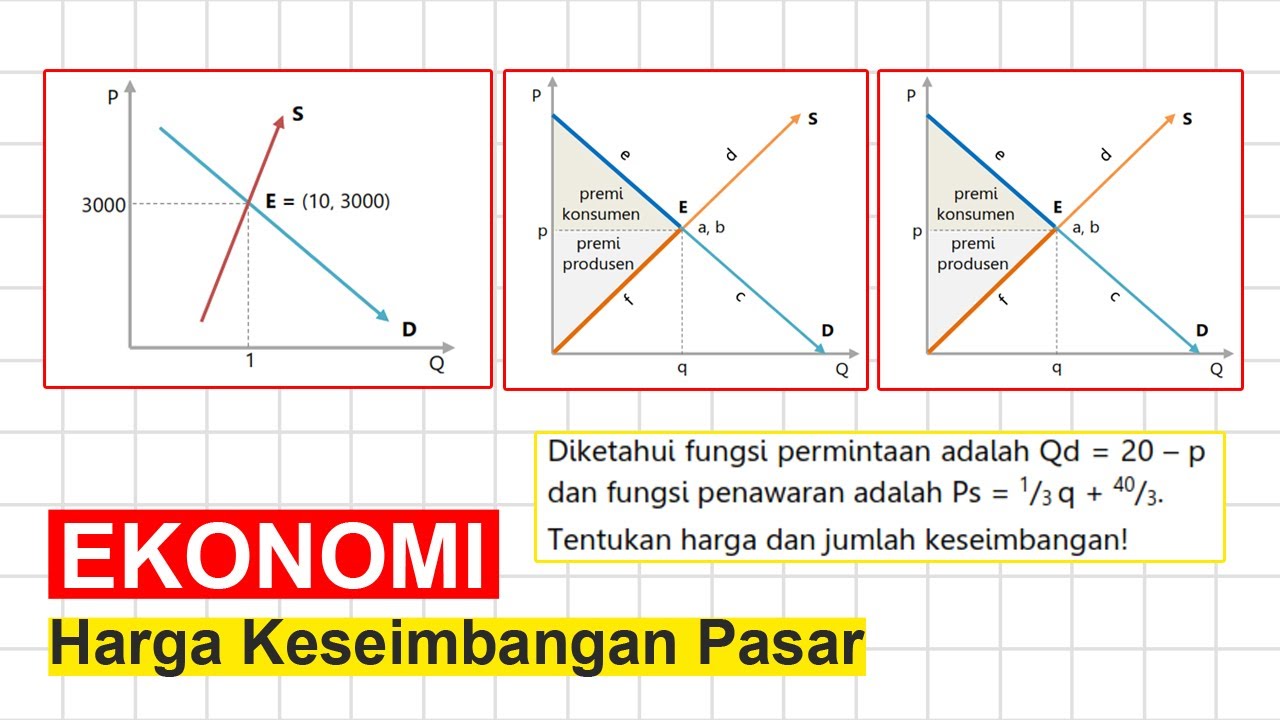
Proses Terbentuknya Harga Pasar | Ekonomi Kelas X - KHATULISTIWA MENGAJAR
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of a market, highlighting the interaction between buyers and sellers in both traditional and modern settings. It introduces key economic terms like demand and supply, showcasing a negotiation scenario over fruit prices. The video explains how the equilibrium price is formed when the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied, and how fluctuations in price can lead to surplus demand or supply. The ultimate goal of achieving a balanced market price is to ensure fairness for both consumers and producers.
Takeaways
- 😀 A market is a place where buyers and sellers meet to exchange goods or services.
- 😀 Buyers usually seek the lowest possible price for a product, while sellers aim to sell at the highest price.
- 😀 The negotiation between the buyer and seller results in an agreed price, also known as the market price.
- 😀 Price equilibrium, or the market equilibrium price, is the point where supply and demand balance each other.
- 😀 When the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied at a certain price, market equilibrium is achieved.
- 😀 If the market price is too low, demand will exceed supply, leading to a shortage of goods.
- 😀 If the market price is too high, supply will exceed demand, leading to a surplus of goods.
- 😀 Market equilibrium ensures that both buyers can purchase goods fairly and sellers can make a profit.
- 😀 The price at which demand and supply meet is called the equilibrium price (Pe).
- 😀 Understanding supply and demand curves helps visualize how equilibrium price is reached in a market.
- 😀 A well-balanced market ensures fairness, where no party (buyer or seller) is at a disadvantage.
Q & A
What is a market?
-A market is a place where buyers and sellers come together to engage in the buying and selling of goods or services, whether it is a traditional or modern market.
What is the relationship between supply and demand in a market?
-In a market, supply refers to the quantity of goods or services that sellers are willing to offer, while demand refers to the quantity that buyers are willing to purchase. The interaction between supply and demand determines the market price.
What does 'price equilibrium' or 'market price' mean?
-Price equilibrium, or market price, is the price at which the quantity of goods demanded by buyers equals the quantity supplied by sellers, leading to a balance in the market.
How does price influence the demand and supply of goods?
-When the price is low, demand increases because buyers want to purchase more at a lower cost, but sellers may supply less because of lower profits. When the price is high, demand decreases while supply increases as sellers aim for higher profits.
What happens if the price is below the equilibrium price?
-If the price is below the equilibrium price, there will be excess demand, meaning more buyers want to purchase the product than there are goods available, leading to a shortage.
What happens if the price is above the equilibrium price?
-If the price is above the equilibrium price, there will be excess supply, meaning there will be more goods available than what buyers are willing to purchase, resulting in a surplus.
What is the significance of the point where the demand and supply curves intersect?
-The intersection of the demand and supply curves represents the equilibrium point, where the price and quantity of goods are balanced, and there is no surplus or shortage.
Why is price equilibrium important for buyers and sellers?
-Price equilibrium ensures that buyers can purchase goods at a fair price, and sellers or producers can still make a profit. It helps avoid market imbalances that could negatively affect either side.
How does a buyer's position in a market influence their actions?
-As a buyer, a person typically wants to negotiate a lower price, especially when demand exceeds supply. This is done to ensure they get the best deal possible.
What role does negotiation play in determining market price?
-Negotiation between buyers and sellers is crucial in determining the final market price. Through bargaining, both sides may agree on a price that reflects their respective interests, ultimately reaching the equilibrium price.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)