Pemeriksaan Kadar Air Tanah
Summary
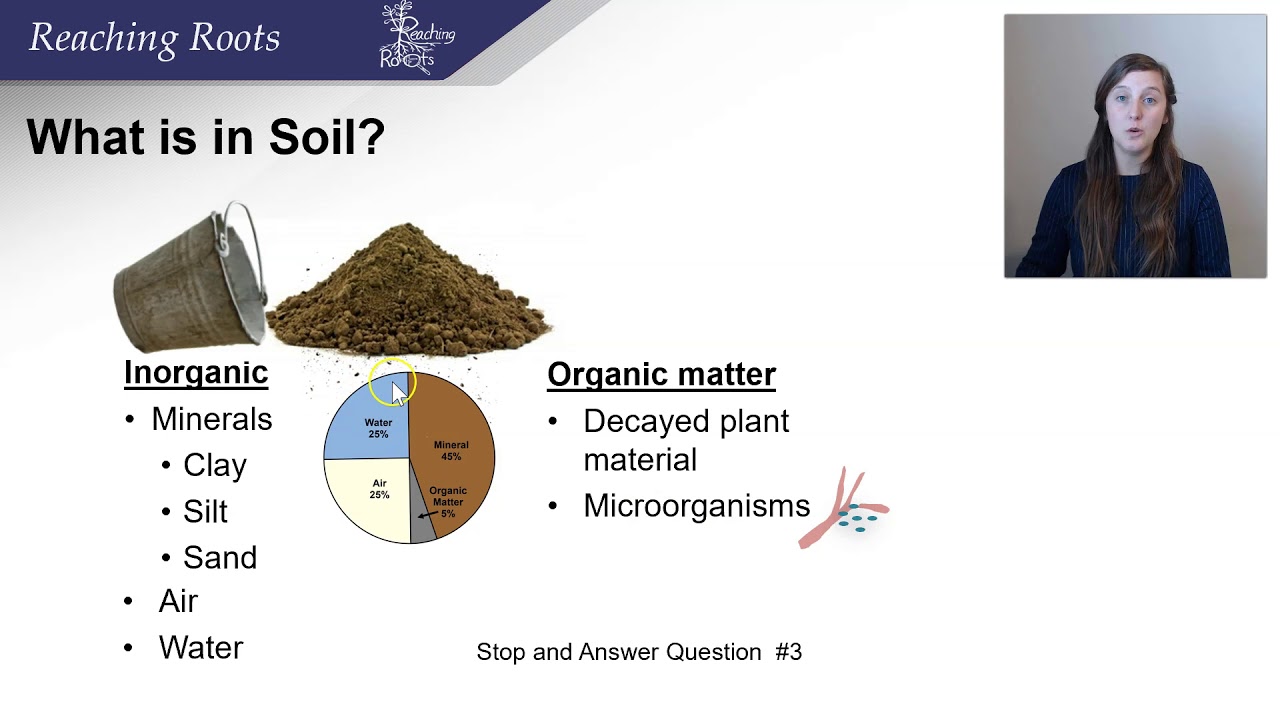
TLDRThis video explains the concept of water content in soil (*kadar air*), a crucial measurement for various applications in agriculture and engineering. It covers the conditions of wet and dry soil, detailing the soil's three phases: solid, liquid, and gas. The process of measuring water content involves weighing a soil sample before and after drying, calculating the amount of water present. The video walks through the calculation method using an example, showing how to determine the percentage of water in soil samples and explaining the significance of this measurement in practical scenarios.
Takeaways
- 😀 Understanding water content in soil is essential for various practical applications in civil engineering and land analysis.
- 😀 Water content in soil can be categorized based on two conditions: wet soil and dry soil.
- 😀 Wet soil contains both water and air in its pores, while dry soil lacks water, with only air present in the pores.
- 😀 To measure water content, the weight of the soil sample is compared before and after drying.
- 😀 The purpose of determining water content is to know how much water is present in the soil, which is important for both lab work and real-world applications.
- 😀 The calculation of water content in soil involves determining the mass of water compared to the mass of solid soil.
- 😀 Water content can be expressed as a percentage, which indicates how much water is present in the soil compared to its solid mass.
- 😀 A practical experiment to measure water content involves drying the soil sample for 24 hours to ensure as much water as possible is removed.
- 😀 Calculations for water content involve using the formula: (Weight of Water / Weight of Solid Soil) * 100%.
- 😀 Multiple soil samples (usually three) should be taken to ensure the results are representative and accurate, reducing potential errors in the water content measurement.
Q & A
What is the purpose of determining the water content in soil?
-The purpose of determining the water content in soil is to understand how much water is present within the soil and its influence on the soil's properties, which is important for various practical applications like civil engineering and land management.
What are the two conditions of soil mentioned in the script?
-The two conditions of soil mentioned are wet soil and dry soil. Wet soil contains water, while dry soil has lost its moisture.
What causes soil to be wet, as described in the video?
-Soil becomes wet because it contains water in its pore spaces, along with air and solid particles. This moisture is present within the soil structure, and it can be absorbed or released depending on external conditions.
How can the water content of soil be measured?
-The water content of soil can be measured by comparing the weight of the soil before and after it is dried. This is done by drying the soil sample for 24 hours to remove the water, and then calculating the water content as a percentage of the dry weight.
Why is it necessary to dry the soil sample for 24 hours?
-The soil sample is dried for 24 hours to ensure that it is as close to completely dry as possible. Although it might not be 100% dry, 24 hours provides a sufficient period to remove most of the moisture.
What is the role of the container in measuring the water content?
-The container holds the soil sample during the drying process. Its weight is accounted for in the calculation to determine the mass of the soil and the water within it, ensuring that the weight of the container does not affect the results.
What formula is used to calculate the water content in the soil?
-The formula used to calculate the water content is: (Weight of wet soil + container) - (Weight of dry soil + container) ÷ (Weight of dry soil) × 100%. This gives the percentage of water content relative to the dry weight of the soil.
Why is it recommended to take multiple soil samples for water content testing?
-It is recommended to take multiple soil samples because a single sample may not be representative of the entire soil's water content. By averaging the results of several samples, the measurement becomes more accurate and reliable.
What are the results of the water content calculation for the three soil samples?
-The water content calculations for the three soil samples resulted in values of 11.30%, 12.80%, and 11.20%, which were then averaged to give a final water content of 11.80%.
What does the term 'water content' mean in the context of the soil?
-In this context, 'water content' refers to the percentage of water present in the soil compared to the dry weight of the soil. It indicates how much moisture is in the soil at the time of testing.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)