wan haliza stats interview
Summary
TLDRThis research focuses on exploring the properties and applications of low-dimensional materials, which are created by reducing the dimensionality of materials from 3D to 2D, 1D, or 0D. Such changes impact the material's electronic and optical properties, including the energy bandgap, and are explained by quantum mechanics. By controlling the size and structure, researchers can engineer materials with desired properties for applications such as nano-generators, hydrogen production, and various biological uses. The ultimate goal is to harness these materials for new technologies and devices, offering exciting possibilities for energy production and other innovations.
Takeaways
- 😀 Low-dimensional materials exhibit unique properties when their dimensions are reduced from 3D to 2D, 1D, and even 0D.
- 😀 The reduction in material size causes a change in its energy band gap, affecting its electronic and optical properties.
- 😀 Quantum mechanics can explain how the reduction in dimensionality impacts material properties like conductivity and color.
- 😀 Materials in 2D (like sheets) or 1D (like wires) display distinct behavior compared to their 3D counterparts.
- 😀 When materials are reduced to 0D, their motion is confined in all directions, resulting in a crystalline form.
- 😀 The motivation for researching low-dimensional materials is their potential to create new technologies and devices with customized properties.
- 😀 The energy band gap of a material increases as its size decreases, leading to changes in its color and other characteristics.
- 😀 By controlling the size of low-dimensional materials, researchers can tailor their properties for specific applications.
- 😀 Real-world applications of low-dimensional materials include nano-generators, energy production, and catalysis.
- 😀 The synthesis and exploration of low-dimensional materials are key activities in advancing new technologies and materials science.
- 😀 One example of a successful product made from these materials is a nano-generator that can extract energy from low-dimensional materials.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the research discussed in the transcript?
-The primary focus of the research is to produce scientific knowledge and develop new technologies related to low-dimensional materials. The aim is to explore how reducing the dimensions of materials affects their properties and potential applications.
How is the dimensionality of materials defined in the research?
-Dimensionality refers to the number of directions in which particles can move freely. Materials are categorized based on their dimensionality: 3D (bulk), 2D (sheet-like), 1D (wire-like), and 0D (crystals with no extended structure).
What happens to the properties of a material when its dimensions are reduced?
-When the dimensions of a material are reduced, its properties change significantly. For example, the energy band gap increases, and the material's color may change, leading to new and more interesting applications due to these altered properties.
What is meant by the 'energy band gap' in this context?
-The energy band gap refers to the difference in energy between the valence band and the conduction band in a material. Reducing the size of the material increases the energy band gap, which can affect its electrical and optical properties.
How does quantum mechanics explain the changes in material properties?
-Quantum mechanics explains these changes through quantum size effects. As the material's size decreases, the movement of particles becomes more restricted, leading to changes in energy levels and other properties. This allows for better control over the material's behavior.
Why is it important to control the size of low-dimensional materials?
-Controlling the size of low-dimensional materials is crucial because it directly influences their properties. By manipulating the size, researchers can engineer materials with desired characteristics for specific applications.
What are some potential applications of low-dimensional materials?
-Low-dimensional materials have numerous potential applications, including in nano-generators, energy production (such as hydrogen generation), catalysis, and as components in electronic devices. These applications benefit from the unique properties that emerge at smaller dimensions.
What are nano-generators and how do low-dimensional materials play a role?
-Nano-generators are devices that harvest energy from small mechanical vibrations or movements. Low-dimensional materials can be used to build these generators, enabling efficient energy extraction from nanoscale motions.
How can low-dimensional materials be used in energy production?
-Low-dimensional materials can be used in energy production, particularly in hydrogen generation. These materials can assist in breaking down compounds to produce hydrogen, which is a clean energy source for electricity generation and fuel cells.
What is the impact of reducing material dimensions from 3D to 1D or 0D?
-Reducing the material dimensions from 3D to 1D or 0D results in changes to the material's behavior, including quantization of particle movement. In 1D, particles are confined to move in only one direction, while in 0D, they are restricted in all three directions, resulting in unique electronic and optical properties.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

The chemistry of Metal-Organic Frameworks -MOFs- (ICMol)
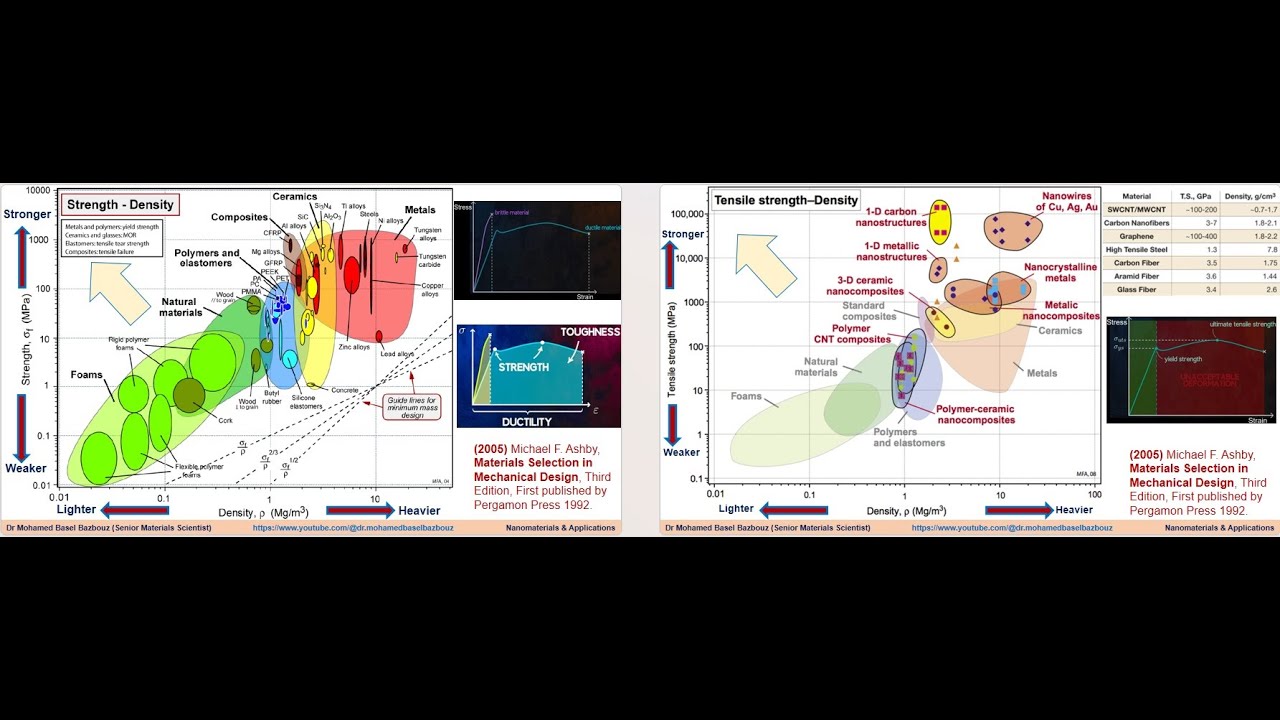
Ashby plots of Strength versus density for materials and nanomaterials المتانة والوزن النوعي

【宇宙の謎】次元とは一体何なのか!?
These Nanostructures Are Hacking Nature

Bahan, Alat, dan Teknik berkarya seni rupa 3 dimensi ( Video Pembelajaran Seni Budaya )

The 3D Filament Tier List! Which Should YOU Use?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
