EKN 1 1 FIN
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson, Yulinar, the economics teacher, introduces the concept of market equilibrium, which represents the agreed-upon price between sellers and buyers for a specific product or service. The lesson explores key concepts such as demand, supply, price elasticity, and market equilibrium calculation. It also looks at the effects of taxes and subsidies on prices, different market types, and real-life price phenomena. Students will engage in fieldwork, interviewing market participants to observe price changes leading up to holidays, and then report their findings in an article for a website. The lesson aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of economic principles.
Takeaways
- 😀 The lesson is about 'Market Equilibrium', focusing on the agreement between buyers and sellers on price and quantity for a product or service.
- 😀 Students will explore key economic concepts, including demand, supply, price elasticity, and market equilibrium.
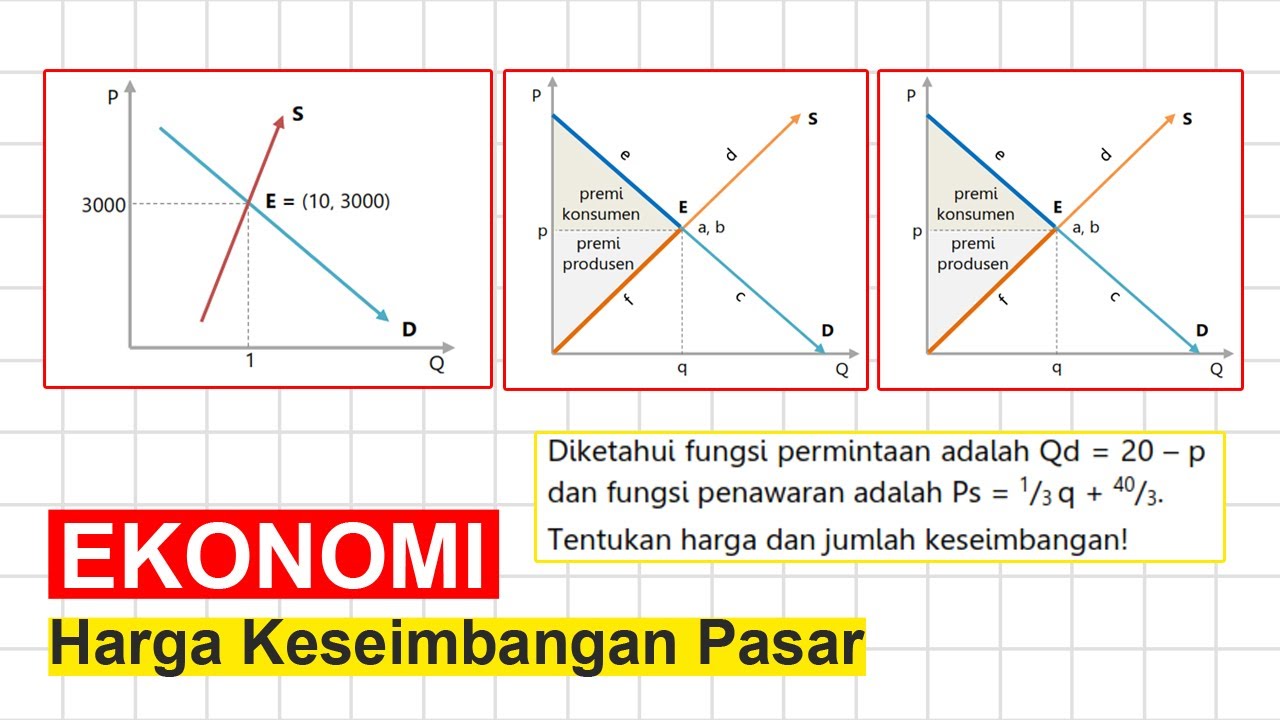
- 😀 The script introduces the concept of market equilibrium, which is where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded at a specific price.
- 😀 The lesson will cover how price fluctuations occur in the market and the factors affecting those changes.
- 😀 Topics like the impact of taxes and subsidies on market equilibrium will be discussed in-depth.
- 😀 Students will analyze different types of markets and how they function in terms of price determination.
- 😀 The course will involve practical activities like observing and interviewing economic actors in local traditional markets.
- 😀 Students will explore real-world examples of price changes, especially around major holidays.
- 😀 At the end of the lesson, students will write an article based on their observations and interviews, to be published on a website.
- 😀 The teacher encourages students to follow the entire learning process to ensure a complete understanding of the subject matter, ensuring success in their final task.
Q & A
What is market equilibrium?
-Market equilibrium is the point of agreement between sellers and buyers regarding the price of a product or service, where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded at a specific price level.
How do transactions like shopping or using online services relate to the concept of market equilibrium?
-Transactions such as shopping in markets, paying for online services, or assisting in store operations are all examples of buying and selling activities, which are part of the larger economic process that influences market equilibrium and price determination.
Why do product prices fluctuate?
-Product prices fluctuate due to various factors, including changes in supply and demand, production costs, market competition, and external influences like government policies or global events.
What are the key concepts involved in understanding market equilibrium?
-The key concepts include demand, supply, price elasticity, the calculation of market equilibrium, the effects of taxes and subsidies on equilibrium, types of markets, and the analysis of price phenomena in real-world scenarios.
What is the relationship between demand and supply in determining market prices?
-Market prices are determined by the interaction of demand and supply. When demand increases and supply remains constant, prices tend to rise. Conversely, when supply increases and demand stays the same, prices usually decrease.
What is price elasticity, and how does it affect market equilibrium?
-Price elasticity refers to the sensitivity of the quantity demanded or supplied to changes in price. If demand is elastic, a small price change can lead to a large change in quantity demanded. This influences how markets adjust to achieve equilibrium.
What role do taxes and subsidies play in market equilibrium?
-Taxes and subsidies can shift the supply and demand curves. Taxes tend to decrease supply by raising production costs, leading to higher prices. Subsidies, on the other hand, lower costs and increase supply, potentially lowering prices.
How do different types of markets affect the concept of equilibrium?
-Different market structures, such as perfect competition, monopolies, and oligopolies, affect how prices are set and how market equilibrium is reached. In competitive markets, prices tend to adjust more freely, while in monopolistic markets, a single seller may control pricing.
What is the significance of observing price changes around major holidays?
-Observing price changes around major holidays helps understand how seasonal demand affects prices. For example, during holidays like Ramadan or Christmas, demand for certain goods may increase, causing price fluctuations as suppliers adjust to meet consumer needs.
What is the final outcome expected from studying market equilibrium in this lesson?
-The final outcome is for students to conduct an observation and interview with market participants in traditional markets about price changes before major holidays. The findings will be compiled into an article, offering real-world insight into the dynamics of market equilibrium.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)