Lipídeos | Compostos Orgânicos | Prof. Paulo Jubilut
Summary
TLDRThis educational script provides an in-depth look at lipids, exploring their types, structures, and biological functions. It covers key lipid groups like triglycerides, phospholipids, sterols, and carotenoids, highlighting their roles in energy storage, cell membrane formation, hormone regulation, insulation, and protection. The transcript also contrasts saturated and unsaturated fats, explaining their impact on health, and dives into the significance of cholesterol and trans fats. Overall, it offers a comprehensive overview of lipids, emphasizing their vital importance in both plant and animal biology.
Takeaways
- 😀 The cachalote (sperm whale) has a unique fatty organ called the basset in its head, which helps regulate its buoyancy by changing the consistency of the oil inside it.
- 😀 Lipids are organic compounds that are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents like alcohol and ether. They are primarily made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
- 😀 Unlike carbohydrates and proteins, lipids are not polymers; they consist of individual molecules that serve various biological functions.
- 😀 The main function of lipids is energy storage, with fats and oils being used by both plants and animals for this purpose.
- 😀 Phospholipids play a crucial role in the formation of cell membranes, with their amphipathic nature (hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads) allowing them to create bilayers that separate water-soluble environments.
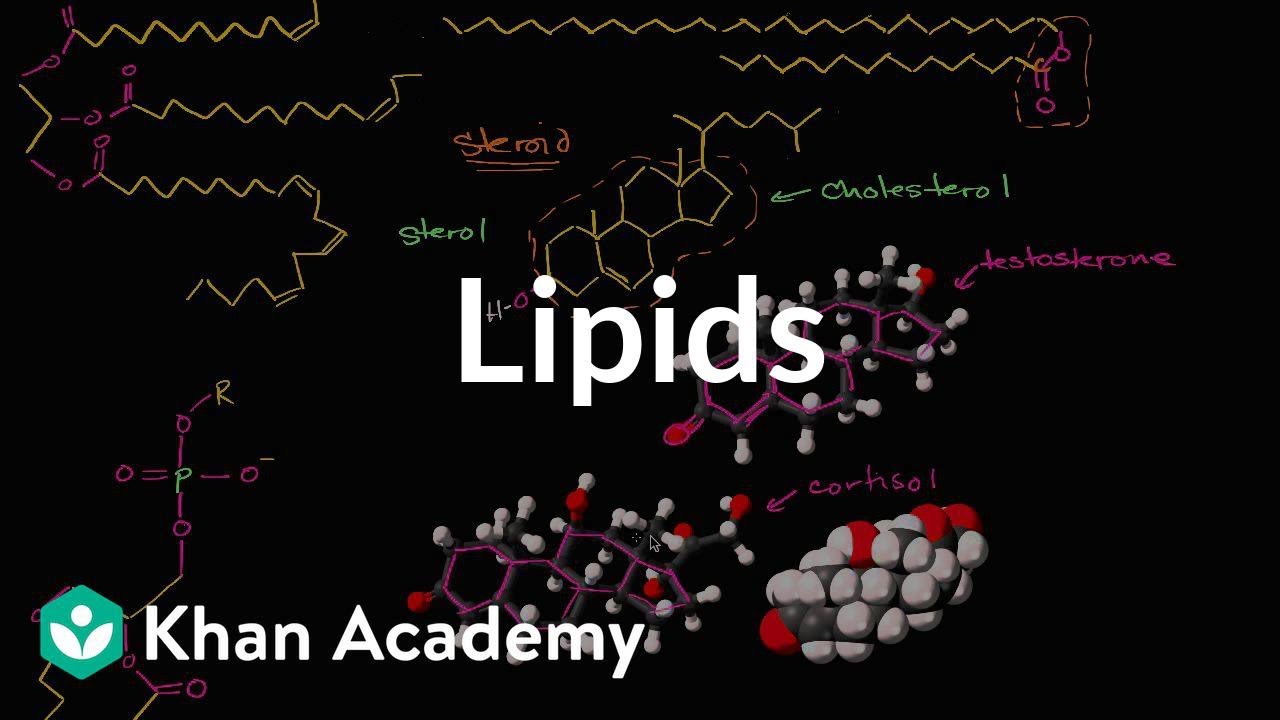
- 😀 Steroids, such as cholesterol, are lipids with a structure of four carbon rings. Cholesterol is vital for regulating bodily functions and forming cell membranes.
- 😀 Carotenoids are plant pigments that assist in photosynthesis and are important for human health. Beta-carotene, a type of carotenoid, is converted into Vitamin A in the body.
- 😀 Saturated fats have only single bonds between carbon atoms, making them solid at room temperature, while unsaturated fats contain double bonds and remain liquid at room temperature.
- 😀 Trans fats, created through hydrogenation, are a type of unsaturated fat that has been chemically altered. These fats can accumulate in blood vessels and cause cardiovascular issues.
- 😀 Lipids are more energy-dense than carbohydrates, making them a more efficient storage form of energy, as they do not require water for storage and occupy less space.
Q & A
What is the primary function of lipids?
-The primary function of lipids is energy storage. They store energy in the form of fats and oils, which can be mobilized by organisms when needed.
What is the role of the 'spermaceti organ' in sperm whales?
-The spermaceti organ in sperm whales contains a liquid fat that helps the whale regulate its buoyancy. This fat solidifies when the whale dives, increasing its density, and becomes liquid again when it ascends, decreasing its density and helping it rise more easily.
What is the difference between lipids and carbohydrates?
-Lipids are non-polar molecules composed mostly of carbon and hydrogen, and are insoluble in water. In contrast, carbohydrates have more oxygen in their structure and are generally soluble in water.
How do saturated and unsaturated fats differ?
-Saturated fats have only single bonds between carbon atoms, making them solid at room temperature. Unsaturated fats have one or more double bonds between carbon atoms, making them liquid at room temperature.
Why do animals store energy in the form of lipids rather than carbohydrates?
-Lipids store more energy in a smaller space compared to carbohydrates. Additionally, lipids do not require water for storage, unlike carbohydrates, which must be stored with water, making lipids a more efficient form of energy storage.
What is the difference between triglycerides and phospholipids?
-Triglycerides are formed by the combination of one glycerol molecule with three fatty acids. Phospholipids, on the other hand, consist of glycerol, two fatty acids, and a phosphate group. The phosphate group gives phospholipids a polar nature, making them essential for cell membranes.
What are carotenes and their role in plants?
-Carotenes, such as beta-carotene, are lipids found in plants that act as pigments, helping plants absorb light for photosynthesis. Beta-carotene is also converted into vitamin A, which is important for vision in animals.
What is the function of cholesterol in the body?
-Cholesterol is a vital steroid that plays a role in forming cell membranes, particularly the plasma membrane. It also helps produce hormones like testosterone and estrogen, and aids in fat digestion in the intestines.
What is the significance of phospholipids in cell membranes?
-Phospholipids are crucial for forming cell membranes due to their amphipathic nature. Their hydrophilic (water-attracting) heads face outward, while the hydrophobic (water-repelling) tails face inward, creating a bilayer that is essential for membrane structure and function.
What are trans fats, and why are they harmful?
-Trans fats are artificially created by hydrogenating unsaturated fats, which makes them solid at room temperature. They are harmful because they can accumulate in blood vessels, leading to cardiovascular diseases like atherosclerosis.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

LIPIDS (TagLish): Phospholipids | Saturated & Unsaturated Fatty Acids | Types of Cholesterols
Lipid overview | Macromolecules | Biology | Khan Academy

002-Biological Molecules

4 Biological Molecules: Structure and Their Function || A quick guide to Understanding biomolecules

Lipids Structure, types and Functions Part 1

Bioquímica - Aula 08 - Lipídios
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
