Photosynthesis vs. Cellular Respiration Comparison
Summary
TLDRIn this video, we dive into the processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration, explaining how organisms harness and transform energy. We explore the role of ATP as a key energy carrier, the reagents and products of each process, and the locations where they occur. By comparing photosynthesis in plants and cellular respiration in animals, we highlight how these processes work together in ecosystems. Key steps like glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the Calvin cycle are broken down, along with how chemiosmosis plays a critical role in energy conversion. This video provides a clear and engaging overview of energy transformation in biology.
Takeaways
- 😀 Photosynthesis stores energy, while cellular respiration releases energy for use.
- 😀 ATP is a crucial energy source in cells, powering most cellular processes.
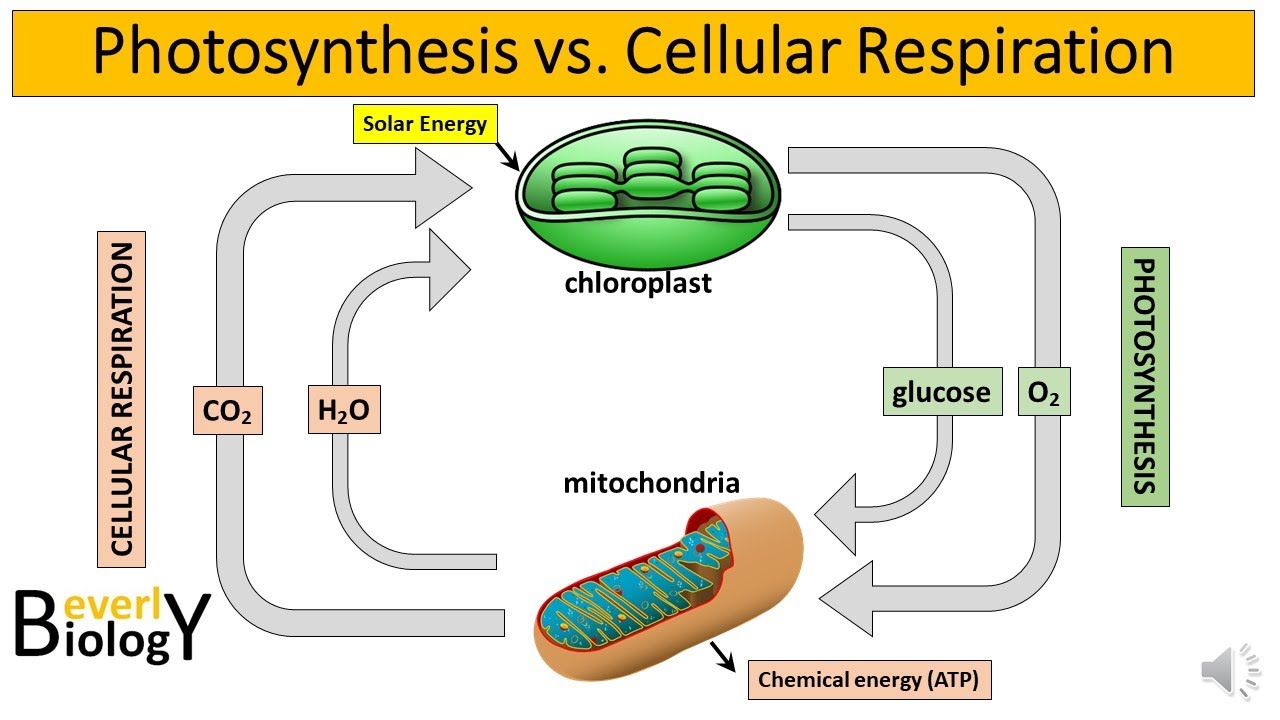
- 😀 The products of photosynthesis (glucose and oxygen) are the reagents for cellular respiration.
- 😀 Both photosynthesis and cellular respiration occur in specialized cell compartments: chloroplasts for photosynthesis and mitochondria for respiration.
- 😀 Photosynthesis involves two main stages: light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle (light-independent reactions).
- 😀 Cellular respiration consists of three main steps: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain.
- 😀 ATP is recharged through cellular respiration, while it is depleted in photosynthesis.
- 😀 In photosynthesis, energy from sunlight is absorbed to convert CO2 into glucose, while oxygen is released as a byproduct.
- 😀 Chemiosmosis is the process in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration that involves ATP synthase and proton gradients to generate ATP.
- 😀 Some organisms can perform both photosynthesis and cellular respiration, while others do only one or the other.
- 😀 The relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration reflects a cyclical exchange of energy and matter within ecosystems.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
-Photosynthesis stores energy, while cellular respiration releases energy for use by organisms.
What molecule is central to the energy processes in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
-ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the central molecule, as it stores and provides energy for cellular processes.
What are the reagents and products of photosynthesis?
-The reagents of photosynthesis are sunlight, ATP, carbon dioxide (CO2), and water. The products are glucose and oxygen.
How does the process of cellular respiration differ from photosynthesis in terms of reagents and products?
-In cellular respiration, the reagents are glucose and oxygen, and the products are ATP, carbon dioxide, water, and heat. This contrasts with photosynthesis, where glucose and oxygen are produced using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.
What is chemiosmosis, and how does it function in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
-Chemiosmosis is the process in which protons (H+) flow through ATP synthase to generate ATP. It occurs in both photosynthesis (in the chloroplasts) and cellular respiration (in the mitochondria).
Why do plants use cellular respiration even though they also perform photosynthesis?
-Plants use cellular respiration during germination, when they lack leaves to perform photosynthesis, and at night when photosynthesis cannot occur due to the absence of sunlight.
What is the role of the thylakoid and stroma in photosynthesis?
-The thylakoid is where the light-dependent reactions occur, involving the absorption of light energy. The stroma is the fluid surrounding the thylakoids where the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle) take place.
What are the three main stages of aerobic cellular respiration?
-The three main stages of aerobic cellular respiration are glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain.
How does the electron transport chain contribute to ATP production?
-The electron transport chain pumps protons across a membrane, creating a proton gradient. Protons flow back through ATP synthase, driving the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP.
What is the significance of oxygen in cellular respiration?
-Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, enabling the continuation of the chain and facilitating the production of ATP. It combines with electrons and protons to form water as a byproduct.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Grade 9 Science Q1 Ep 8 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Part 2

Bioenergetics: The transformation of free energy in living systems | MCAT | Khan Academy

Hubungan Respirasi dan Fotosintesis & Tahapan Respirasi

مسابقة موهوب - (علوم الأحياء): الطاقة الخلوية

Cellular Respiration (Overview) - updated
Photosynthesis vs Cellular Respiration
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
